Cpu Cache Memory And Its Types For Fast Computation A cache is a smaller, faster memory, located closer to a processor core, which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations, avoiding the need to always refer to main memory which may be tens to hundreds of times slower to access. Cpu cache memory helps improve system performance by reducing the need for a cpu to access main memory each time it needs data or an instruction. storing this information closer to the processor can be accessed more quickly, resulting in significantly faster processing times.
Cpu Cache Memory And Its Types For Fast Computation A cpu cache is a small, fast memory area built into a cpu (central processing unit) or located on the processor's die. the cpu cache stores frequently used data and instructions from the main memory to reduce the number of times the cpu has to access the main memory for this information. Cache memory is a special type of high speed memory located close to the cpu in a computer. it stores frequently used data and instructions, so that the cpu can access them quickly, improving the overall speed and efficiency of the computer. Cache memory is an extremely fast memory type so that it provides high speed data access to a computer microprocessor. cache splits into l1d (for data) and l1i (for instructions) and almost all current cpus with caches have a split l1 cache. Cache memory is a chip based computer component that makes retrieving data from the computer's memory more efficient. it acts as a temporary storage area that the computer's processor can retrieve data from easily.

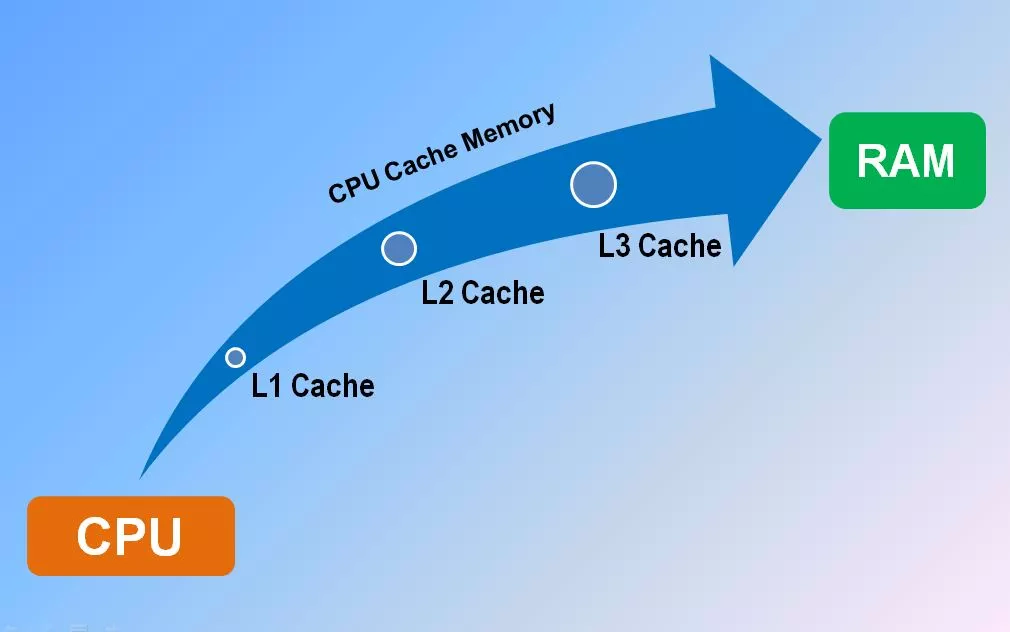
Types Of Cache Memory In A Cpu Cache memory is an extremely fast memory type so that it provides high speed data access to a computer microprocessor. cache splits into l1d (for data) and l1i (for instructions) and almost all current cpus with caches have a split l1 cache. Cache memory is a chip based computer component that makes retrieving data from the computer's memory more efficient. it acts as a temporary storage area that the computer's processor can retrieve data from easily. Overview: l1 cache is the first and fastest cache level, integrated directly into the cpu chip. it is the closest cache to the processor cores and is often split into two types: the l1d for data and the l1i for instructions. size & speed: typically, l1 cache is small, usually ranging from 16kb to 128kb per core. Cache memory is typically organized in a hierarchy, consisting of multiple levels that vary in size, speed, and proximity to the cpu. the most common levels of cache are: size: usually. Cache memory is a small, ultra fast type of volatile memory that temporarily stores copies of data and instructions that the cpu is likely to reuse. this memory operates faster than ram, allowing it to keep pace with the cpu’s rapid processing demands. Cache memory consists of different levels called l1, l2, l3 and occasionally l4, which differ in location, speed and size. the cache memory is extremely fast and positioned as close as.