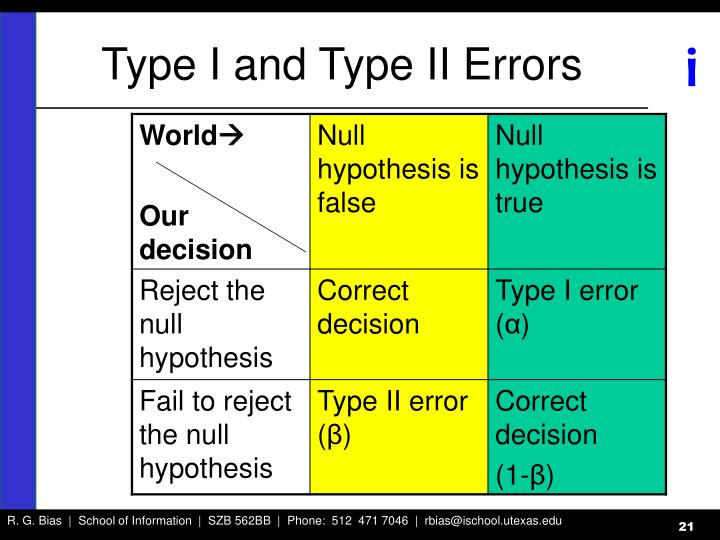
Difference Between Type I And Type Ii Errors With Comparison Chart Images The main difference between type i and type ii errors is type i error crops up when the researcher notice some difference, when in fact there is none, whereas type ii error arises when the researcher does not discovers any difference, when in truth there is one. In statistics, a type i error is a false positive conclusion, while a type ii error is a false negative conclusion. making a statistical decision always involves uncertainties, so the risks of making these errors are unavoidable in hypothesis testing.

Difference Between Type I And Type Ii Errors With Comparison Chart Images Type ii error is the error that occurs when the null hypothesis is accepted when it is not true. in simple words, type ii error means accepting the hypothesis when it should not have been accepted. the type ii error results in a false negative result. Type i and type ii errors are central for hypothesis testing, false discovery refers to a type i error where a true null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected. on the other end of the spectrum, type ii errors occur when a true null hypothesis fails to get rejected. The errors are generally classified as type i and type ii errors. a type i error is the rejection of the true null hypothesis whereas type ii error is the non rejection of a false null hypothesis. Type ii error, also known as a "false negative": the error of not rejecting a null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is the true state of nature. in other words, this is the error of failing to accept an alternative hypothesis when you don't have adequate power.
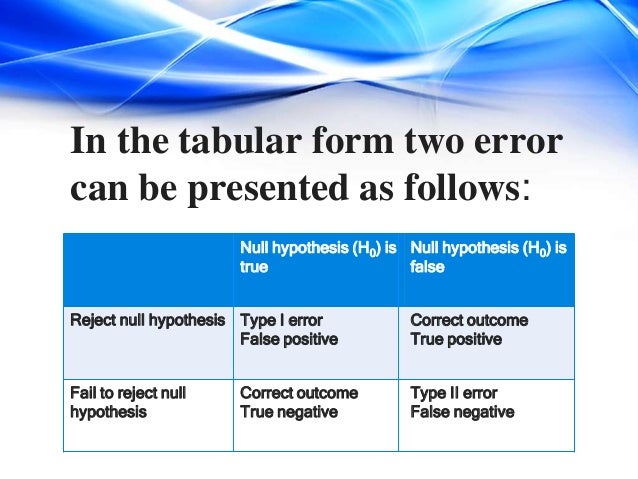
Difference Between Type I And Type Ii Errors With Comparison Chart Images The errors are generally classified as type i and type ii errors. a type i error is the rejection of the true null hypothesis whereas type ii error is the non rejection of a false null hypothesis. Type ii error, also known as a "false negative": the error of not rejecting a null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is the true state of nature. in other words, this is the error of failing to accept an alternative hypothesis when you don't have adequate power. Key differences between type i & ii errors in statistical hypothesis testing, a type i error is caused by disapproving a null hypothesis that is otherwise correct while in contrast, type ii error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected even though it is not true. Type i errors can be thought of as errors of commission, in which the status quo is erroneously rejected in favour of new, misleading information. type ii errors can be thought of as errors of omission, in which a misleading status quo is allowed to remain due to failures in identifying it as such. What is a type ii error (β)? the situation opposite to a type i error (α) is when the null hypothesis h₀ is false, but we accept the corresponding null hypothesis h₀ and reject the correct. Type i errors occur when a true null hypothesis is mistakenly rejected, leading to unnecessary interventions. type ii errors happen when a false null hypothesis is not rejected, causing missed diagnoses or overlooked effects.

Difference Between Type I And Type Ii Errors With Comparison Chart Images Key differences between type i & ii errors in statistical hypothesis testing, a type i error is caused by disapproving a null hypothesis that is otherwise correct while in contrast, type ii error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected even though it is not true. Type i errors can be thought of as errors of commission, in which the status quo is erroneously rejected in favour of new, misleading information. type ii errors can be thought of as errors of omission, in which a misleading status quo is allowed to remain due to failures in identifying it as such. What is a type ii error (β)? the situation opposite to a type i error (α) is when the null hypothesis h₀ is false, but we accept the corresponding null hypothesis h₀ and reject the correct. Type i errors occur when a true null hypothesis is mistakenly rejected, leading to unnecessary interventions. type ii errors happen when a false null hypothesis is not rejected, causing missed diagnoses or overlooked effects.

Type I And Type Ii Errors In Statistics With Pdf Type I And Type What is a type ii error (β)? the situation opposite to a type i error (α) is when the null hypothesis h₀ is false, but we accept the corresponding null hypothesis h₀ and reject the correct. Type i errors occur when a true null hypothesis is mistakenly rejected, leading to unnecessary interventions. type ii errors happen when a false null hypothesis is not rejected, causing missed diagnoses or overlooked effects.

Difference Between Type I And Type Ii Errors With Comparison Chart