
Sliding Filament Model Of Contraction Pdf Muscle Contraction Actin Learn how thick and thin filaments slide past each other in sarcomeres to cause muscle contraction. see diagrams, definitions, and examples of the sliding filament theory and its mechanisms. The sliding filament theory is a widely accepted explanation of the mechanism that underlies muscle contraction. [6] this model shows the four main and significant steps of the sliding filament theory as well as with a detailed visual.
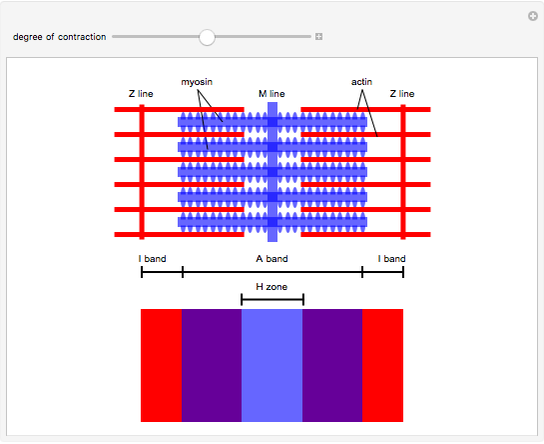
Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Wolfram Demonstrations The sliding filament theory is a fundamental concept in muscle physiology that explains how muscles contract to generate force. this theory is based on the interactions between two types of protein filaments—actin (thin filaments) and myosin (thick filaments)—within the muscle fibers. The sliding filament theory is the most accepted theory that explains how muscle fibers contract. it states that when a muscle contracts, the actin and myosin filaments slide past each other, causing the sarcomere to shorten. The sliding filament model for muscle is almost like setting the stage. now we need to know what the various actors actually do to get the whole muscle show on the road, and what happens when the players forget their lines. Learn how actin and myosin filaments slide past each other to produce muscle tension and shorten the sarcomere. see diagrams, analogies, and examples of the sliding filament theory and its molecular mechanisms.
Muscle Contraction Using Sliding Filament Model Labelled Diagram The sliding filament model for muscle is almost like setting the stage. now we need to know what the various actors actually do to get the whole muscle show on the road, and what happens when the players forget their lines. Learn how actin and myosin filaments slide past each other to produce muscle tension and shorten the sarcomere. see diagrams, analogies, and examples of the sliding filament theory and its molecular mechanisms. When signaled by a motor neuron, a skeletal muscle fiber contracts as the thin filaments are pulled and then slide past the thick filaments within the fiber’s sarcomeres. this process is known as the sliding filament model of muscle contraction (figure 10.10). The sliding filament model of muscle contraction describes how muscles generate force and produce movement. muscle contraction occurs as a result of the sliding of thin filaments (actin) over thick filaments (myosin) within muscle fibers. The sliding filament model describes the process used by muscles to contract. it is a cycle of repetitive events that causes actin and myosin myofilaments to slide over each other, contracting the sarcomere and generating tension in the muscle. These filaments slide in and out between each other causing muscle contractions, hence the name sliding filament theory! eccentric muscle contraction – the muscle is lengthening and is typically used to resist or slow motion (eg. lowering phase of a bicep curl or squat).

Video Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Osmosis When signaled by a motor neuron, a skeletal muscle fiber contracts as the thin filaments are pulled and then slide past the thick filaments within the fiber’s sarcomeres. this process is known as the sliding filament model of muscle contraction (figure 10.10). The sliding filament model of muscle contraction describes how muscles generate force and produce movement. muscle contraction occurs as a result of the sliding of thin filaments (actin) over thick filaments (myosin) within muscle fibers. The sliding filament model describes the process used by muscles to contract. it is a cycle of repetitive events that causes actin and myosin myofilaments to slide over each other, contracting the sarcomere and generating tension in the muscle. These filaments slide in and out between each other causing muscle contractions, hence the name sliding filament theory! eccentric muscle contraction – the muscle is lengthening and is typically used to resist or slow motion (eg. lowering phase of a bicep curl or squat).

Video Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Osmosis The sliding filament model describes the process used by muscles to contract. it is a cycle of repetitive events that causes actin and myosin myofilaments to slide over each other, contracting the sarcomere and generating tension in the muscle. These filaments slide in and out between each other causing muscle contractions, hence the name sliding filament theory! eccentric muscle contraction – the muscle is lengthening and is typically used to resist or slow motion (eg. lowering phase of a bicep curl or squat).