
Neural Circuitry Of Fear Diagram Quizlet Red arrows and letters indicate structures and projections involved during specific contextual fear memory phases. gray arrows and projections indicate hypothesized functional connectivity during specific contextual fear memory phases. More recently, brain researchers have found that fear and anxiety worry may have distinct neural circuitry. fear can be thought of as the response to an immediate and present danger, while.

Neural Mechanisms In Aggression Diagram Quizlet A large volume of experimental work has examined the neurocircuitry associated with fear responses, mainly in rodents, using primarily fear conditioning, inhibitory avoidance, and fear potentiated startle models. Recent fmri studies on specific animal phobias, particularly spider phobia (arachnophobia), have identified a large variety of specific brain regions involved in normal and disturbed fear. Both implicit and explicit fear processing activated amygdala, declive, fusiform gyrus, and middle frontal gyrus, suggesting that these two types of fear processing share a common neural substrate. At the forefront of this emotional regulation is the amygdala, a small almond shaped structure located in the medial temporal lobe. the amygdala is critically involved in the processing of fear and is responsible for the threat detection that triggers automatic defensive behaviors.

Neural Activities Behavior And Cognition Flashcards Quizlet Both implicit and explicit fear processing activated amygdala, declive, fusiform gyrus, and middle frontal gyrus, suggesting that these two types of fear processing share a common neural substrate. At the forefront of this emotional regulation is the amygdala, a small almond shaped structure located in the medial temporal lobe. the amygdala is critically involved in the processing of fear and is responsible for the threat detection that triggers automatic defensive behaviors. Data show that fear of painful stimuli, predators and aggressive members of the same species are processed in independent neural circuits that involve the amygdala and downstream. Recent fmri studies on specific animal phobias, particularly spider phobia (arachnophobia), have identified a large variety of specific brain regions involved in normal and disturbed fear processing. both functional and structural brain abnormalities have been identified among phobic patients. The amygdala, often called the brain’s alarm system, is a primary area for processing fear. it receives sensory information, assesses potential threats, and initiates a cascade of signals to prepare the body to react when a threat is detected. Pavlovian or classical fear conditioning is recognized as a model system to investigate the neurobiological mechanisms of learning and memory in the mammalian brain and to understand the root of fear related disorders in humans.

A Neural Switch For Fear Science In School Data show that fear of painful stimuli, predators and aggressive members of the same species are processed in independent neural circuits that involve the amygdala and downstream. Recent fmri studies on specific animal phobias, particularly spider phobia (arachnophobia), have identified a large variety of specific brain regions involved in normal and disturbed fear processing. both functional and structural brain abnormalities have been identified among phobic patients. The amygdala, often called the brain’s alarm system, is a primary area for processing fear. it receives sensory information, assesses potential threats, and initiates a cascade of signals to prepare the body to react when a threat is detected. Pavlovian or classical fear conditioning is recognized as a model system to investigate the neurobiological mechanisms of learning and memory in the mammalian brain and to understand the root of fear related disorders in humans.
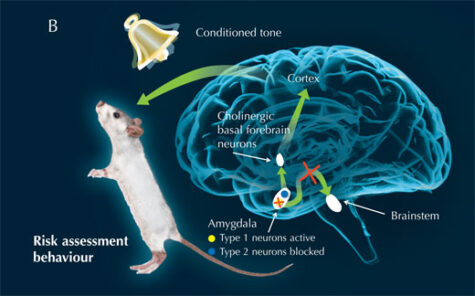
A Neural Switch For Fear Science In School The amygdala, often called the brain’s alarm system, is a primary area for processing fear. it receives sensory information, assesses potential threats, and initiates a cascade of signals to prepare the body to react when a threat is detected. Pavlovian or classical fear conditioning is recognized as a model system to investigate the neurobiological mechanisms of learning and memory in the mammalian brain and to understand the root of fear related disorders in humans.