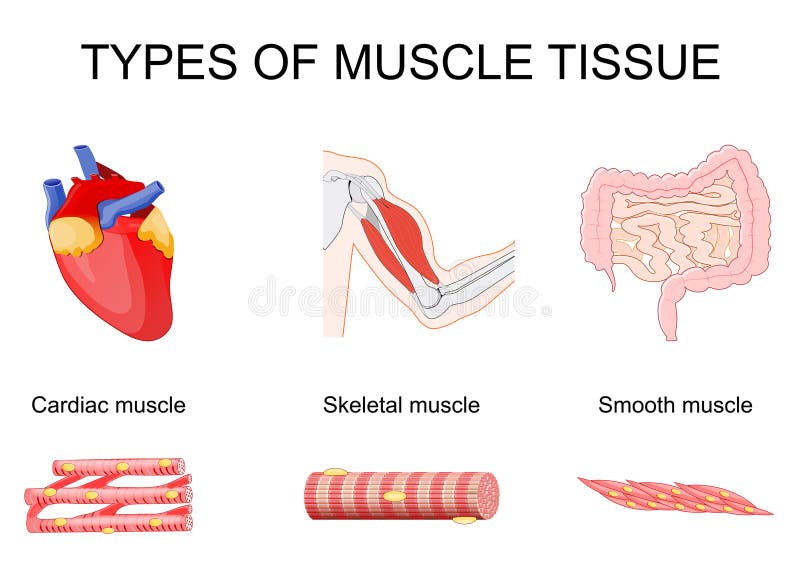
Muscular Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Muscle The main difference between cardiac skeletal and smooth muscle is that cardiac muscles perform involuntary muscular movements of the heart, aiding the heart to pump blood throughout the body, while skeletal muscles perform a voluntary muscular movements of bones, aiding physical movements of the body such as walking, running, and writing and. Skeletal muscles undergo powerful and rapid contractions with short rest periods and hence get fatigued easily. they are supplied by voluntary nervous system (cns and pns).

Muscular Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Muscle Based on structure and function, the muscle tissues of vertebrates (including humans) are classified into three types, viz. skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue is classified into three types according to structure and function: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth (table 4.2). skeletal muscle is attached to bones and its contraction makes possible locomotion, facial expressions, posture, and other voluntary movements of the body. forty percent of your body mass is made up of skeletal muscle. Muscle tissue is subdivided into three broad categories: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. the three types of muscle can be distinguished by both their locations and their microscopic features. skeletal muscle is found attached to bones. it consists of long multinucleate fibers. There are 3 types of muscle tissue in the human body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. in this video and article compilation, i’m going to discuss all three types of muscle tissue. skeletal muscles most commonly attach to bones, and they help you move your body.
Muscular Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Muscle Muscle tissue is subdivided into three broad categories: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. the three types of muscle can be distinguished by both their locations and their microscopic features. skeletal muscle is found attached to bones. it consists of long multinucleate fibers. There are 3 types of muscle tissue in the human body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. in this video and article compilation, i’m going to discuss all three types of muscle tissue. skeletal muscles most commonly attach to bones, and they help you move your body. Contrast the structure and function of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissue. identify morphological differences in smooth muscle across tissues. identify the functional components of a neuromuscular junction. identify some key pathological examples relevant to muscle histology. muscles are multicellular contractile units. Search search build circle toolbar fact check homework cancel exit reader mode. Skeletal muscles, viewed under a microscope, appear striated. smooth muscles are found in the walls of hollow structures, including veins and blood vessels. cardiac muscles appear striped or striated when viewed under a microscope. human muscular system: what's the busiest muscle in the body?. At the most basic level we can separate muscle tissue into smooth and striated, where the striations originate from a repeating pattern of regularly arranged proteins, whereas "smoothness" is conferred by an irregular arrangement without a repeating pattern.

Muscular Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Muscle Contrast the structure and function of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissue. identify morphological differences in smooth muscle across tissues. identify the functional components of a neuromuscular junction. identify some key pathological examples relevant to muscle histology. muscles are multicellular contractile units. Search search build circle toolbar fact check homework cancel exit reader mode. Skeletal muscles, viewed under a microscope, appear striated. smooth muscles are found in the walls of hollow structures, including veins and blood vessels. cardiac muscles appear striped or striated when viewed under a microscope. human muscular system: what's the busiest muscle in the body?. At the most basic level we can separate muscle tissue into smooth and striated, where the striations originate from a repeating pattern of regularly arranged proteins, whereas "smoothness" is conferred by an irregular arrangement without a repeating pattern.