
Mechanisms Of Neuroinflammation Intechopen 2 immune surveillance and brain barrier system maintaining cns homeostasis relies on tightly regulated mechanisms that control immune cell trafficking and prevent the infiltration of harmful substances that could trigger neuroinflammation. This review explores the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying neuroinflammation, focusing on the roles of microglia, astrocytes, and peripheral immune cells.

Cellular Mechanisms Of Inflammation And Neuroinflammation A Neuroinflammation is documented in all neurological disorders spanning immune etiologic multiple sclerosis (ms) to acute insults such as stroke and traumatic cns injuries, to classic chronic neurodegenerative disorders such as alzheimer’s disease (ad) and parkinson’s disease (pd). Results: glial cells play a crucial role in neuroinflammation, but several pathways can be activated in response to different inflammatory stimuli, inducing cell death by apoptosis, pyroptosis or necroptosis. Neuroinflammation is an inflammatory response in which the homeostasis of the central nervous system (cns) is disrupted. it is a hot topic in contemporary neuroscience [1]. this inflammatory response may be caused by different etiologies, such as intracranial trauma and infection. Neuroinflammation can be triggered by various biological mechanisms including oxidative stress and glial reactions (agostinho et al., 2010; alcendor et al., 2012; allaman et al., 2011; niranjan, 2014).

Schematic Overview Of The General Mechanisms Of Neuroinflammation After Neuroinflammation is an inflammatory response in which the homeostasis of the central nervous system (cns) is disrupted. it is a hot topic in contemporary neuroscience [1]. this inflammatory response may be caused by different etiologies, such as intracranial trauma and infection. Neuroinflammation can be triggered by various biological mechanisms including oxidative stress and glial reactions (agostinho et al., 2010; alcendor et al., 2012; allaman et al., 2011; niranjan, 2014). Exploring these mechanisms offers the potential to mitigate chronic inflammation while preserving its protective aspects, paving the way for innovative therapies to combat the progression of neurological disorders. Neuroinflammation is the response of the central nervous system (cns) to disturbed homeostasis and typifies all neurological diseases. the main reactive components of the cns include microglial cells and infiltrating myeloid cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and the blood–brain barrier, cytokines, and cytokine signaling. Inflammation is associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, including alzheimer's disease, parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and multiple sclerosis. in this review, we discuss inducers, sensors, transducers, and effectors of neuroinflammation that contribute to neuronal dysfunction and death. Cns diseases including traumatic brain injury, ischemic stroke, brain tumor, and cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases trigger a cascade of events broadly defined as neuroinflammation, which is characterized by the activation of the microglia and astrocyte population.
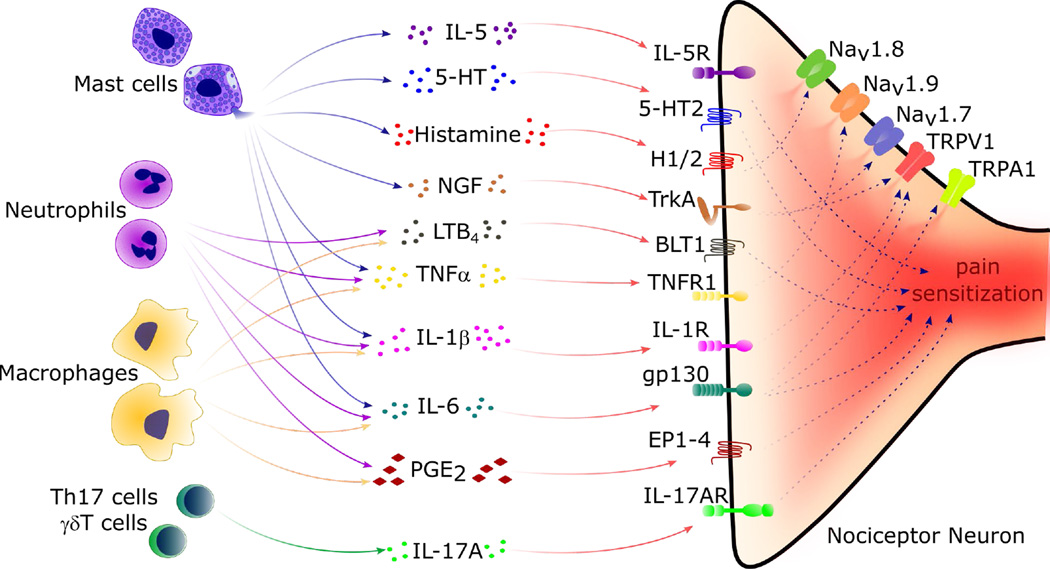
Understanding Neurogenic Inflammation Genoskin Exploring these mechanisms offers the potential to mitigate chronic inflammation while preserving its protective aspects, paving the way for innovative therapies to combat the progression of neurological disorders. Neuroinflammation is the response of the central nervous system (cns) to disturbed homeostasis and typifies all neurological diseases. the main reactive components of the cns include microglial cells and infiltrating myeloid cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and the blood–brain barrier, cytokines, and cytokine signaling. Inflammation is associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, including alzheimer's disease, parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and multiple sclerosis. in this review, we discuss inducers, sensors, transducers, and effectors of neuroinflammation that contribute to neuronal dysfunction and death. Cns diseases including traumatic brain injury, ischemic stroke, brain tumor, and cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases trigger a cascade of events broadly defined as neuroinflammation, which is characterized by the activation of the microglia and astrocyte population.
