
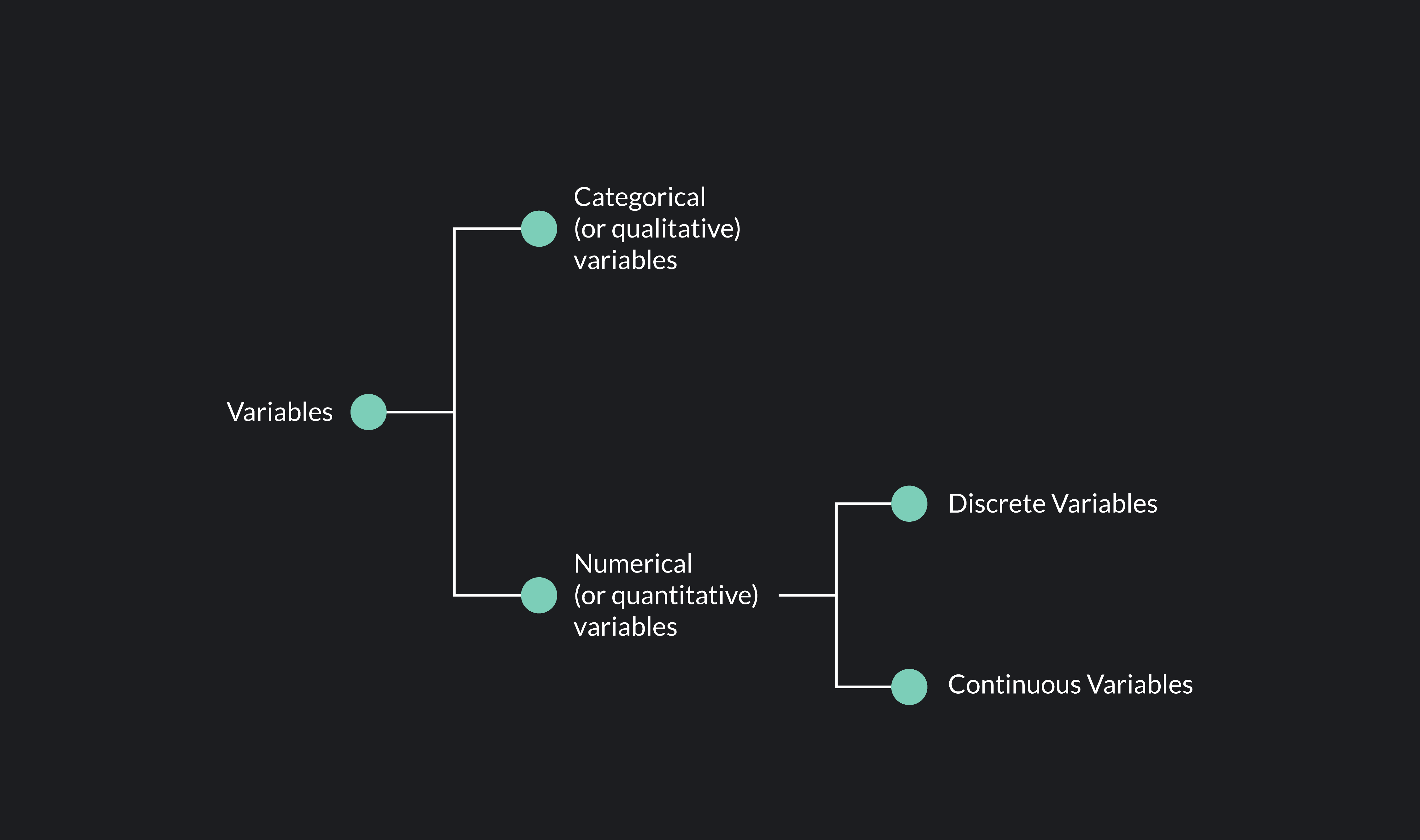
Distinguishing Between Discrete And Continuous Random Variables A The main difference between discrete data and continuous data is that discrete data is data collected for a discrete random variable, while continuous data is data collected for a continuous random variable. Two fundamental types of variables are discrete and continuous variables. discrete variables have distinct, separate values with gaps between them, while continuous variables have an unbroken sequence of values.

Learn Discrete Vs Continuous Random Variables Pdf Probability The discrete versus continuous classification we’ll explore below specifically refers to how quantitative variables behave. let’s examine these concepts using a clear visual representation and detailed explanation. Discrete variables are countable, distinct values such as number of letters in a word or number of traffic accidents in a day. on the other hand, continuous variables are uncountable, infinite data such as distance, weight or time. typically, continuous variables are measured instead of counted. Discrete random variables take on countable, specific values, while continuous random variables assume uncountably infinite values. understanding the properties of both types is crucial in many statistical applications. Discrete vs. continuous variables if a variable can take on any value between two specified values, it is called a continuous variable; otherwise, it is called a discrete variable. some examples will clarify the difference between discrete and continuous variables.
