
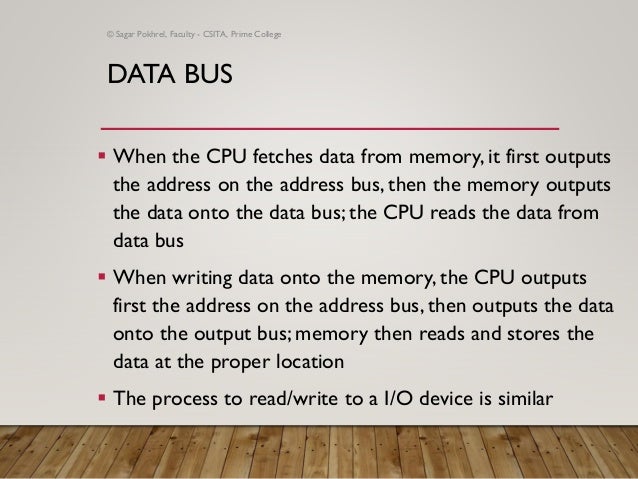
Control Bus Address Bus Data Bus It details the functions and interactions of various computer components, including the types of buses (address, data, and control) that facilitate data transfer. In a computer system, each peripheral or memory location is identified by a numerical value, called an address and the address bus is used to carry this numerical value as well as it also contains a few control lines to carry control commands.
Introduction To Bus Address Data Control Bus The electrically conducting path along which data is transmitted inside any digital electronic device. a computer bus consists of a set of parallel conductors, which may be conventional wires, copper tracks on a printed circuit board, or microscopic aluminum trails on the surface of a silicon chip. The computer bus is a communication link used in a computer system to send data, addresses , control signals, and power to various hardware components in a computer system. The address bus is used to carry the address from one component to another. it also consists of different wires like a data bus. it is used to connect the central processing unit (cpu) and main memory, and main memory like ram. Introduction a bus is simply the name given for links, channels or wires, along which you can send one of three types of information. these are: data addresses control information.
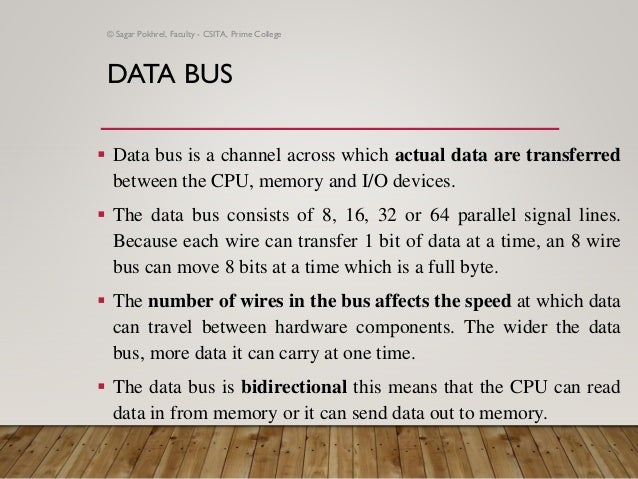
Introduction To Bus Address Data Control Bus The address bus is used to carry the address from one component to another. it also consists of different wires like a data bus. it is used to connect the central processing unit (cpu) and main memory, and main memory like ram. Introduction a bus is simply the name given for links, channels or wires, along which you can send one of three types of information. these are: data addresses control information. What is a bus? how fast is a bus? 1. address bus. 2. data bus. 3. control bus. 1. is the control bus unidirectional or not? 2. what is the direction of the address bus? 3. how does a control bus work? 4. how is bus speed measured? 5. what determines the size of a bus? 6. can data be transferred in both directions on a data bus? 7. The address bus is unidirectional, information flows over it only in one direction, from the cpu to the memory or i o devices. the cpu generates addresses on the lines of the address bus. each of the addresses corresponds to one memory location or one i o device. The address bus carries addressing signals from the processor to memory, i o (or peripherals), and other addressable devices around the processor. control signals move out of the processor, but not in to it. figure 1: internal system bus. The bus is a medium used to transfer data, memory addresses, and control signals within a computer system. it connects internal components like the cpu, main memory, and i o ports. there are different types of buses: data buses transfer data, address buses transfer memory addresses, and control buses transfer timing and control signals.