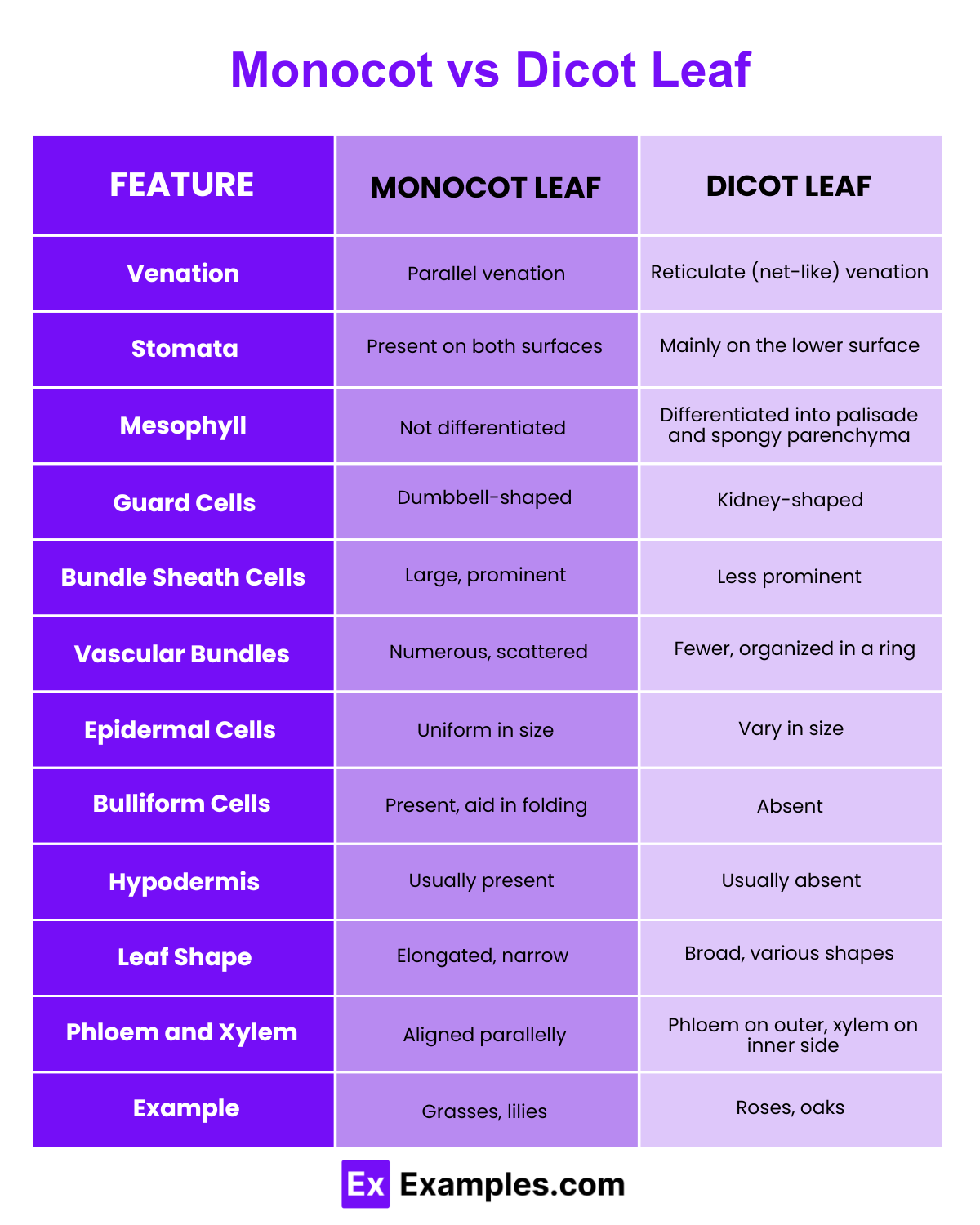
Monocot And Dicot Leaf Cross Section Differences Infoupdate Org Monocots and dicots differ in four distinct structural features: seeds, leaves, stems, roots, and flowers. however, the difference starts from the very beginning of their life cycle in the form of a seed. within the seed lies the embryo or the baby plant. Monocots and dicots are the two broad groups of flowering plants or angiosperms. historically, scientists classified plants as monocots or dicots based on distinct differences between them.
