
Solved Equilibrium Quantity Equilibrium Price Chegg What is the equilibrium price and quantity in this market? why do consumers not consume more than this equilibrium quantity? tip: consider a q point on either side of equilibrium and explain why they do not consume at that point. here’s the best way to solve it. This intersection of the supply and the demand functions is called the point of market equilibrium, or equilibrium point. the price at this point is referred to as the equilibrium price. the standard economic theory says that a free and open market will naturally settle on the equilibrium price.
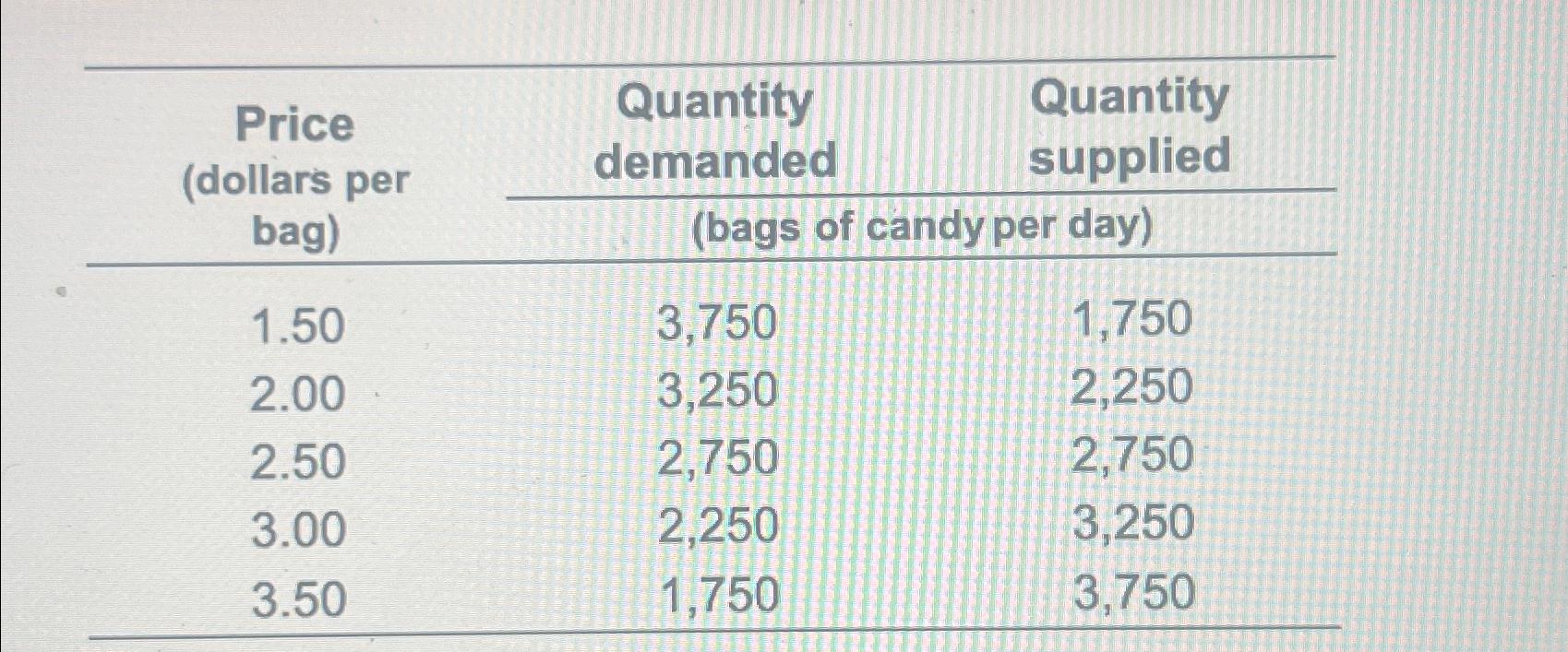
Solved Find The Equilibrium Price And Equilibrium Quantity Chegg Solve for the equilibrium price 'p' and quantity (q: qd = qs): p* = $ 5 qd = qs = q* = 85 units given that qd = qs 90− p= 10 15p90− p= 10 15p collect like terms: 90− 10= 15p p 80= 16p divide by 16 to solve for p p = 8016= 5p = 8016= 5 substitute into either equation to solve for q: qd = 90− p*= 90− 5= 85. There are two settings where we derive equilibrium price and quantity. the first involves a price taking (i.e. perfectly competitive) industry, and the second involves a monopoly. let's consider each setting. a. finding equilibrium in a perfectly competitive industry: 1. set demand equal to marginal cost, and then solve for q*: 2. There are 2 steps to solve this one. solving for the equilibrium price (p*) and equilibrium quantity (q*), we know that equilibrium price and quantity clear the market. at one certain price, there will be no surplus or shortage. supply and demand will be equal to each other. This point signifies the price at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, also known as the equilibrium point. steps to determine equilibrium price: set the quantity demanded equal to the quantity supplied and solve for the price.

