How The Tectonic Plates Move
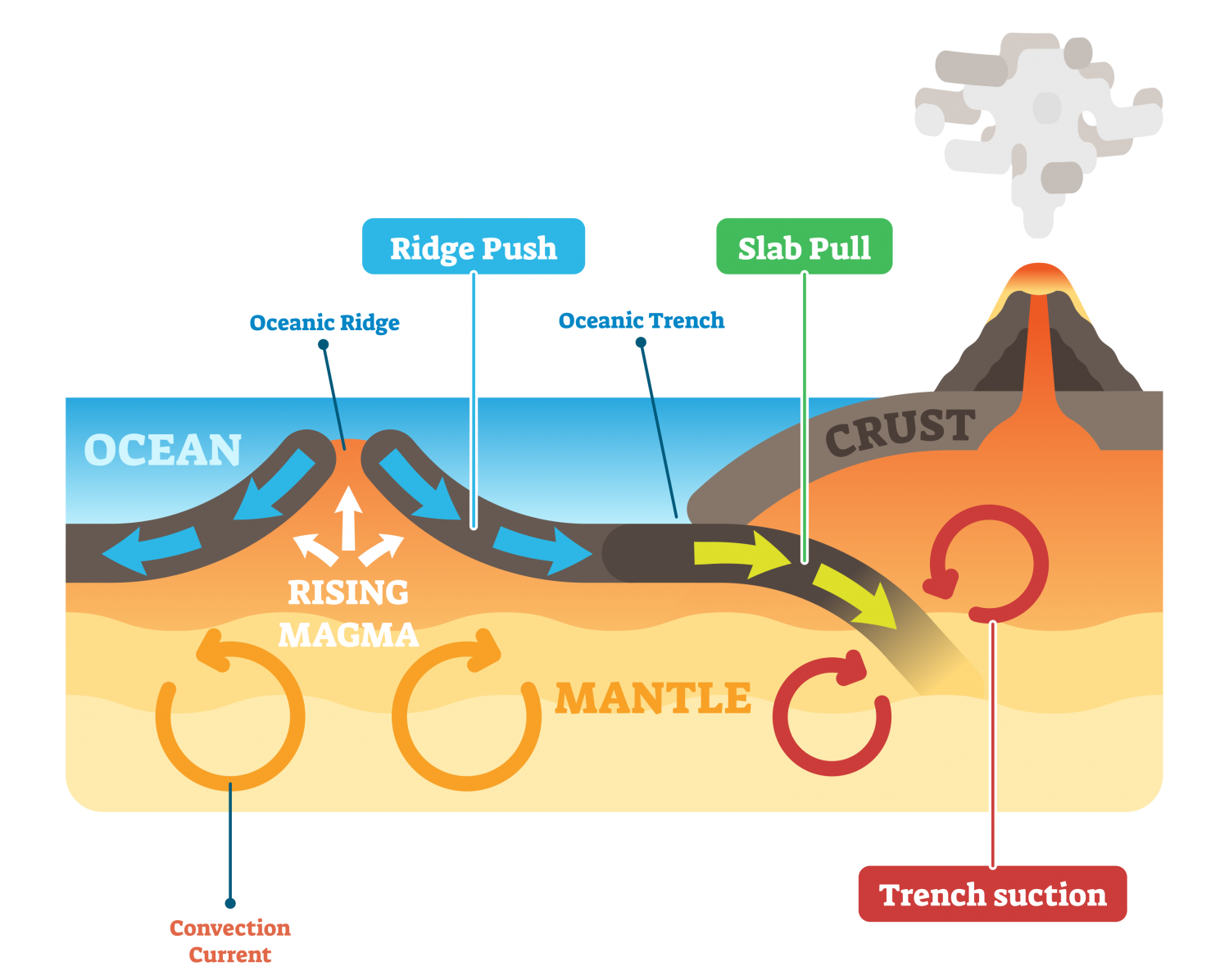
Week 2 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains how major landforms are created as a result of earth’s subterranean movements. the theory, which solidified in the 1960s, transformed the earth sciences by explaining many phenomena, including mountain building events, volcanoes, and earthquakes. in plate tectonics, earth’s outermost. Introduction. a tectonic plate is a large slab of solid rock with an irregular shape that is made up of the oceanic and continental lithosphere. the size of the plate varies to a large extent, ranging from a few hundred to thousands of kilometers. plates at the surface of the earth move due to intense heat from the core of the planet.
