
Solved Equilibrium Quantity Equilibrium Price Chegg Solve for the equilibrium price and quantity using the equations below. q^d = 100 .50 p q^s = 70 .80p suppose there is a shift in demand so that: q^d = 200 .50 p q^s = 70 .80 p find the new values for equilibrium price and quantity. your solution’s ready to go!. In order to solve for the equilibrium price and quantity, we will set the two equations equal to each other. this works because we are trying to mathematically find the equilibrium point on the graph where price and quantity are equal (hence setting qs=qd).
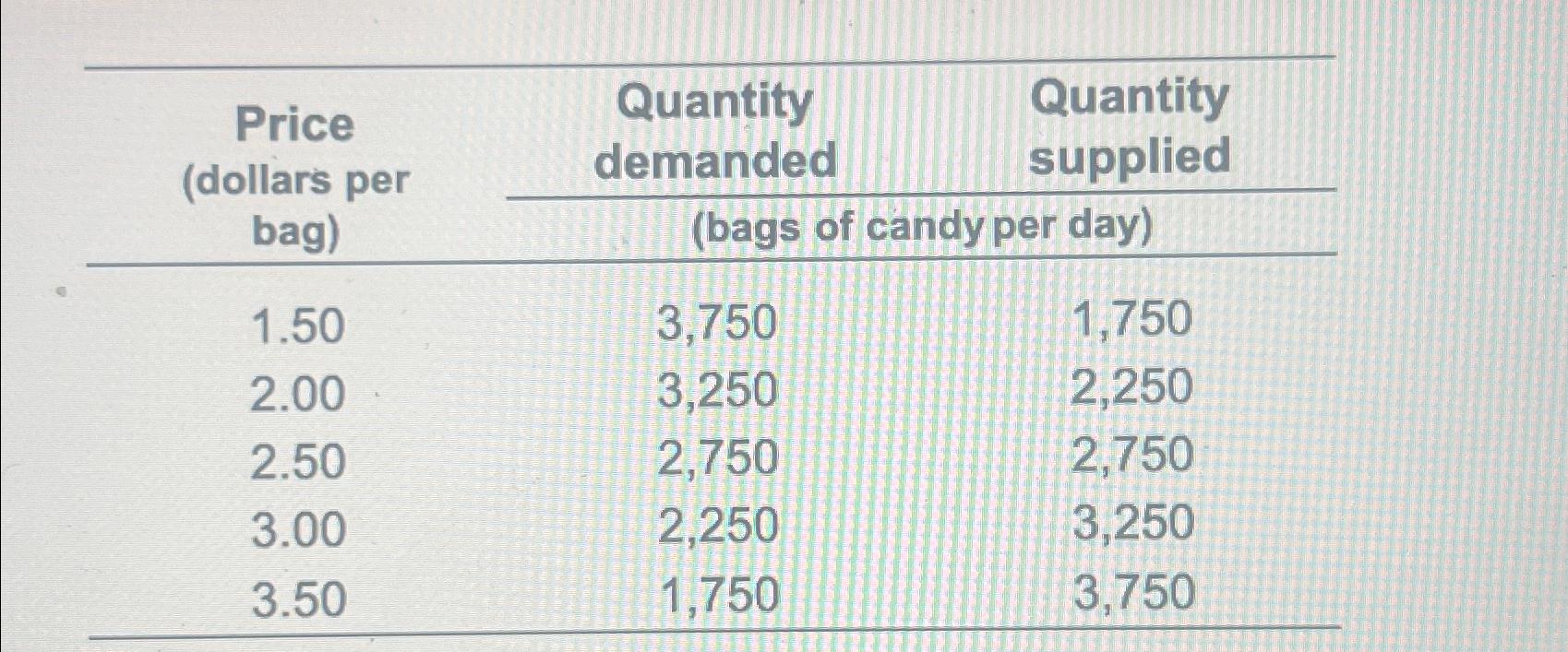
Solved Find The Equilibrium Price And Equilibrium Quantity Chegg The equilibrium price is the only price where the desires of consumers and the desires of producers agree—that is, where the amount of the product that consumers want to buy (quantity demanded) is equal to the amount producers want to sell (quantity supplied). There are two settings where we derive equilibrium price and quantity. the first involves a price taking (i.e. perfectly competitive) industry, and the second involves a monopoly. let's consider each setting. a. finding equilibrium in a perfectly competitive industry: 1. set demand equal to marginal cost, and then solve for q*: 2. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like given the following equations: demand: qd= 90− pqd= 90− p supply: qs= 10 15pqs= 10 15p solve for the equilibrium price 'p' and quantity (q: qd = qs): p* = $ 5 qd = qs = q* = 85 units given that qd = qs 90− p= 10 15p90− p= 10 15p collect like terms. To find equilibrium, solve the supply and demand equations where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded. use graphs to check if calculated equilibrium price and quantity match the supply and demand curve intersection.

