
Internal Structure Of A Leaf And Functions Learn about the internal structure and function of a leaf, including the epidermis, mesophyll, vascular bundles, and stomata. explore how leaves are adapted to different environmental conditions, such as cold, hot, and aquatic climates. Leaf, in botany, any usually flattened green outgrowth from the stem of a vascular plant. as the primary sites of photosynthesis, leaves manufacture food for plants, which in turn ultimately nourish and sustain all land animals. botanically, leaves are an integral part of the stem system.

Leaf Structure And Function Leaf Structure And Function Study In this section, we will explore how each tissue’s structure contributes to the production of food. a cross section of a leaf shows that it is a complex organ built of several different kinds of specialized tissues. the tissues, in turn, are built of specialized cells, and the cells, of organelles. Plants adapt in order to efficiently collect raw materials required for photosynthesis. these raw materials must be transported through the plant and various factors can affect the rate of. In this section, we will explore how each tissue’s structure contributes to the production of food. a cross section of a leaf shows that it is a complex organ built of several different kinds of specialized tissues. the tissues, in turn, are built of specialized cells, and the cells, of organelles. Leaves are the main sites for photosynthesis: the process by which plants synthesize food. most leaves are usually green, due to the presence of chlorophyll in the leaf cells. however, some leaves may have different colors, caused by other plant pigments that mask the green chlorophyll.
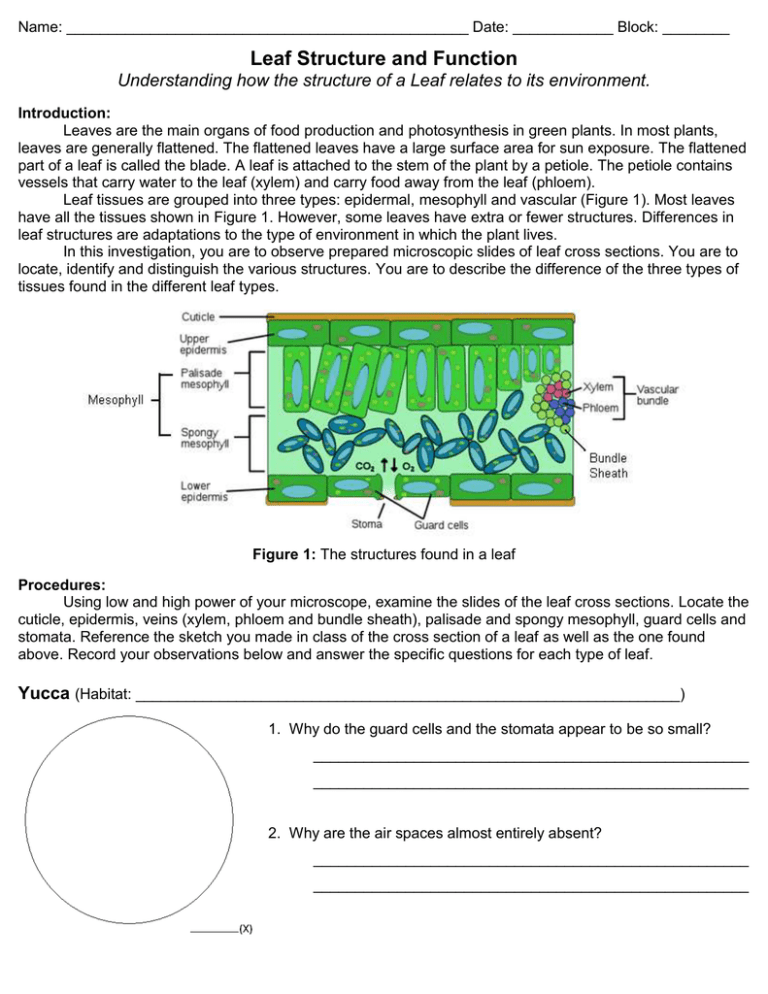
Leaf Structure And Function In this section, we will explore how each tissue’s structure contributes to the production of food. a cross section of a leaf shows that it is a complex organ built of several different kinds of specialized tissues. the tissues, in turn, are built of specialized cells, and the cells, of organelles. Leaves are the main sites for photosynthesis: the process by which plants synthesize food. most leaves are usually green, due to the presence of chlorophyll in the leaf cells. however, some leaves may have different colors, caused by other plant pigments that mask the green chlorophyll. Explore the structure and functions of different leaf parts with a detailed diagram. understand leaf anatomy and its role in plant life processes. Learn about the structure and function of leaves, the main lateral appendage of vascular plants. find out how leaves perform photosynthesis, transpiration, guttation, storage and defense, and explore the six major types of leaf. Detailed breakdown of a leaf’s structure with labeled diagram parts, including veins, petiole, lamina, and stomata. learn about their roles in plant functions.

