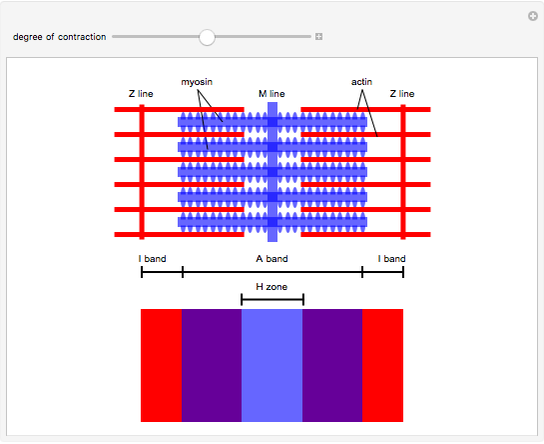
Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Wolfram Demonstrations The sliding filament model of muscle contraction describes how muscles generate force and produce movement. muscle contraction occurs as a result of the sliding of thin filaments (actin) over thick filaments (myosin) within muscle fibers. Sliding filament theory explains how muscles contract at a cellular level. learn more and test yourself with our quizzes here: more.
Muscle Contraction Using Sliding Filament Model Labelled Diagram Contraction of muscle is caused by sliding of thick and thin filaments in the sarcomere. this sliding requires binding of calcium to the filaments and energy in the form of atp. The sliding filament theory is a fundamental concept in muscle physiology that explains how muscles contract to generate force. this theory is based on the interactions between two types of protein filaments—actin (thin filaments) and myosin (thick filaments)—within the muscle fibers. By studying sarcomeres, the basic unit controlling changes in muscle length, scientists proposed the sliding filament theory to explain the molecular mechanisms behind muscle. The sliding filament model explains how muscle fibers contract and relax, resulting in movement. this model involves a fascinating interplay between various chemical signals and structural components.

Video Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Osmosis By studying sarcomeres, the basic unit controlling changes in muscle length, scientists proposed the sliding filament theory to explain the molecular mechanisms behind muscle. The sliding filament model explains how muscle fibers contract and relax, resulting in movement. this model involves a fascinating interplay between various chemical signals and structural components. The sliding filament theory states that the two main types of muscle filaments slide past each other during contraction, causing the muscle to shorten. the actin filaments are thin and have a double helix structure, while the myosin filaments are thick and have a globular head. In this video, dr mike explains how skeletal muscle contracts via the sliding filament theory (mechanism). But how exactly do muscles contract? what happens inside a muscle when we move? one of the most widely accepted explanations of muscle contraction is the sliding filament theory. this theory describes how muscle fibers contract by the sliding movement of protein filaments within the muscle cells. The sliding filament model of muscle contraction describes how muscles generate force and produce movement. muscle contraction occurs as a result of the sliding of thin filaments (actin) over thick filaments (myosin) within muscle fibers.

Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Labelled Diagram Quizlet The sliding filament theory states that the two main types of muscle filaments slide past each other during contraction, causing the muscle to shorten. the actin filaments are thin and have a double helix structure, while the myosin filaments are thick and have a globular head. In this video, dr mike explains how skeletal muscle contracts via the sliding filament theory (mechanism). But how exactly do muscles contract? what happens inside a muscle when we move? one of the most widely accepted explanations of muscle contraction is the sliding filament theory. this theory describes how muscle fibers contract by the sliding movement of protein filaments within the muscle cells. The sliding filament model of muscle contraction describes how muscles generate force and produce movement. muscle contraction occurs as a result of the sliding of thin filaments (actin) over thick filaments (myosin) within muscle fibers.