
Excitation Contraction Coupling In Smooth Muscles Its Different Than In cardiac muscle, the extrusion of this calcium through the electrogenic na ca exchanger modulates the action potential, feeding back on excitation, but is also causally involved in cardiac arrhythmias (sipido et al., 2006). Excitation contraction coupling in smooth muscles || its different than in skeletal muscle nonstop neuron 171k subscribers subscribed.

Excitation Contraction Coupling In Smooth Muscle Diagram Quizlet However, both the mechanism of increase in free ca ion concentration as a result of excitation and the molecular mechanism of activation of the contractile protein system by ca ion are quite different from those in skeletal muscle. This is the main difference between the excitation contraction coupling of cardiac and skeletal muscle, explored in more detail by eisner et al (2017). smooth muscle have a totally different third variant of l type voltage gated calcium channels on the surface membrane, which get blocked by all kinds of calcium channel blocker drugs (wherein. Most important, essentially the same attractive forces between myosin and actin filaments cause contraction in smooth muscle as in skeletal muscle, but the internal physical arrangement of smooth muscle fibers is different. There are, however, major differences between the physical organization of smooth muscle and that of skeletal muscle, as well as differences in excitation contraction coupling, control of the contractile process by calcium ions, duration of contraction, and the amount of energy required for contraction.

Muscle Excitation Contraction Coupling Diagram Quizlet Most important, essentially the same attractive forces between myosin and actin filaments cause contraction in smooth muscle as in skeletal muscle, but the internal physical arrangement of smooth muscle fibers is different. There are, however, major differences between the physical organization of smooth muscle and that of skeletal muscle, as well as differences in excitation contraction coupling, control of the contractile process by calcium ions, duration of contraction, and the amount of energy required for contraction. Understand the differences in excitation contraction coupling between skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. describe the two stage phospho regulatory cascade that initiates smooth muscle contraction. compare and contrast how skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle are controlled by the nervous system. Contraction develops more slowly but lasts longer than skeletal muscle. the actual rate varies greatly between groups of smooth muscle. atp usage is much less than for a similar contraction of skeletal muscle. calcium flux is the primary ionic event, and sodium plays a smaller role in smooth muscle action potentials. In skeletal muscle, cross bridge formation and contraction requires the presence of calcium (ca ) inside the muscle cell. excitation signalling of action potentials from the motor neuron are coupled with calcium release. In this study, we reveal intimate functional interactions between the process of excitation induced contraction and the process of excitation induced transcriptional activity in skeletal.
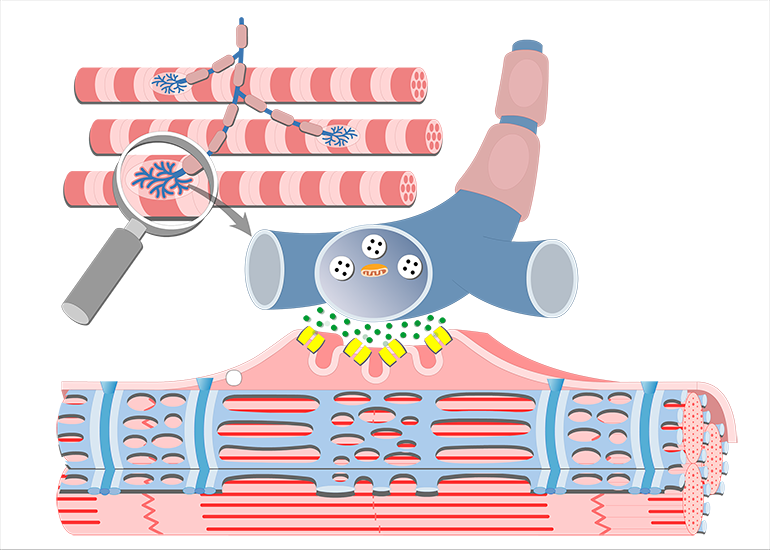
Excitation Contraction Coupling Getbodysmart Understand the differences in excitation contraction coupling between skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. describe the two stage phospho regulatory cascade that initiates smooth muscle contraction. compare and contrast how skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle are controlled by the nervous system. Contraction develops more slowly but lasts longer than skeletal muscle. the actual rate varies greatly between groups of smooth muscle. atp usage is much less than for a similar contraction of skeletal muscle. calcium flux is the primary ionic event, and sodium plays a smaller role in smooth muscle action potentials. In skeletal muscle, cross bridge formation and contraction requires the presence of calcium (ca ) inside the muscle cell. excitation signalling of action potentials from the motor neuron are coupled with calcium release. In this study, we reveal intimate functional interactions between the process of excitation induced contraction and the process of excitation induced transcriptional activity in skeletal.

Excitation Contraction Coupling Skeletal And Smooth Muscle Flashcards In skeletal muscle, cross bridge formation and contraction requires the presence of calcium (ca ) inside the muscle cell. excitation signalling of action potentials from the motor neuron are coupled with calcium release. In this study, we reveal intimate functional interactions between the process of excitation induced contraction and the process of excitation induced transcriptional activity in skeletal.

Muscle Physiology Excitation Contraction Coupling Diagram Quizlet