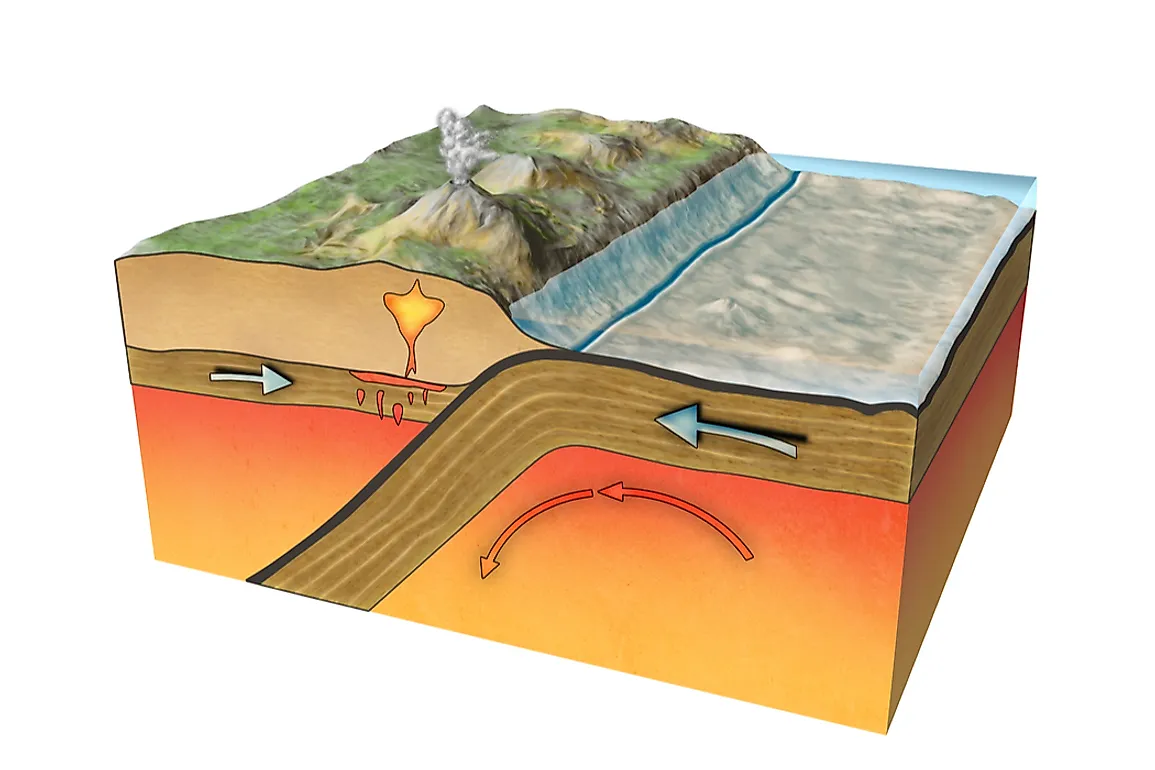
How Do Tectonic Plates Move Worldatlas In essence, plate tectonic theory is elegantly simple. earth ’s surface layer, 50 to 100 km (30 to 60 miles) thick, is rigid and is composed of a set of large and small plates. together, these plates constitute the lithosphere, from the greek lithos, meaning “ rock.”. the lithosphere rests on and slides over an underlying partially molten. Plate tectonics (from latin tectonicus, from ancient greek τεκτονικός (tektonikós) 'pertaining to building') [1] is the scientific theory that earth 's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. [2][3][4] the model builds on the concept of continental drift. At the “seams” where tectonic plates come in contact, the crustal rocks may grind violently against each other, causing earthquakes and volcano eruptions. the relatively fast movement of the tectonic plates under california explains the frequent earthquakes that occur there. tectonic shift is the movement of the plates that make up earth. Tectonic plates are essentially rigid segments of the earth’s lithosphere, a layer that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. they range in size from a few hundred to thousands of kilometers across. the tectonic plates connect the parts of earth’s lithosphere, much like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle.