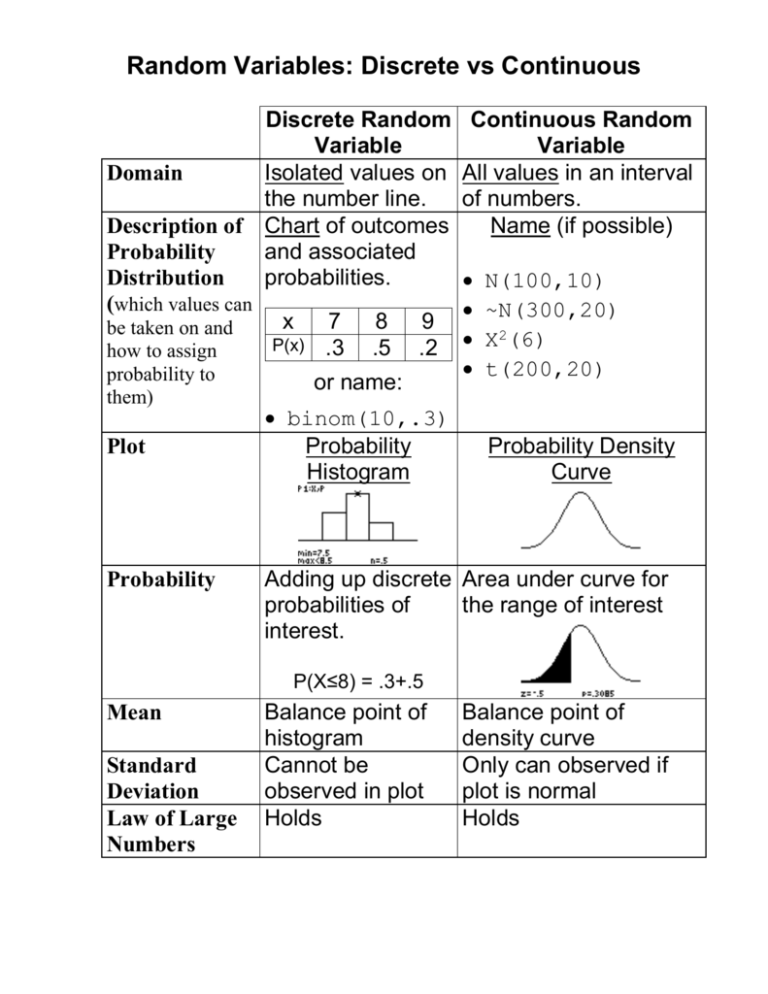
Discrete Vs Continuous Random Variables Comparison Discrete random variables take on countable, specific values, while continuous random variables assume uncountably infinite values. understanding the properties of both types is crucial in many statistical applications. Discrete vs. continuous variables if a variable can take on any value between two specified values, it is called a continuous variable; otherwise, it is called a discrete variable. some examples will clarify the difference between discrete and continuous variables. In statistics, continuous and discrete variables are distinct statistical data types which are described with different probability distributions. a continuous variable is a variable such that there are possible values between any two values. Discrete probability distributions are associated with variables that take on a finite or countably infinite number of distinct values. continuous probability distributions deal with random variables that can take on any value within a given range or interval. Discrete data are a type of quantitative data that can take only fixed values. they are always numerical. these are data that can be counted, but not measured. for example, if you conducted a household survey, you’d find that there are only certain numbers of individuals who can live under one roof. 1, 2, 3 people, and so on. “learn the key differences between discrete and continuous random variables with simple explanations and examples. i would highly suggest you to read the my below article. loosely speaking, the random variable is a variable whose value depends on the outcome of a random event.
Discrete Vs Continuous Variables Meaning And Differences Outlier In statistics, continuous and discrete variables are distinct statistical data types which are described with different probability distributions. a continuous variable is a variable such that there are possible values between any two values. Discrete probability distributions are associated with variables that take on a finite or countably infinite number of distinct values. continuous probability distributions deal with random variables that can take on any value within a given range or interval. Discrete data are a type of quantitative data that can take only fixed values. they are always numerical. these are data that can be counted, but not measured. for example, if you conducted a household survey, you’d find that there are only certain numbers of individuals who can live under one roof. 1, 2, 3 people, and so on. “learn the key differences between discrete and continuous random variables with simple explanations and examples. i would highly suggest you to read the my below article. loosely speaking, the random variable is a variable whose value depends on the outcome of a random event.

Discrete Vs Continuous Random Variable Discrete data are a type of quantitative data that can take only fixed values. they are always numerical. these are data that can be counted, but not measured. for example, if you conducted a household survey, you’d find that there are only certain numbers of individuals who can live under one roof. 1, 2, 3 people, and so on. “learn the key differences between discrete and continuous random variables with simple explanations and examples. i would highly suggest you to read the my below article. loosely speaking, the random variable is a variable whose value depends on the outcome of a random event.