
Reading A Data File In Ascii Text Format Download Free Pdf In this video we will learn text presentation using ascii, extended ascii and unicode, using denary and hexadecimal coding methods for o levels more. Data representation text, sound & images character sets. what is a character set? what is ascii? !, @, #, … what is unicode? exam questions often ask you to compare ascii & unicode, for example the number of bits, number of characters and what they store. used to represent characters in the english language.

Data Representation Pdf Character Encoding Ascii Ascii and unicode include more than just characters from written languages. ascii represents english letters, numbers and symbols. unicode supports other symbols beyond written text, including mathematical symbols, emojis and non text elements. use python to explore the conversion of characters from character codes to the represented characters. Understand how and why a computer represents text and the use of character sets, including american standard code for information interchange (ascii) and unicode. Each character in text is stored as a number that represents the character. in personal computers, a common way to do this is to use ascii the american standard code for information interchange or unicode. In this section, we will explore how computers represent different types of data, including text, sound, and images. computers process data in binary format (0s and 1s), so each type of data needs to be converted into binary to be processed and stored by computers effectively.
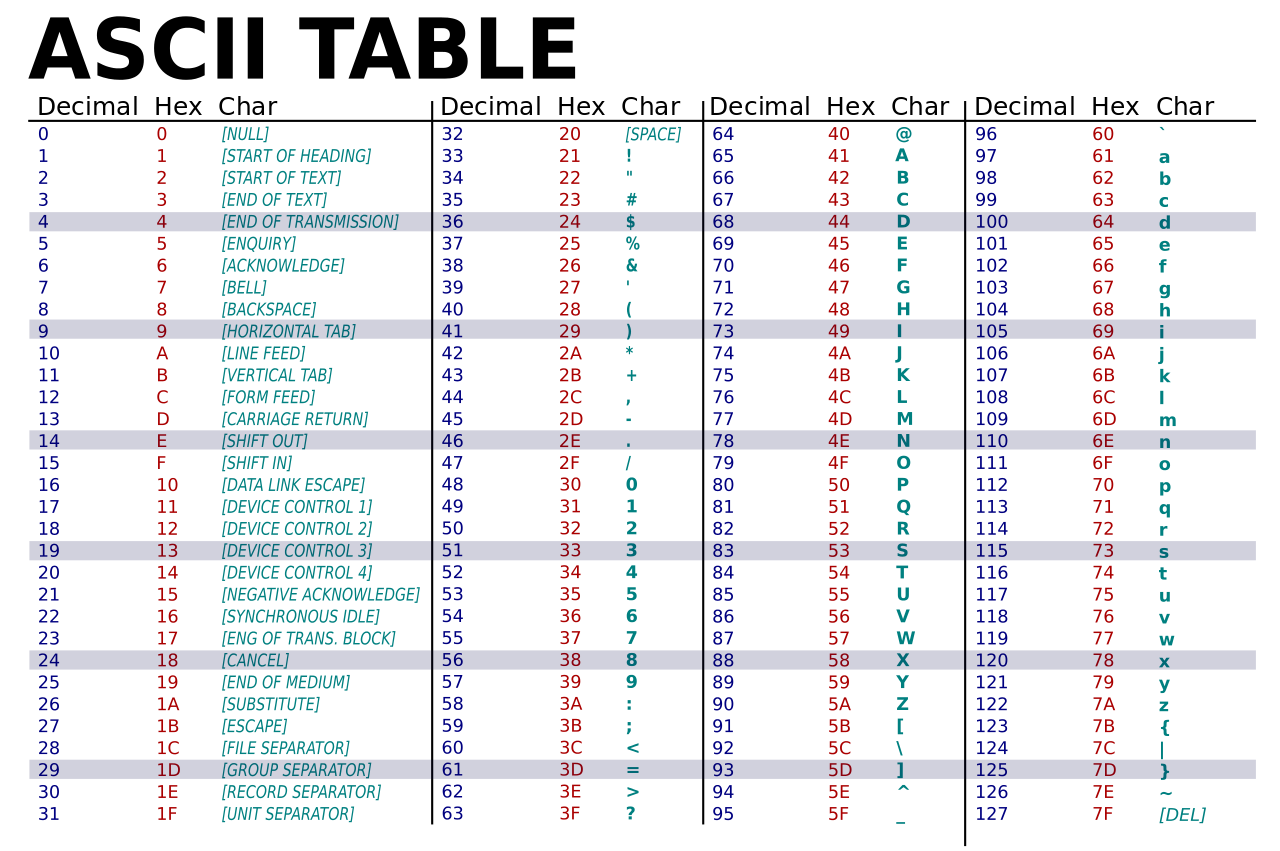
Ascii Extended Ascii And Unicode A Level Computer Science Each character in text is stored as a number that represents the character. in personal computers, a common way to do this is to use ascii the american standard code for information interchange or unicode. In this section, we will explore how computers represent different types of data, including text, sound, and images. computers process data in binary format (0s and 1s), so each type of data needs to be converted into binary to be processed and stored by computers effectively. Explain the difference between the ascii and unicode character sets. unicode has a greater range of characters than ascii. unicode represents most written languages in the world while ascii does not (is used for english only.) ascii uses 7 or 8 bits or one byte whereas unicode uses up to 4 bytes per character. Ascii: represents 128 characters using 7 bit binary values, extending to 256 characters in its 8 bit version (extended ascii). unicode: extends beyond ascii, accommodating characters from various languages and symbol sets globally. encryption: converts data into a secure format for storage or transmission. Unlike ascii, unicode is a universal character set that can represent text from almost any language or script. it uses 16 bits per character, which means it can represent a massive 65,536 characters. unicode includes characters from languages that use latin, arabic, and chinese scripts, among many others. The document discusses different methods for representing various types of digital data, including text, sound, images, and compression techniques. it describes ascii, extended ascii, and unicode character encoding standards. it also covers how sound is converted to digital form through sampling and midi mp3 file formats.

