
Magnetic Induction Qs Study Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field. michael faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1831, and james clerk maxwell mathematically described it as faraday's law of induction. Learn about the principle of magnetic induction, which states that magnetic fields can produce electric currents. understand the concept of magnetic flux and how to calculate it using faraday's law and lenz's law.

Magnetic Induction Clever Scientific Laboratory At its core, induction involves creating an electric current by changing magnetic fields. but what does this mean? how does an invisible magnetic force create an electric flow? how did scientists discover this mysterious relationship, and how do we harness it in everyday technology?. The basic process of generating currents with magnetic fields is called induction; this process is also called magnetic induction to distinguish it from charging by induction, which uses the electrostatic coulomb force. Learn about magnetic induction, the production of voltage across a conductor in a varying magnetic field. find formulas, examples, faqs and a video on faraday's law of induction. Learn what magnetic induction is, how it works, and why it is important for electrical devices. find out faraday's law, lenz's law, and examples of magnetic induction in generators, transformers, inductors, and more.
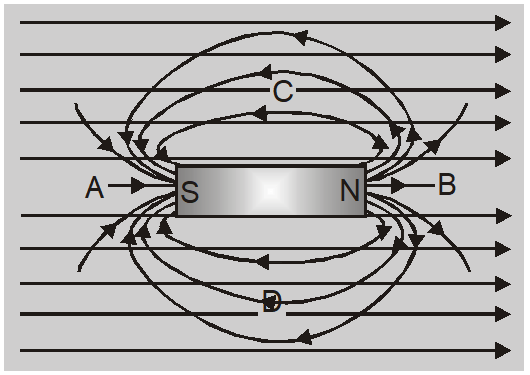
Magnetic Induction Magnetism And Matters Class 12 Learn about magnetic induction, the production of voltage across a conductor in a varying magnetic field. find formulas, examples, faqs and a video on faraday's law of induction. Learn what magnetic induction is, how it works, and why it is important for electrical devices. find out faraday's law, lenz's law, and examples of magnetic induction in generators, transformers, inductors, and more. Electromagnetic induction, a fundamental principle of physics, is the process by which a conductor placed in a changing magnetic field, or a conductor moving through a stationary magnetic field, induces an electric current. discovered by michael faraday in 1831, this phenomenon has vast implications and applications in modern technology. Faraday’s law of induction, in physics, a quantitative relationship expressing that a changing magnetic field induces a voltage in a circuit, developed on the basis of experimental observations made in 1831 by the english scientist michael faraday. Learn how a changing magnetic field can produce an electromotive force (emf) and a current in a circuit, according to faraday’s law of induction. understand the concept of magnetic flux, lenz’ law, and the energy conservation involved in induction. What is magnetic induction? magnetic induction is the phenomenon through which a magnetic field generates an electric field. when an electric field is generated in a conductive material, the charge carriers are exposed to a force, and an electric current is induced in the conductor.

Magnetic Induction Motor Overview Stable Diffusion Online Electromagnetic induction, a fundamental principle of physics, is the process by which a conductor placed in a changing magnetic field, or a conductor moving through a stationary magnetic field, induces an electric current. discovered by michael faraday in 1831, this phenomenon has vast implications and applications in modern technology. Faraday’s law of induction, in physics, a quantitative relationship expressing that a changing magnetic field induces a voltage in a circuit, developed on the basis of experimental observations made in 1831 by the english scientist michael faraday. Learn how a changing magnetic field can produce an electromotive force (emf) and a current in a circuit, according to faraday’s law of induction. understand the concept of magnetic flux, lenz’ law, and the energy conservation involved in induction. What is magnetic induction? magnetic induction is the phenomenon through which a magnetic field generates an electric field. when an electric field is generated in a conductive material, the charge carriers are exposed to a force, and an electric current is induced in the conductor.