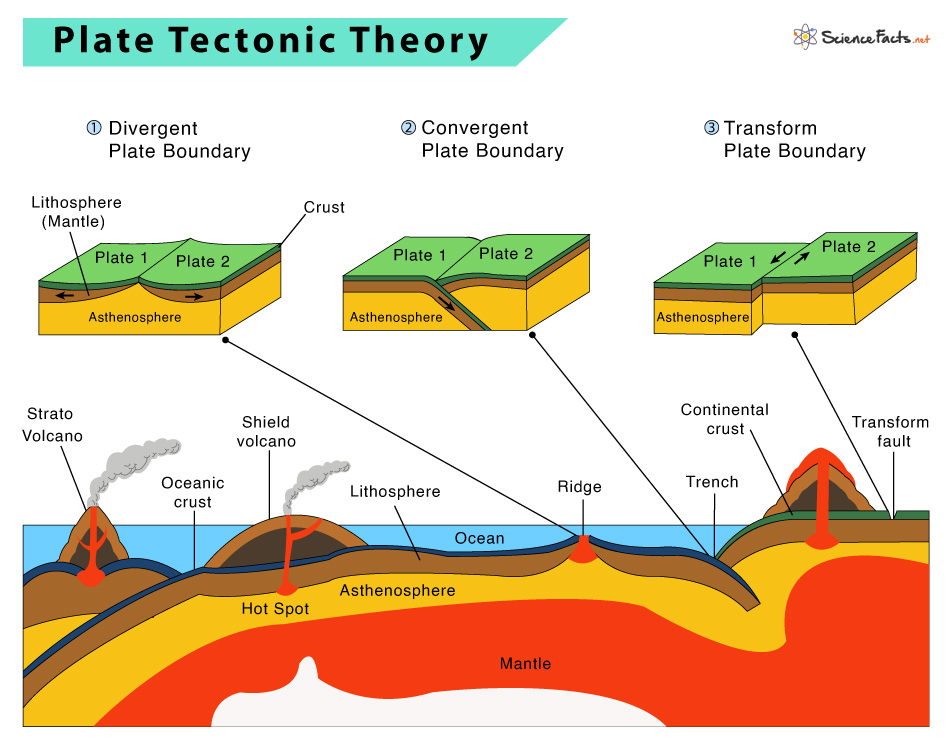
Plate Tectonics Plate Boundaries And Hotspot Explanation At the “seams” where tectonic plates come in contact, the crustal rocks may grind violently against each other, causing earthquakes and volcano eruptions. the relatively fast movement of the tectonic plates under california explains the frequent earthquakes that occur there. tectonic shift is the movement of the plates that make up earth. Tectonic plates are essentially rigid segments of the earth’s lithosphere, a layer that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. they range in size from a few hundred to thousands of kilometers across. the tectonic plates connect the parts of earth’s lithosphere, much like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. The movement of the plates creates three types of tectonic boundaries: convergent, where plates move into one another; divergent, where plates move apart; and transform, where plates move sideways. Tectonic plates, the massive slabs of earth’s lithosphere that help define our continents and ocean, are constantly on the move. plate tectonics is driven by a variety of forces: dynamic movement in the mantle, dense oceanic crust interacting with the ductile asthenosphere, even the rotation of the planet.

Plate Tectonics Definition Theory Facts Evidence Britannica The movement of the plates creates three types of tectonic boundaries: convergent, where plates move into one another; divergent, where plates move apart; and transform, where plates move sideways. Tectonic plates, the massive slabs of earth’s lithosphere that help define our continents and ocean, are constantly on the move. plate tectonics is driven by a variety of forces: dynamic movement in the mantle, dense oceanic crust interacting with the ductile asthenosphere, even the rotation of the planet.

Tectonic Plates

Comments are closed.