How Do We Decide What To Believe

How Do We Decide What To Believe Galatians 1 10 2 10 12th Feb 2023 In one sense, beliefs are not under our control. i cannot, strictly speaking, choose to believe something. in the philosophy classes i teach, i often discuss the nature of belief with my students. What should we believe? these days we receive information from countless sources. claim testing empowers us to assess the trustworthiness of a concept, asser.
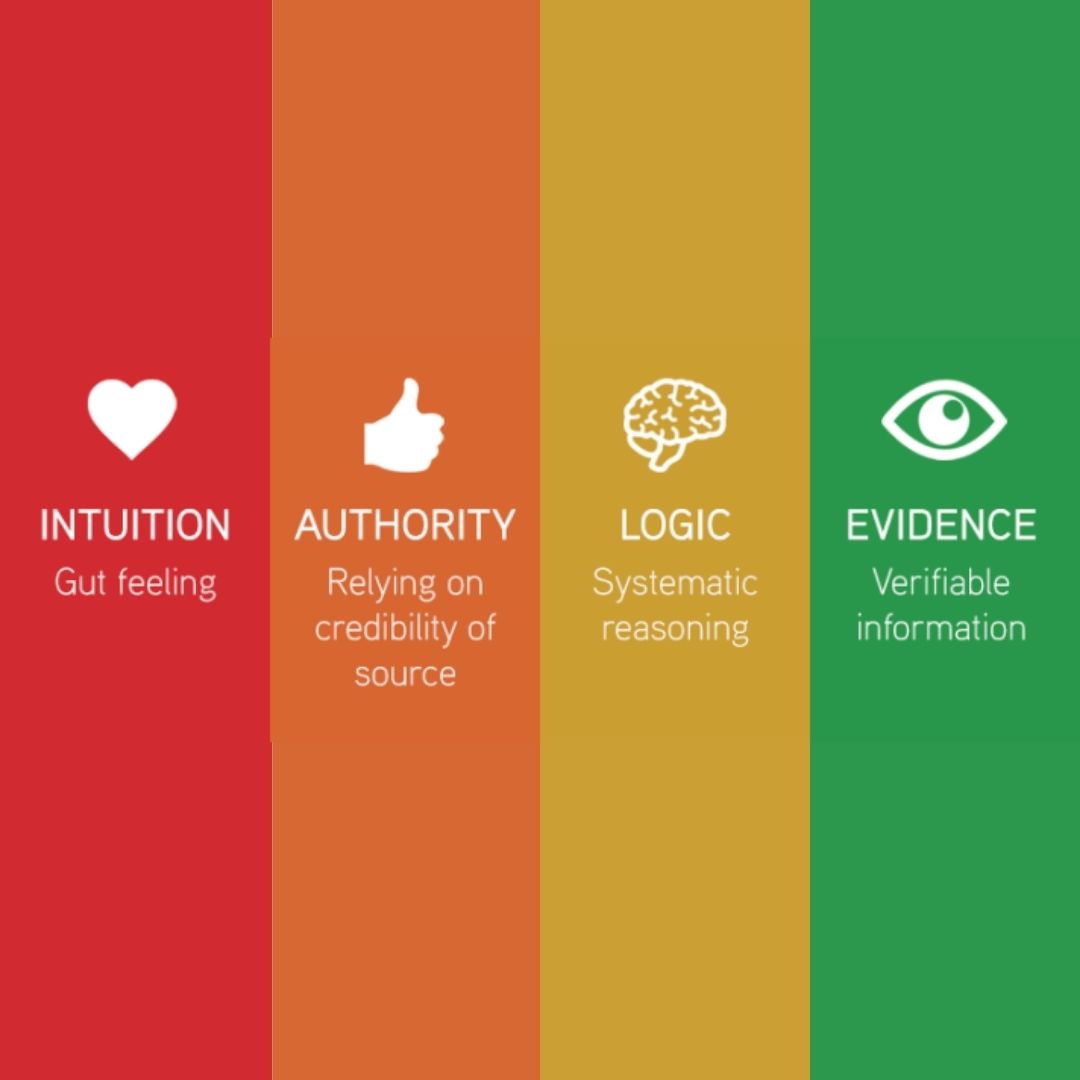
How Do We Decide What We Believe вђ Helping Students Learn How To The mindset of the entrepreneur is like a mental algorithm that wants to learn and improve as quickly as possible. the more data it can absorb, the better. entrepreneurs must deal with belief in. Affinity bias is the common tendency to believe, or agree with, the ideas of people you like or admire, and to discount or disagree with those you dislike. reactance bias is the tendency to do the. The important point, shermer says, is that we form our beliefs first and then look for evidence in support of them afterwards. he gives the names 'patternicity' and 'agenticity' to the brain's. The points are: we can have our beliefs based on our strong emotions related to specific feeling, that make us believe that our feelings must be fulfilled (satisfied) (the closest extent). we can have our beliefs, when those are derived from our deductive thinking nor empirical justification (the farthest extent).

How Do You Decide What To Believe Ppt Download The important point, shermer says, is that we form our beliefs first and then look for evidence in support of them afterwards. he gives the names 'patternicity' and 'agenticity' to the brain's. The points are: we can have our beliefs based on our strong emotions related to specific feeling, that make us believe that our feelings must be fulfilled (satisfied) (the closest extent). we can have our beliefs, when those are derived from our deductive thinking nor empirical justification (the farthest extent). The princeton psychology experiments found evidence for both theories. "across all studies, participants routinely indicated that what a believer ought to believe, or was justified in believing. Descartes divided the mind up into two faculties: intellect and will. the intellect gathers up data from the world and presents the mind with various potential beliefs that it might endorse; the will then chooses which of them to endorse. we can look at the evidence for or against a particular belief, but the final choice about what to believe remains a matter of choice. this raises the.

How Do You Decide What To Believe Ppt Download The princeton psychology experiments found evidence for both theories. "across all studies, participants routinely indicated that what a believer ought to believe, or was justified in believing. Descartes divided the mind up into two faculties: intellect and will. the intellect gathers up data from the world and presents the mind with various potential beliefs that it might endorse; the will then chooses which of them to endorse. we can look at the evidence for or against a particular belief, but the final choice about what to believe remains a matter of choice. this raises the.

Critical Thinking Deciding What To Believe What To Do Creativity

Comments are closed.