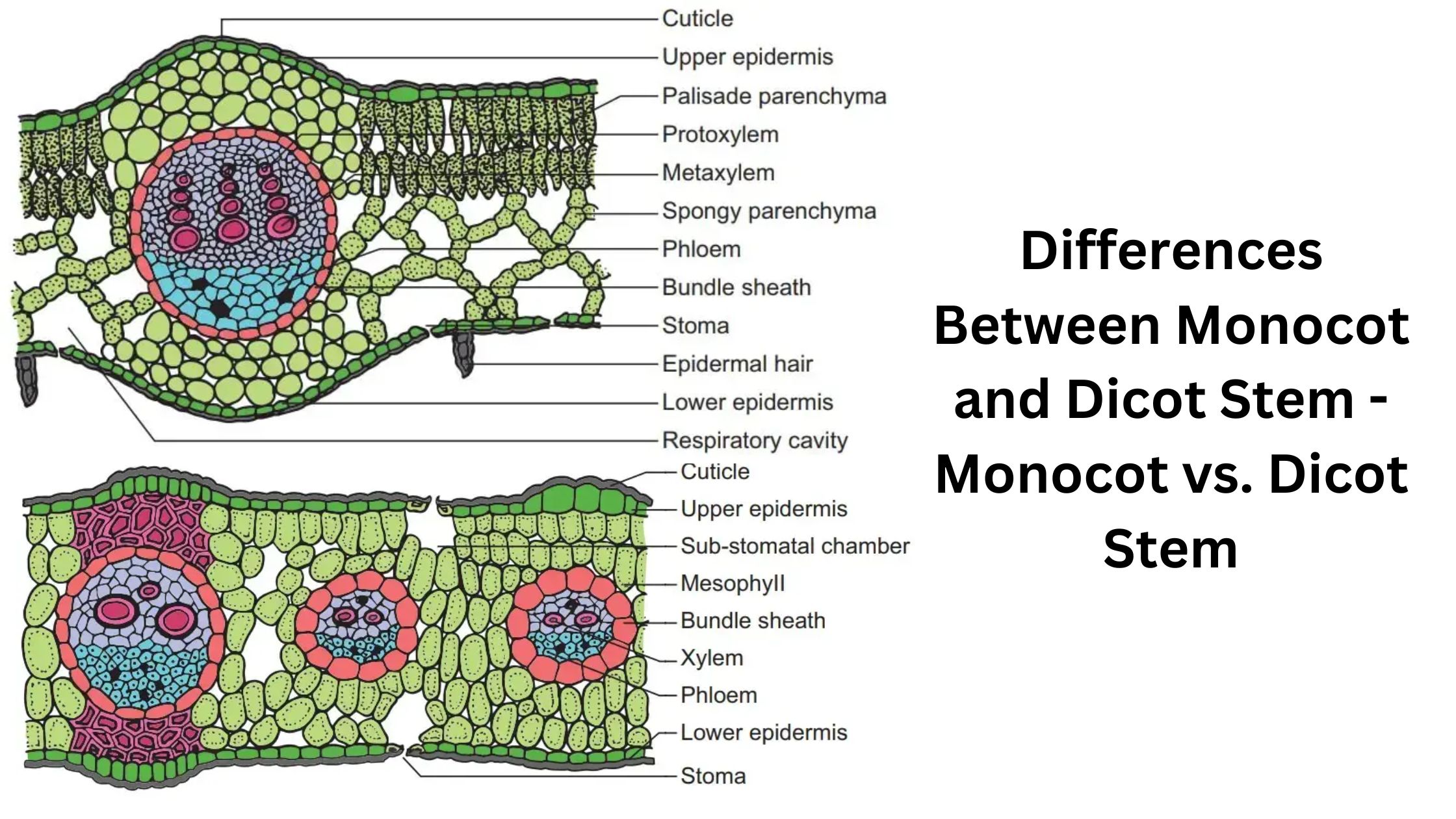
Monocot And Dicot Leaf Cross Section Differences Infoupdate Org Flowering plants are divided into monocots (or monocotyledons) and dicots (or dicotyledons). this comparison examines the morphological differences in the leaves, stems, flowers and fruits of monocots and dicots. Unlike monocots, dicots are not a group of plants arising from a single ancestor; rather, they are assumed to have evolved from different lineages. thus dicots are paraphyletic. the types of plants in dicots range from garden plants, shrubs, and herbs to broadleaf plants like roses and geraniums. Now that you know a bit more about the two main groups of flowering plants, let’s have a look at how dicots and monocots differ: monocots have just one cotyledon. dicots come with two embryonic leaves. monocots’ leaf veins typically have a parallel arrangement. dicotyledons’ leaf veins are generally branched (or reticulated). Eld trying to identify a plant using a key. the names or these groups are derived from the number of cotyledons or seed leaves tha. the embryonic seedling has within its seed. a monocot, which an abbreviation for monocotyledon, will have only one cotyledon and a dic.