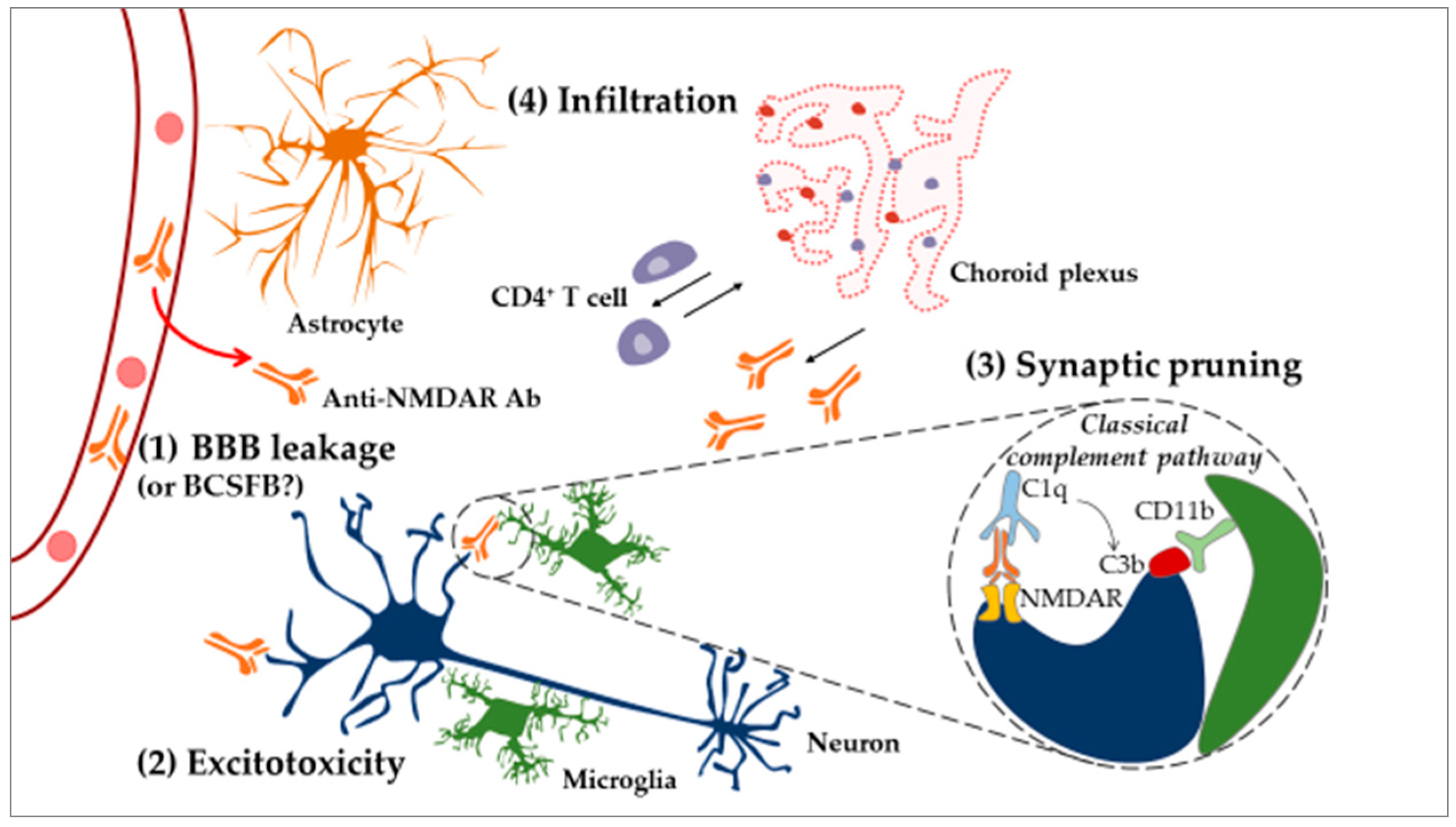
Neuroinflammation Inflammation is associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, including alzheimer's disease, parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and multiple sclerosis. in this review, we discuss inducers, sensors, transducers, and effectors of neuroinflammation that contribute to neuronal dysfunction and death. Cns diseases including traumatic brain injury, ischemic stroke, brain tumor, and cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases trigger a cascade of events broadly defined as neuroinflammation, which is characterized by the activation of the microglia and astrocyte population.