Solved Solve For The Equilibrium Price And Quantity Show Chegg There are 2 steps to solve this one. solving for the equilibrium price (p*) and equilibrium quantity (q*), we know that equilibrium price and quantity clear the market. at one certain price, there will be no surplus or shortage. supply and demand will be equal to each other. This point signifies the price at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, also known as the equilibrium point. steps to determine equilibrium price: set the quantity demanded equal to the quantity supplied and solve for the price. What happens to the equilibrium price and quantity for winter clothes in the following scenarios. please illustrate your answers using shifts in the supply and demand curves the price of wool globally increases and at the same time there is a warning of a severe snowstorm. What will happen to the market equilibrium price and quantity? equilibrium price will rise; equilibrium quantity will rise. we have an expert written solution to this problem! an early frost in the vineyards of napa valley would cause a (n): decrease in the supply of wine, increasing price. To find the equilibrium price and quantity, you need to set the quantity supplied equal to the quantity demanded (qs = qd) and solve for p (equilibrium price). once you have the equilibrium price, you can substitute it back into either the supply or demand equation to find the equilibrium quantity. Assume the market for blue jeans starts in equilibrium. what will happen to equilibrium price and quantity if the cost of denim cloth increases? the quantity of blue jeans will increase, and the price will decrease. the price of blue jeans will increase, and the quantity will decrease. the price and quantity of blue jeans will increase.
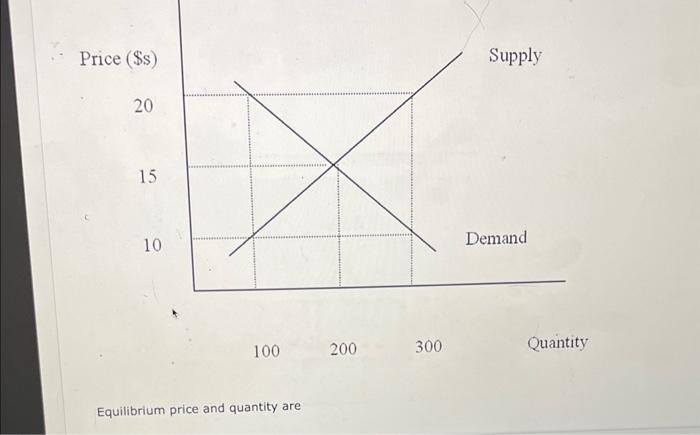
Solved Equilibrium Price And Quantity Are Chegg What happens to the equilibrium price and quantity for winter clothes in the following scenarios. please illustrate your answers using shifts in the supply and demand curves the price of wool globally increases and at the same time there is a warning of a severe snowstorm. What will happen to the market equilibrium price and quantity? equilibrium price will rise; equilibrium quantity will rise. we have an expert written solution to this problem! an early frost in the vineyards of napa valley would cause a (n): decrease in the supply of wine, increasing price. To find the equilibrium price and quantity, you need to set the quantity supplied equal to the quantity demanded (qs = qd) and solve for p (equilibrium price). once you have the equilibrium price, you can substitute it back into either the supply or demand equation to find the equilibrium quantity. Assume the market for blue jeans starts in equilibrium. what will happen to equilibrium price and quantity if the cost of denim cloth increases? the quantity of blue jeans will increase, and the price will decrease. the price of blue jeans will increase, and the quantity will decrease. the price and quantity of blue jeans will increase.