Leaf Structure And Function Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Explore the structure and functions of different leaf parts with a detailed diagram. understand leaf anatomy and its role in plant life processes. Learn about the structure and function of leaves, the main lateral appendage of vascular plants. find out how leaves perform photosynthesis, transpiration, guttation, storage and defense, and explore the six major types of leaf. Detailed breakdown of a leaf’s structure with labeled diagram parts, including veins, petiole, lamina, and stomata. learn about their roles in plant functions.
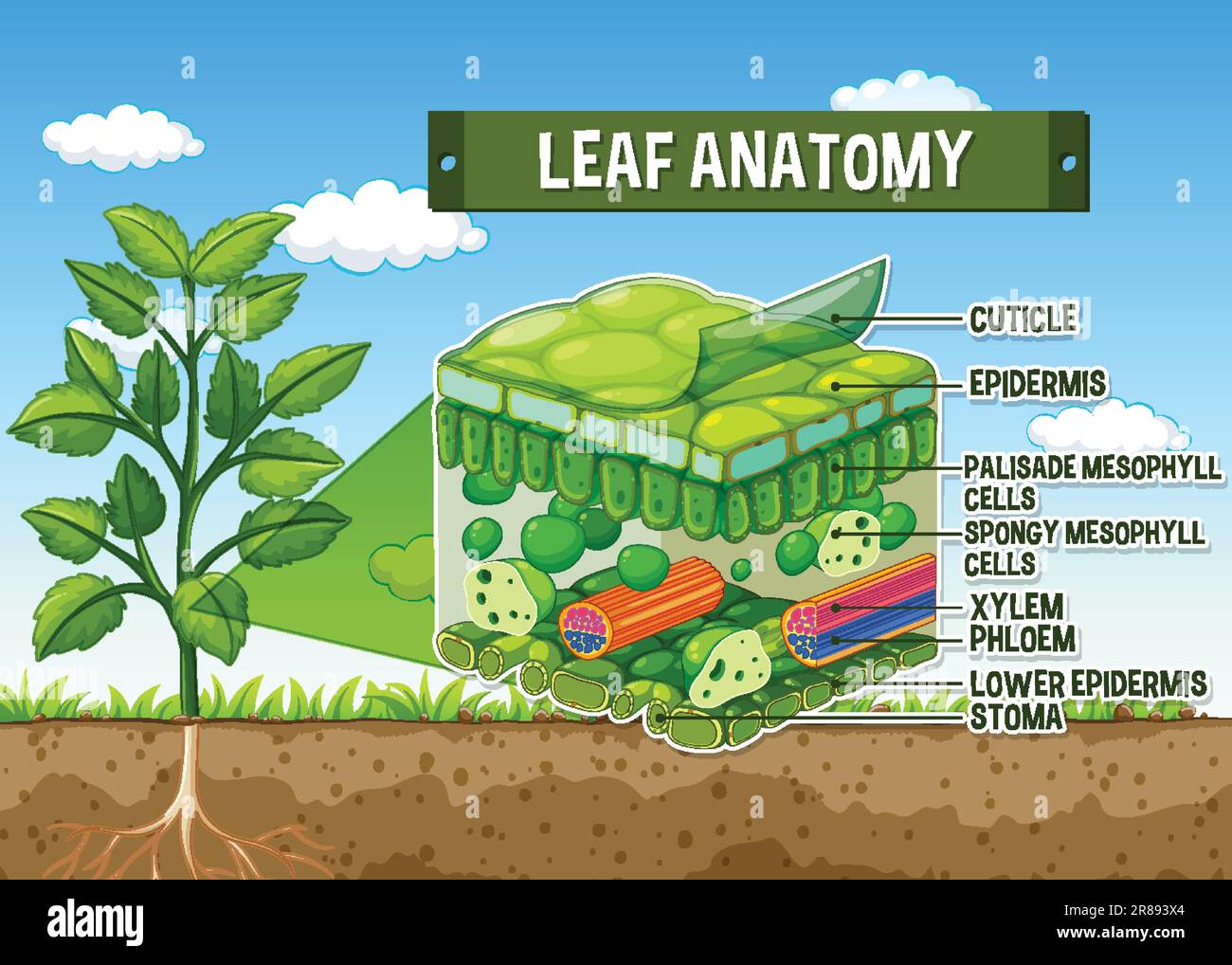
Function Of Leaf Structure At Anthony Hilder Blog Detailed breakdown of a leaf’s structure with labeled diagram parts, including veins, petiole, lamina, and stomata. learn about their roles in plant functions.