
Gravity Leveled Text Set Booklets By The Science Squad Tpt Newton's "law" of gravity is a mathematical description of the way bodies are observed to attract one another, based on many scientific experiments and observations. the gravitational equation says that the force of gravity is proportional to the product of the two masses (m 1 and m 2), and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between their centers of mass. mathematically. A new satellite mission sheds light on earth's gravity field and provides clues about changing sea levels.
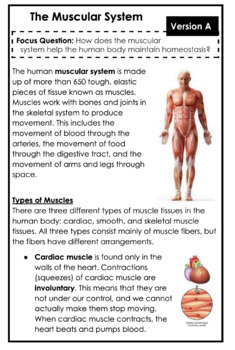
Muscular System Leveled Text Set Booklets By The Science Squad Tpt Gravitational pull see gravity gravity the force of attraction between two objects which is influenced by the mass of the two objects and the distance between the two objects. gyroscope a heavy wheel or disk mounted so that its axis can turn freely in one or more directions. a spinning gyroscope tends to resist change in the direction of its axis. Gravity causes the last of the star's matter to collapse inward and compact. this is the white dwarf stage which is extremely dense. white dwarfs shine with a white hot light but once all of their energy is gone, they die. the star has now reached the black dwarf phase. A glacier is a large accumulation of many years of snow, transformed into ice. this solid crystalline material deforms (changes) and moves. glaciers, also known as “rivers of ice,” actually flow. gravity is the cause of glacier motion; the ice slowly flows and deforms (changes) in response to gravity. a glacier molds itself to the land and also molds the land as it creeps down the valley. A glacier is a huge mass of many years of snow, ice, rock, sediment, and water. it originates on land and moves down slope under the influence of its own weight and gravity. each glacier is different in its own special way and each glacier has a different surrounding environment.

The Atom Leveled Text Set Booklets By The Science Squad Tpt A glacier is a large accumulation of many years of snow, transformed into ice. this solid crystalline material deforms (changes) and moves. glaciers, also known as “rivers of ice,” actually flow. gravity is the cause of glacier motion; the ice slowly flows and deforms (changes) in response to gravity. a glacier molds itself to the land and also molds the land as it creeps down the valley. A glacier is a huge mass of many years of snow, ice, rock, sediment, and water. it originates on land and moves down slope under the influence of its own weight and gravity. each glacier is different in its own special way and each glacier has a different surrounding environment. A galaxy is a cluster of stars, dust, and gas which is held together by gravity. galaxies are scattered throughout the universe and they vary greatly in size. a galaxy may be alone or it may be in a large group of galaxies called a "supercluster". galaxies are classified by scientists according to their shape and appearance. an irregular galaxy has an undefined shape and is full of young stars. 1. introduction: review the definition of gravity drop a ball and explain why it falls downward explain that the strength of a gravitational pull is determined by the masses of the objects involved and the distance between the objects hold up a scale model of earth and a scale model of the sun. inquire as to which object would exert a stronger pull. Nasa’s twin gravity recovery and climate experiment (grace) satellites can detect groundwater by measuring subtle variations in earth’s gravity. this image shows the world’s average annual cycle of water storage on land, computed from four years of grace gravity data. colors indicate how much groundwater comes and goes, each year, in various regions; red indicates high levels of annual. As more and more of the gas (which is mostly hydrogen) is pulled together by gravity into a cloud, the cloud starts to spin. the gas atoms start to bump into each other faster and faster. this creates heat energy. the cloud gets hotter and hotter. finally, it gets so hot within the cloud that something called "nuclear fusion" happens.

Gravity Leveled Text Set Booklets By The Science Squad Tpt A galaxy is a cluster of stars, dust, and gas which is held together by gravity. galaxies are scattered throughout the universe and they vary greatly in size. a galaxy may be alone or it may be in a large group of galaxies called a "supercluster". galaxies are classified by scientists according to their shape and appearance. an irregular galaxy has an undefined shape and is full of young stars. 1. introduction: review the definition of gravity drop a ball and explain why it falls downward explain that the strength of a gravitational pull is determined by the masses of the objects involved and the distance between the objects hold up a scale model of earth and a scale model of the sun. inquire as to which object would exert a stronger pull. Nasa’s twin gravity recovery and climate experiment (grace) satellites can detect groundwater by measuring subtle variations in earth’s gravity. this image shows the world’s average annual cycle of water storage on land, computed from four years of grace gravity data. colors indicate how much groundwater comes and goes, each year, in various regions; red indicates high levels of annual. As more and more of the gas (which is mostly hydrogen) is pulled together by gravity into a cloud, the cloud starts to spin. the gas atoms start to bump into each other faster and faster. this creates heat energy. the cloud gets hotter and hotter. finally, it gets so hot within the cloud that something called "nuclear fusion" happens.