
Bayesian Linear Regression Made Simple With Python Code Data Science Bayesian statistics ( ˈbeɪziən bay zee ən or ˈbeɪʒən bay zhən) [1] is a theory in the field of statistics based on the bayesian interpretation of probability, where probability expresses a degree of belief in an event. Conclusion bayesian statistical methods are useful tools to add to your toolkit, and include a variety of methods that combine prior knowledge with new data to make decisions. bayesian statistics help practitioners update beliefs as new information comes in, an approach that works well in many fields like healthcare, finance, and machine learning.
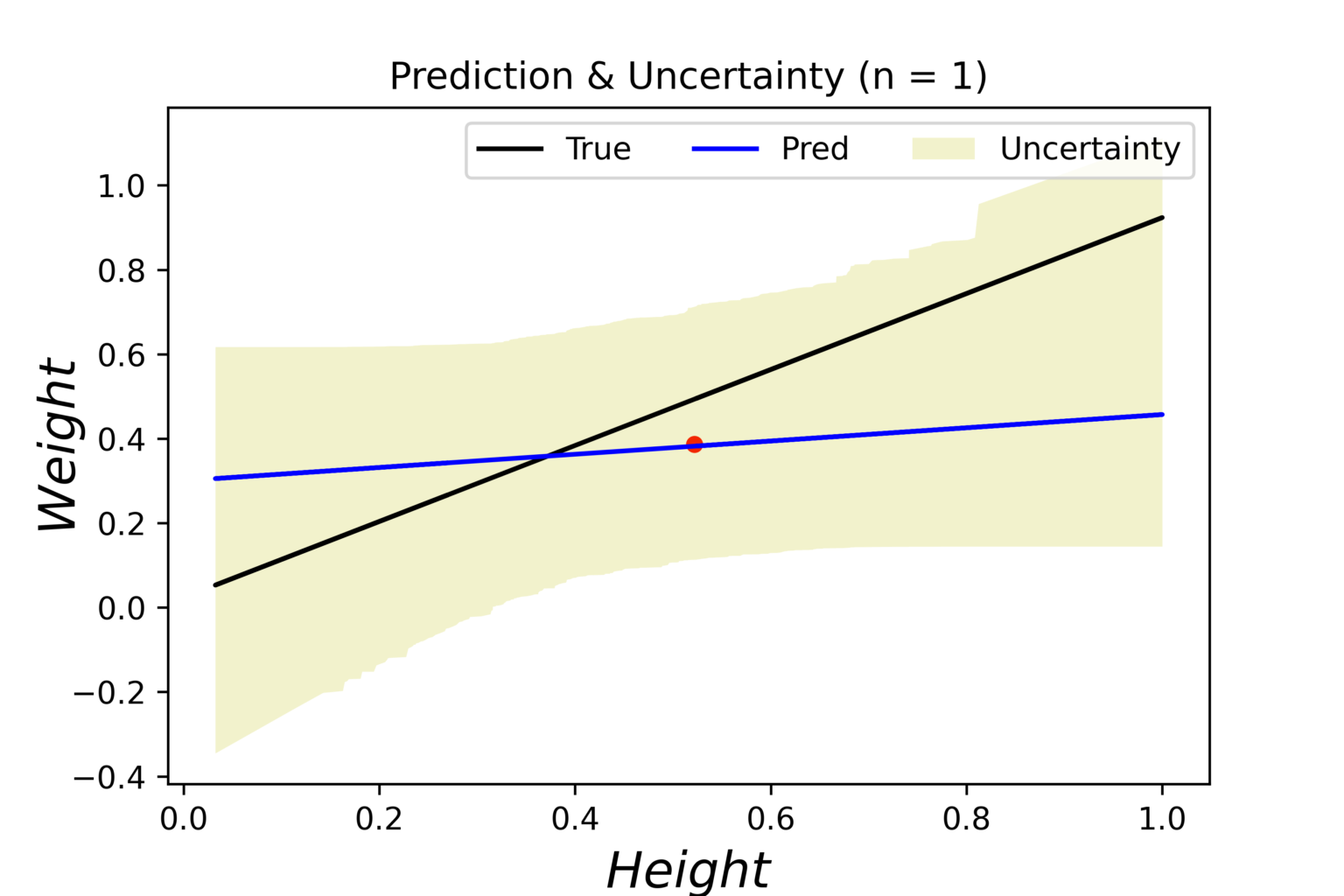
Bayesian Linear Regression Data Automaton Bayesian modelling methods provide natural ways for people in many disciplines to structure their data and knowledge, and they yield direct and intuitive answers to the practitioner’s questions. there are many varieties of bayesian analysis. the fullest version of the bayesian paradigm casts statistical problems in the framework of decision. Bayesian statistics is a powerful tool for making sense of data through probability. unlike traditional statistics, which focuses on frequency or likelihood of events, bayesian statistics incorporates existing beliefs, or priors, and updates these beliefs as new data is available. Put simply, bayesian statistics is a data analysis approach based on bayes’ theorem. according to this theorem, available knowledge regarding parameters in statistical models is updated using the information gathered from observed data. The meaning of bayesian is being, relating to, or involving statistical methods that assign probabilities or distributions to events (such as rain tomorrow) or parameters (such as a population mean) based on experience or best guesses before experimentation and data collection and that apply bayes' theorem to revise the probabilities and.
