
Beginners Bandwidth Throughput Latency Jitter In Mobile Networks Ppt The document explains key concepts related to mobile network performance metrics, including bandwidth, latency, jitter, and throughput. it outlines the definitions and measurement methods for these metrics, as well as industry standards for latency in 5g systems. In mobile networks, the end user throughput is the amount of information received in bits second. throughput is measured at layer 1 2 or even at application layer. in a network, often cell throughput is calculated which is throughput of all simultaneous users in the cell.
Beginners Bandwidth Throughput Latency Jitter In Mobile Networks Ppt The most common network performance metrics include latency (the delay in data transmission), throughput (the data transfer rate), packet loss (the percentage of lost packets), jitter (the variance in packet arrival time), and bandwidth utilization (the percentage of available bandwidth being used). A short presentation & video looking at what is meant by bandwidth, throughput, latency & jitter in mobile networks. we will look at simple examples to explain the concepts and also. In mobile networks, the end user throughput is the amount of information received in bits second. throughput is measured at layer 1 2 or even at application layer. in a network, often cell throughput is calculated which is throughput of all simultaneous users in the cell. ©3g4g fnetwork throughput & network capacity network cell spectral ∑. Channel bandwidth (often referred to as just bandwidth) is the rf bandwidth supporting a single rf carrier with the transmission bandwidth configured in the uplink or downlink of a cell.

Beginners Bandwidth Throughput Latency Jitter In Mobile Networks Ppt In mobile networks, the end user throughput is the amount of information received in bits second. throughput is measured at layer 1 2 or even at application layer. in a network, often cell throughput is calculated which is throughput of all simultaneous users in the cell. ©3g4g fnetwork throughput & network capacity network cell spectral ∑. Channel bandwidth (often referred to as just bandwidth) is the rf bandwidth supporting a single rf carrier with the transmission bandwidth configured in the uplink or downlink of a cell. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like how can we measure the performance of a network?, what are the 2 different contexts to measure bandwidth?, what does the bandwidth in hertz involve? and more. Latency is the time it takes a data packet to travel from point to point on the network. each step your traffic takes through the network will add to its latency. latency higher than 150 milliseconds (ms) will cause unnatural delays in an audio conversation. This presentation is intended to stimulate discussion on some of the exciting current and future developments in digital communications technology and networks. • bandwidth determines the data rate—more bandwidth = higher throughput. • 5g spectrum spans fr1 (sub 7 ghz) and fr2 (24.25–71 ghz), with fr2 often referred to as mmwave.
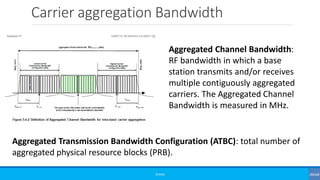
Beginners Bandwidth Throughput Latency Jitter In Mobile Networks Ppt Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like how can we measure the performance of a network?, what are the 2 different contexts to measure bandwidth?, what does the bandwidth in hertz involve? and more. Latency is the time it takes a data packet to travel from point to point on the network. each step your traffic takes through the network will add to its latency. latency higher than 150 milliseconds (ms) will cause unnatural delays in an audio conversation. This presentation is intended to stimulate discussion on some of the exciting current and future developments in digital communications technology and networks. • bandwidth determines the data rate—more bandwidth = higher throughput. • 5g spectrum spans fr1 (sub 7 ghz) and fr2 (24.25–71 ghz), with fr2 often referred to as mmwave.
Beginners Bandwidth Throughput Latency Jitter In Mobile Networks Ppt This presentation is intended to stimulate discussion on some of the exciting current and future developments in digital communications technology and networks. • bandwidth determines the data rate—more bandwidth = higher throughput. • 5g spectrum spans fr1 (sub 7 ghz) and fr2 (24.25–71 ghz), with fr2 often referred to as mmwave.