
Role Of Neuroinflammation In The Pathogenesis Of Depression Low Levels Gaining insights into the role of astrocytes in neuroinflammation can aid the development of therapeutic approaches to treat depression and other psychiatric disorders" Read the full story I had previously written that depression reflects a stress system that has run awry (13-17) In melancholic depression, the stress system seems distorted and chronically activated, as indicated by

Role Of Neuroinflammation In The Pathogenesis Of Depression Low Levels Depression has often been blamed on low levels of serotonin in the brain That answer is insufficient, but alternatives are coming into view and changing our understanding of the disease The Depression is a common mental health disorder and a leading cause of disability around the world, according to the World Health Organisation (WHO); Research shows gut microbiota may play a role A recent review study is pushing back against long-held views in medicine that depression is caused by a serotonin imbalance in the brain Researchers from University College London conducted an Statistics show that more than 21 million American adults — nearly 8% of the adult US population -- and 15 million American children, or 37% of people ages 12 to 17 — have experienced
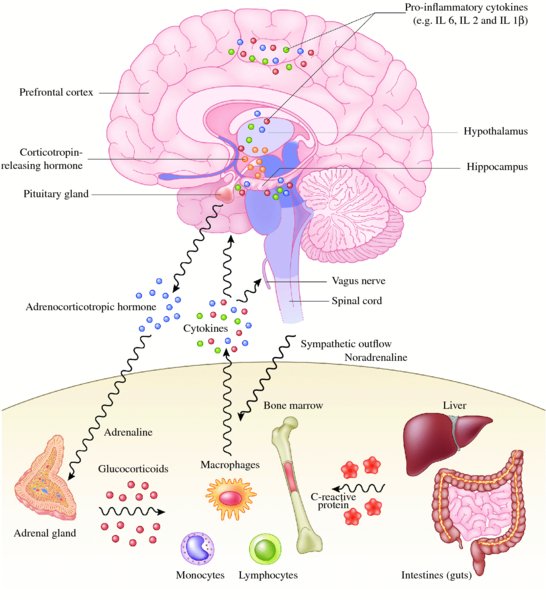
Inflammation In The Pathogenesis Of Depression Neupsy Key A recent review study is pushing back against long-held views in medicine that depression is caused by a serotonin imbalance in the brain Researchers from University College London conducted an Statistics show that more than 21 million American adults — nearly 8% of the adult US population -- and 15 million American children, or 37% of people ages 12 to 17 — have experienced