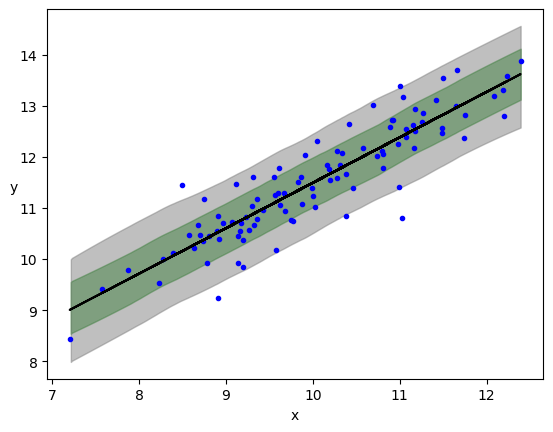
Bayesian Linear Regression Bayesian Reasoning In Data Science Data 644 Put simply, bayesian statistics is a data analysis approach based on bayes’ theorem. according to this theorem, available knowledge regarding parameters in statistical models is updated using the information gathered from observed data. The meaning of bayesian is being, relating to, or involving statistical methods that assign probabilities or distributions to events (such as rain tomorrow) or parameters (such as a population mean) based on experience or best guesses before experimentation and data collection and that apply bayes' theorem to revise the probabilities and. Bayesian statistics is a particular approach to applying probability to statistical problems. it provides us with mathematical tools to update our beliefs about random events in light of seeing new data or evidence about those events. Bayesian inference is a way of making statistical inferences in which the statistician assigns subjective probabilities to the distributions that could generate the data. these subjective probabilities form the so called prior distribution. Explore the fundamentals of bayesian statistics, how they differ from frequentist statistics, and the history, types, common uses, and advantages and disadvantages of using it. when analyzing data, you can take two main statistical approaches: descriptive and inferential. Bayesian probability belongs to the category of evidential probabilities; to evaluate the probability of a hypothesis, the bayesian probabilist specifies a prior probability.
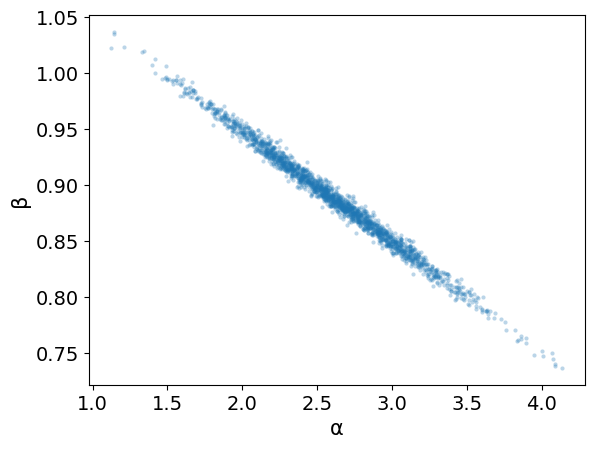
Bayesian Linear Regression Bayesian Reasoning In Data Science Data 644 Bayesian statistics is a particular approach to applying probability to statistical problems. it provides us with mathematical tools to update our beliefs about random events in light of seeing new data or evidence about those events. Bayesian inference is a way of making statistical inferences in which the statistician assigns subjective probabilities to the distributions that could generate the data. these subjective probabilities form the so called prior distribution. Explore the fundamentals of bayesian statistics, how they differ from frequentist statistics, and the history, types, common uses, and advantages and disadvantages of using it. when analyzing data, you can take two main statistical approaches: descriptive and inferential. Bayesian probability belongs to the category of evidential probabilities; to evaluate the probability of a hypothesis, the bayesian probabilist specifies a prior probability.
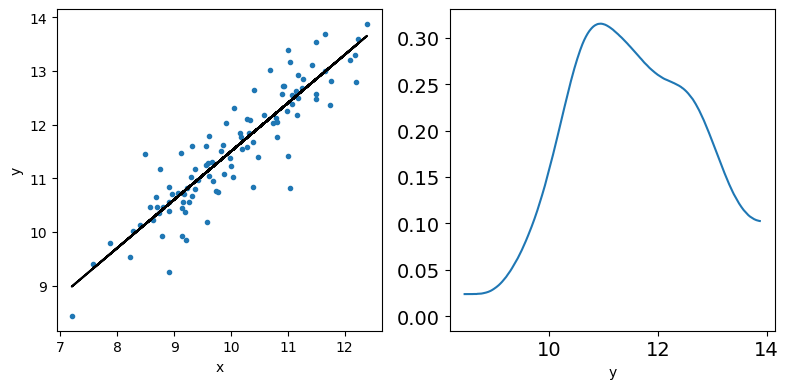
Bayesian Linear Regression Bayesian Reasoning In Data Science Data 644 Explore the fundamentals of bayesian statistics, how they differ from frequentist statistics, and the history, types, common uses, and advantages and disadvantages of using it. when analyzing data, you can take two main statistical approaches: descriptive and inferential. Bayesian probability belongs to the category of evidential probabilities; to evaluate the probability of a hypothesis, the bayesian probabilist specifies a prior probability.
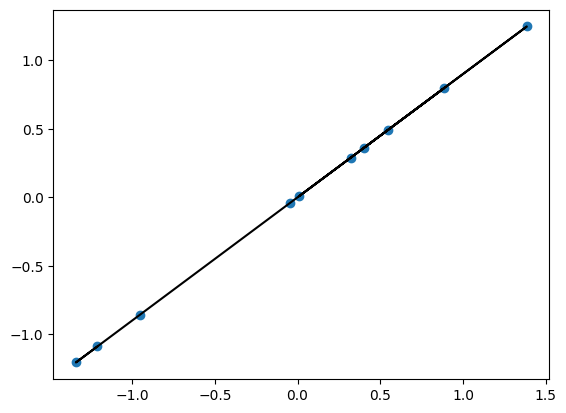
Bayesian Linear Regression Bayesian Reasoning In Data Science Data 644