Week3 Data Representation Pdf Character Encoding Integer Explain the difference between the ascii and unicode character sets. unicode has a greater range of characters than ascii. unicode represents most written languages in the world while ascii does not (is used for english only.) ascii uses 7 or 8 bits or one byte whereas unicode uses up to 4 bytes per character. Ascii: represents 128 characters using 7 bit binary values, extending to 256 characters in its 8 bit version (extended ascii). unicode: extends beyond ascii, accommodating characters from various languages and symbol sets globally. encryption: converts data into a secure format for storage or transmission. Unlike ascii, unicode is a universal character set that can represent text from almost any language or script. it uses 16 bits per character, which means it can represent a massive 65,536 characters. unicode includes characters from languages that use latin, arabic, and chinese scripts, among many others. The document discusses different methods for representing various types of digital data, including text, sound, images, and compression techniques. it describes ascii, extended ascii, and unicode character encoding standards. it also covers how sound is converted to digital form through sampling and midi mp3 file formats.
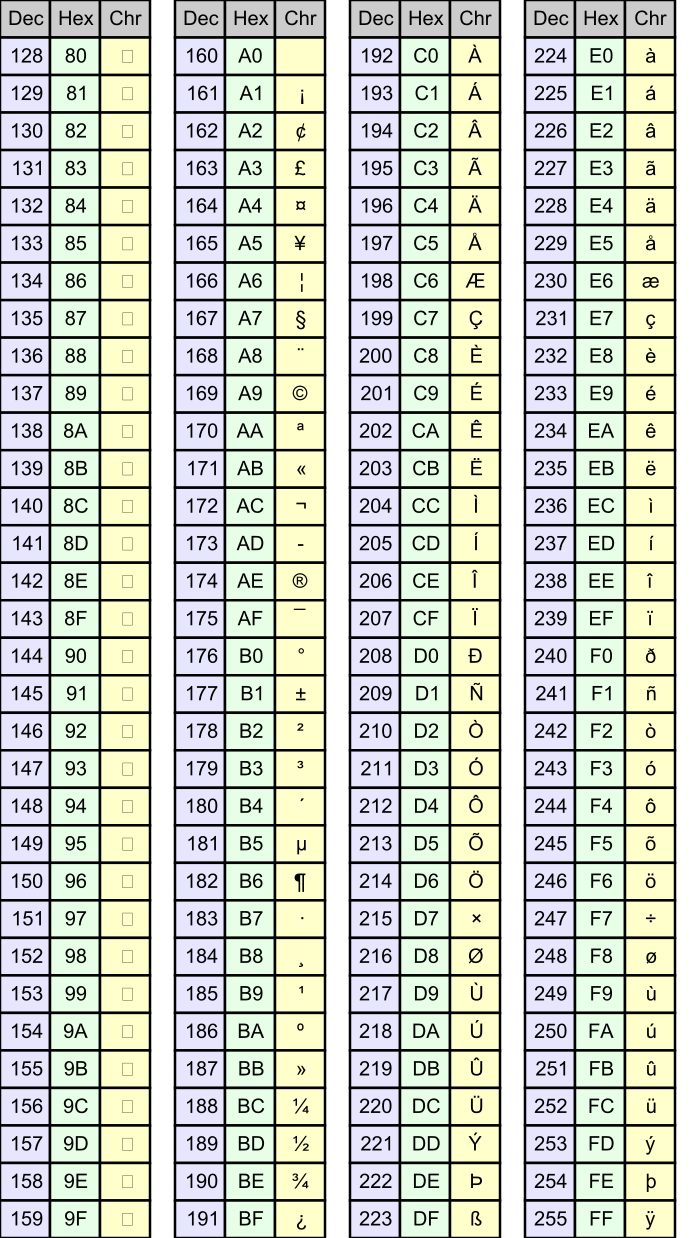
Tenminutetutor Extended Ascii Unlike ascii, unicode is a universal character set that can represent text from almost any language or script. it uses 16 bits per character, which means it can represent a massive 65,536 characters. unicode includes characters from languages that use latin, arabic, and chinese scripts, among many others. The document discusses different methods for representing various types of digital data, including text, sound, images, and compression techniques. it describes ascii, extended ascii, and unicode character encoding standards. it also covers how sound is converted to digital form through sampling and midi mp3 file formats.

Introduction To Ascii Extended Ascii And Unicode Teaching Resources