
Solved A Type I Error Occurs When We Reject A Null Chegg The size of the critical region of a test is determined by the sampling distribution of the test statistic when the null hypothesis is true and the significance level of the test. Type ii error: this results when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis. in context, we would state that it’s a boy genetic labs does not influence the gender outcome of a pregnancy when, in fact, it does.
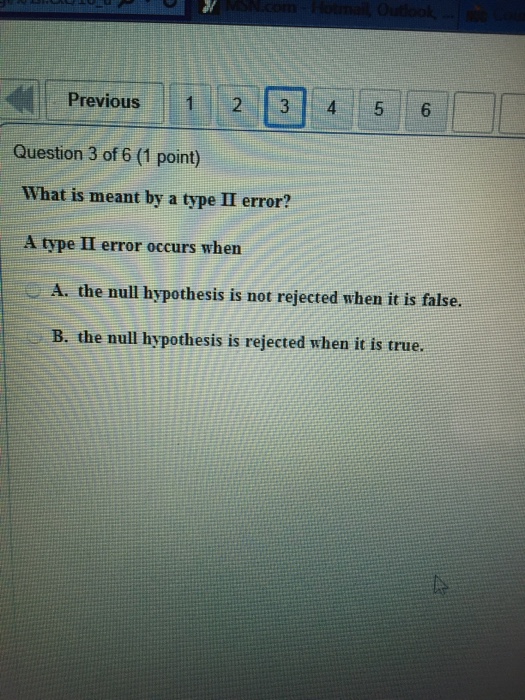
Solved What Is Meant By A Type Ii Error A Type Ii Error Chegg Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like type i error, type i error, type ii error and more. A type ii error, also known as a false negative, occurs when a true null hypothesis is failed to be rejected. the null hypothesis is actually true, but the test fails to identify this. Type ii error is also known as a "false negative": the error of not rejecting a null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is the true state of nature. in other words, when the null hypothesis is false and you fail to reject it, you make a type ii error. When the null hypothesis is false and you fail to reject it, you make a type ii error. the probability of making a type ii error is β, which depends on the power of the test. you can decrease your risk of committing a type ii error by ensuring your test has enough power.

Solved In Hypothesis Testing A Type 2 Error Occurs When A Chegg Type ii error is also known as a "false negative": the error of not rejecting a null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is the true state of nature. in other words, when the null hypothesis is false and you fail to reject it, you make a type ii error. When the null hypothesis is false and you fail to reject it, you make a type ii error. the probability of making a type ii error is β, which depends on the power of the test. you can decrease your risk of committing a type ii error by ensuring your test has enough power. This type of error happens when you say that the null hypothesis is true when it is actually false. for our null hypothesis that dogs live longer than cats, it would be like saying that dogs do live longer than cats, when in fact, they don't. A type ii error, denoted by β (beta), happens when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis known as a "false negative." it's like when your phone's weather app fails to predict a storm, so you go to the beach and get caught in a downpour. Sometimes people fail to reject a false null hypothesis, leading to a type 2 (or type ii) error. this can lead you to make broader inaccurate conclusions about your data. learn more about what type 2 errors are and how you can avoid them in your statistical tests. A type ii error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected by the test (i.e. the test identifies the null hypothesis as true) but in reality the null hypothesis is false.

Solved In Hypothesis Testing Analysis A Type Ii Error Chegg This type of error happens when you say that the null hypothesis is true when it is actually false. for our null hypothesis that dogs live longer than cats, it would be like saying that dogs do live longer than cats, when in fact, they don't. A type ii error, denoted by β (beta), happens when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis known as a "false negative." it's like when your phone's weather app fails to predict a storm, so you go to the beach and get caught in a downpour. Sometimes people fail to reject a false null hypothesis, leading to a type 2 (or type ii) error. this can lead you to make broader inaccurate conclusions about your data. learn more about what type 2 errors are and how you can avoid them in your statistical tests. A type ii error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected by the test (i.e. the test identifies the null hypothesis as true) but in reality the null hypothesis is false.

Solved In A Hypothesis Test A Type I Error Occurs When A Chegg Sometimes people fail to reject a false null hypothesis, leading to a type 2 (or type ii) error. this can lead you to make broader inaccurate conclusions about your data. learn more about what type 2 errors are and how you can avoid them in your statistical tests. A type ii error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected by the test (i.e. the test identifies the null hypothesis as true) but in reality the null hypothesis is false.

Solved In A Hypothesis Test A Type I Error Occurs When A Chegg