Solved Solve For The Equilibrium Price And Quantity Show Chegg Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like given the following equations: demand: qd= 90− pqd= 90− p supply: qs= 10 15pqs= 10 15p solve for the equilibrium price 'p' and quantity (q: qd = qs): p* = $ 5 qd = qs = q* = 85 units given that qd = qs 90− p= 10 15p90− p= 10 15p collect like terms. To find equilibrium, solve the supply and demand equations where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded. use graphs to check if calculated equilibrium price and quantity match the supply and demand curve intersection. Question: solving for the equilibrium price (p*) and equilibrium quantity (q*), we know that equilibrium price and quantity clear the market. at one certain price, there will be no surplus or shortage. supply and demand will be equal to each other. This equilibrium price and quantity calculator can help you calculate both the equilibrium price & quantity in case you have a demand and a supply function both dependants on price. Solving simultaneously: it's crucial to solve the system of equations simultaneously to find the equilibrium prices. units: ensure that the units of price and quantity are consistent throughout the problem. question 2: macroeconomic equilibrium: the equilibrium represents a state where both the goods market and the money market are in balance. At the equilibrium values, calculate the cross price elasticity of demand for lychees with respect to the price of mangoes. what does the sign of this elasticity tell you about whether lychees and mangoes are substitutes or complements?.
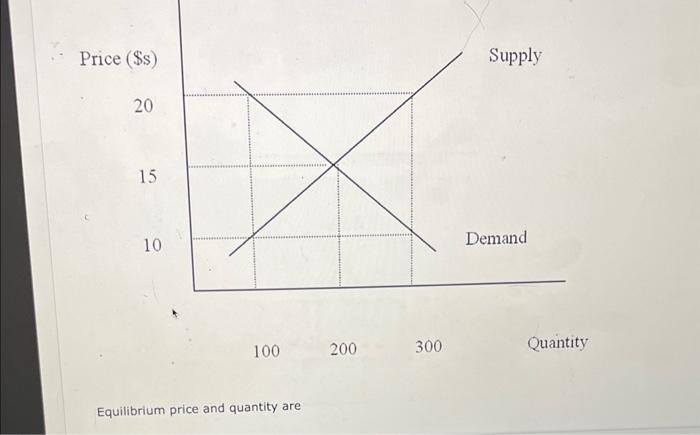
Solved Equilibrium Price And Quantity Are Chegg Question: solving for the equilibrium price (p*) and equilibrium quantity (q*), we know that equilibrium price and quantity clear the market. at one certain price, there will be no surplus or shortage. supply and demand will be equal to each other. This equilibrium price and quantity calculator can help you calculate both the equilibrium price & quantity in case you have a demand and a supply function both dependants on price. Solving simultaneously: it's crucial to solve the system of equations simultaneously to find the equilibrium prices. units: ensure that the units of price and quantity are consistent throughout the problem. question 2: macroeconomic equilibrium: the equilibrium represents a state where both the goods market and the money market are in balance. At the equilibrium values, calculate the cross price elasticity of demand for lychees with respect to the price of mangoes. what does the sign of this elasticity tell you about whether lychees and mangoes are substitutes or complements?.