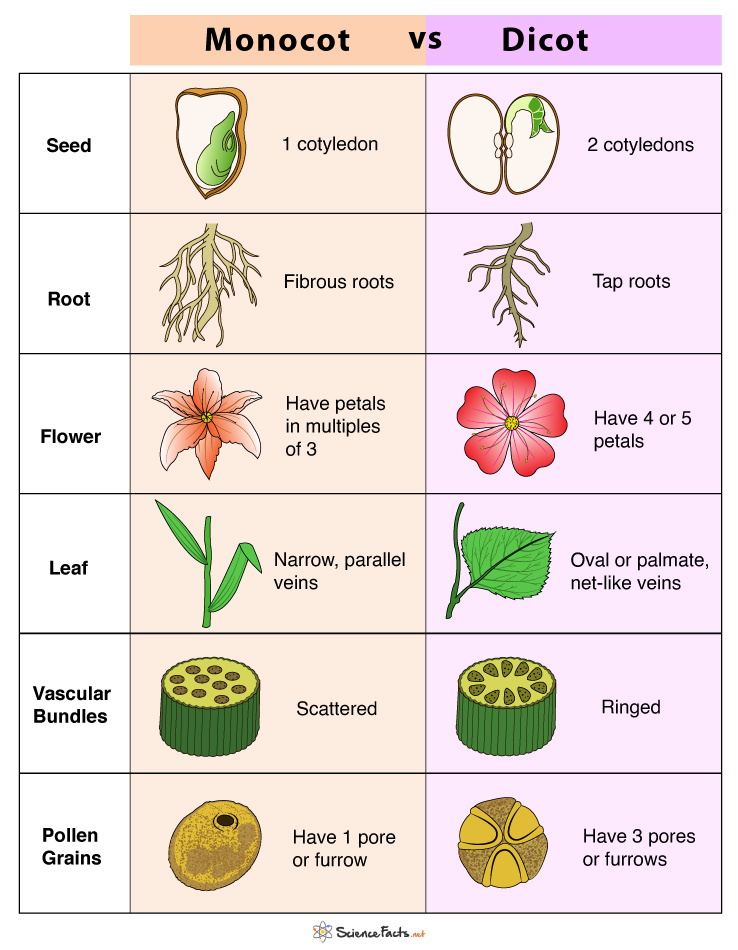
Monocot Vs Dicot Differences And Examples Now that you know a bit more about the two main groups of flowering plants, let’s have a look at how dicots and monocots differ: monocots have just one cotyledon. dicots come with two embryonic leaves. monocots’ leaf veins typically have a parallel arrangement. dicotyledons’ leaf veins are generally branched (or reticulated). Eld trying to identify a plant using a key. the names or these groups are derived from the number of cotyledons or seed leaves tha. the embryonic seedling has within its seed. a monocot, which an abbreviation for monocotyledon, will have only one cotyledon and a dic. Monocot and dicot differ in their roots, stem, leaves, flowers and seeds. the main difference between monocot and dicot is that monocot contains a single cotyledon in its embryo whereas dicot contains two cotyledons in its embryo. Monocots and dicots differ in several ways which help in their identification and understanding of their origins. paleobotanists, scientists who study the origins of plants, hypothesize that dicotyledons evolved first, and monocots branched off about 140 to 150 million years ago either from the fusion of the cotyledons or as a separate line. Monocots have a single cotyledon in their seeds and parallel veined leaves, while dicots have two cotyledons and leaves with a branched vein pattern. monocots and dicots are terms that describe two primary groups of angiosperms, or flowering plants, distinguished mainly by the number of cotyledons (seed leaves) they possess. Monocots and dicots differ in key physical and structural features, including leaves, roots, stems, flowers, and seeds. these distinctions are fundamental to plant classification and cultivation practices. monocots have leaves with parallel venation, where veins run side by side without intersecting. corn and grasses are examples.
