
Solved 71 Problem 10e With An Equilibrium Price Of Pe And An Chegg Your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. see answer. Set up the consumer surplus ∫ qeq 0 d(q)dq−qeqpeq ∫ 0 q eq d (q) d q q eq p eq where qeq q eq is the equilibrium quantity and peq p eq is the equilibrium price.

Solved E Pe And Qe Represent The Equilibrium Point Chegg In this video we explain how to use the demand and supply equations to solve for the equilibrium price and quantity values (often referred to as p* and q*) in a market!. We will analyse the exchanges in the edgeworth box, to find an equilibrium outcome. recap: edgeworth box basics recap: edgeworth box preferences. 1. main concepts of an eb. the wealth of the consumers is not given exogenously: it is determined by the value of their endowment at the prices that will prevail in the exchange process. (c) to calculate the competitive equilibrium price and allocation, we look for a price where z(p) = 0. looking at market 2, we must solve: (2p 1) (a 1 1) a2(p 2) (1 a 2) 3 = 0. this can be rewritten as: (1 a2)(2p 1) (a1 1)a2(p 2) = 3 (a1 1)(1 a2). Part a solution for determination of equilibrium market price and equilibrium quantity of demand and supply 1. find the equilibrium price and quantity in the market if demand function is; =63 3p and supply function is; =4p. where, is quantity demanded, is quantity supplied and p is price.
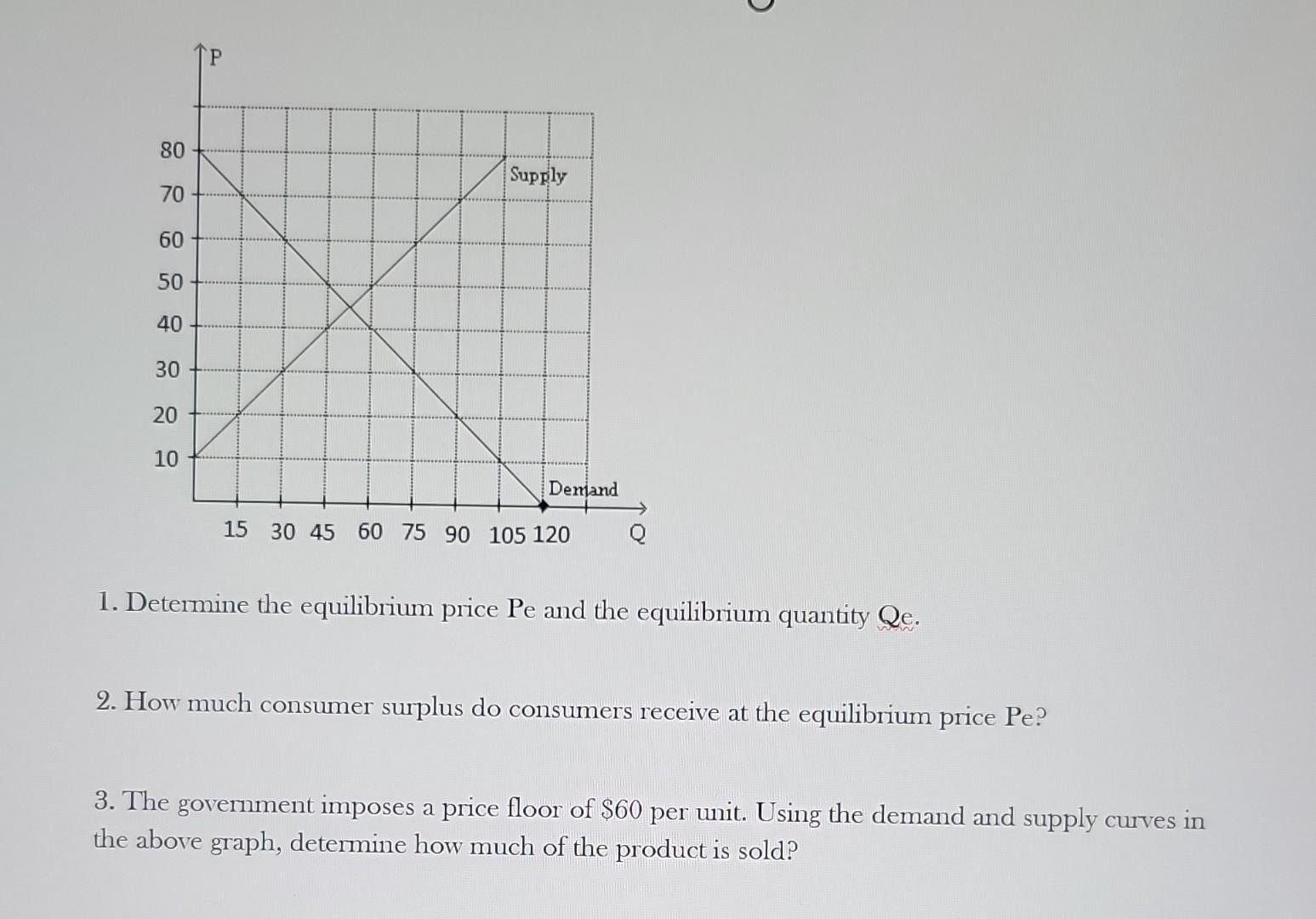
Solved 1 Determine The Equilibrium Price Pe And The Chegg (c) to calculate the competitive equilibrium price and allocation, we look for a price where z(p) = 0. looking at market 2, we must solve: (2p 1) (a 1 1) a2(p 2) (1 a 2) 3 = 0. this can be rewritten as: (1 a2)(2p 1) (a1 1)a2(p 2) = 3 (a1 1)(1 a2). Part a solution for determination of equilibrium market price and equilibrium quantity of demand and supply 1. find the equilibrium price and quantity in the market if demand function is; =63 3p and supply function is; =4p. where, is quantity demanded, is quantity supplied and p is price. The venezuelan government has imposed a price ceiling on the retail price of roasted coffee beans. the accompanying diagram shows the market for coffee beans. in the absence of price controls, the economy is in equilibrium with an equilibrium price of pe and an equilibrium quantity bought and sold of qe price of coffee beans b pe c e d qf. Solution: the indifference curves are right angles with vertices at y1 = x1 and y2 = 4x2, and the consumers can maximize utility by consuming at the vertices for any budget line with positive prices for both goods. Solve forxij∗forj= 1, 2 andi= 1,2 as a function of the pricep 1 and of the endowments. we now solve analytically for the general equilibrium. require that the total sum of the demands for good 1 equals the total sum of the endowments, that is, that x 11 ∗ x 21 ∗=ω 11 ω 21. solve for the general equilibrium pricep∗ 1. Derive horizontal demand intercept (or x intercept) by putting the price paid by the consumer equal to zero (i.e. p d =0) in the demand function and get the value of quantity demanded (i.e. q d) which is 140 units and plot it on the x axis. graphically, the demand and supply can be shown as follows:.