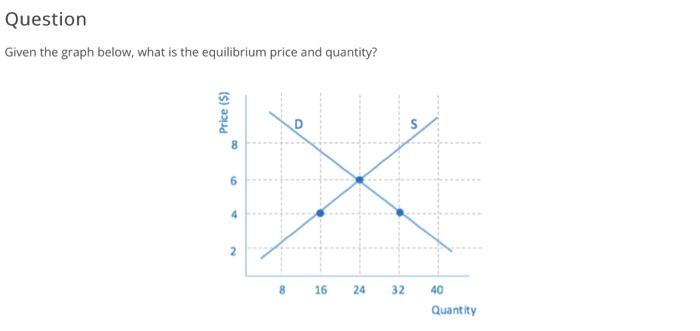
Solved Given The Graph Below What Is The Equilibrium Price Chegg Locate the point where the demand curve intersects the supply curve on the graph. Given that equilibrium indicates no problem exists, typically, the choice offered would depend on the specific situation depicted in the graph. if there’s a surplus, a. lower prices would solve the problem, while for a shortage, b. higher prices would be necessary.
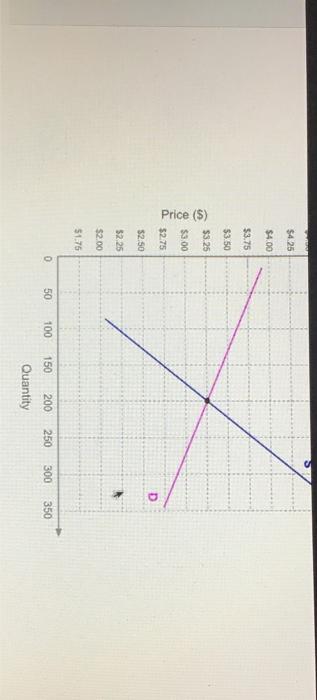
Solved Given The Graph Below What Is The Equilibrium Chegg Equilibrium price is $15 and equilibrium quantity is g. c. the core claim of the question is to determine the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity based on the provided graph. equilibrium price is where the supply and demand curves intersect, which is at $15 in this case. The equilibrium price is the only price where the desires of consumers and the desires of producers agree—that is, where the amount of the product that consumers want to buy (quantity demanded) is equal to the amount producers want to sell (quantity supplied). At the equilibrium values, calculate the cross price elasticity of demand for lychees with respect to the price of mangoes. what does the sign of this elasticity tell you about whether lychees and mangoes are substitutes or complements?. Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity of milk. to help dairy farmers, the government sets a minimum price of $2.50 per gallon of milk. what is the new quantity of milk sold in the marketplace? illustrate your answers to (a) and (b) on a graph.

Solved Given The Graph Below What Is The Equilibrium Chegg At the equilibrium values, calculate the cross price elasticity of demand for lychees with respect to the price of mangoes. what does the sign of this elasticity tell you about whether lychees and mangoes are substitutes or complements?. Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity of milk. to help dairy farmers, the government sets a minimum price of $2.50 per gallon of milk. what is the new quantity of milk sold in the marketplace? illustrate your answers to (a) and (b) on a graph. This intersection of the supply and the demand functions is called the point of market equilibrium, or equilibrium point. the price at this point is referred to as the equilibrium price. the standard economic theory says that a free and open market will naturally settle on the equilibrium price. In a supply and demand graph, the consumer surplus is represented by the area above the equilibrium price and below the demand curve. given your description of the graph, the areas labeled as a and b are above the equilibrium price p1 and below the demand curve. When the price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, it leads to a shortage. this is because at the price ceiling, quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied. quantity demanded is the amount of a product that buyers are willing and able to purchase at a given price. For instance, in the graph below, we see that at the equilibrium price p*, buyers want to buy exactly the same amount that sellers want to sell. if the price were higher, however, we can see that sellers would want to sell more than buyers would want to buy.