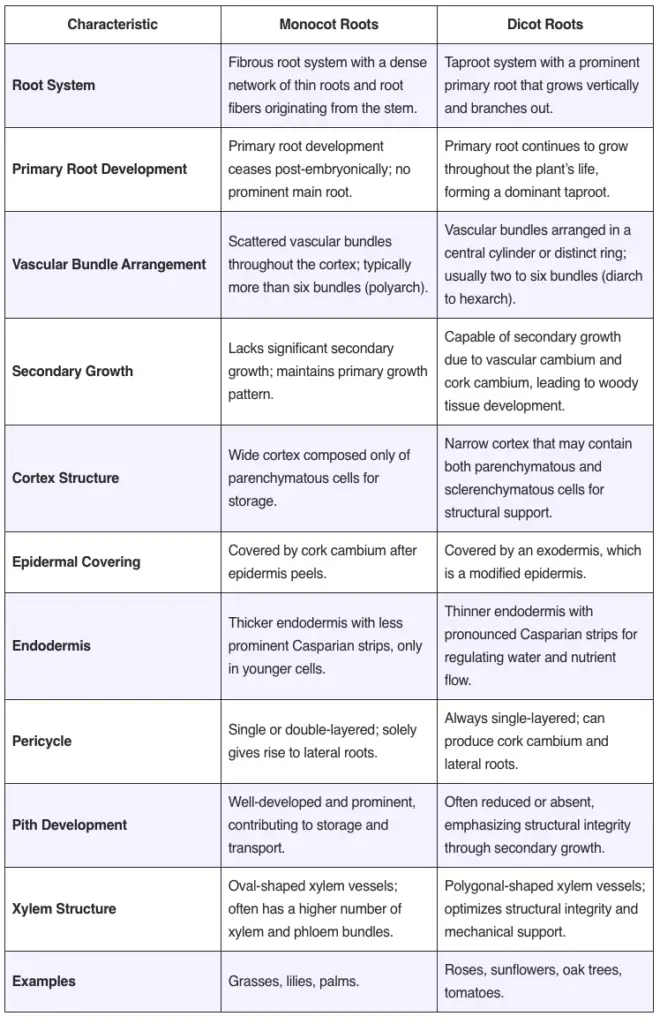
Differences Between Monocot And Dicot Seed Monocot Vs Dicot Seed Monocot and dicot differ in their roots, stem, leaves, flowers and seeds. the main difference between monocot and dicot is that monocot contains a single cotyledon in its embryo whereas dicot contains two cotyledons in its embryo. Monocots and dicots differ in several ways which help in their identification and understanding of their origins. paleobotanists, scientists who study the origins of plants, hypothesize that dicotyledons evolved first, and monocots branched off about 140 to 150 million years ago either from the fusion of the cotyledons or as a separate line. Monocots have a single cotyledon in their seeds and parallel veined leaves, while dicots have two cotyledons and leaves with a branched vein pattern. monocots and dicots are terms that describe two primary groups of angiosperms, or flowering plants, distinguished mainly by the number of cotyledons (seed leaves) they possess. Monocots and dicots differ in key physical and structural features, including leaves, roots, stems, flowers, and seeds. these distinctions are fundamental to plant classification and cultivation practices. monocots have leaves with parallel venation, where veins run side by side without intersecting. corn and grasses are examples.