
Solved Question 13 Consider The Following Demand And Supply Chegg Igneous rock (igneous from latin igneus 'fiery'), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Learn about igneous rocks in geology, including their origin, properties, and classification. get examples and identification tips.

Solved Question 3 1pt The Following Supply And Demand Chegg The igneous rocks are one of the three main types of rock found on earth; the others are sedimentary rock and metamorphic rock. they are the hardest and heaviest rock on earth. Igneous rock, any of various crystalline or glassy rocks formed by the cooling and solidification of molten earth material. igneous rocks constitute one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary. Intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. examples of intrusive igneous rocks are: diabase, diorite, gabbro, granite, pegmatite, and peridotite. Igneous rocks (from the latin word for fire) form when hot, molten rock crystallizes and solidifies. the melt originates deep within the earth near active plate boundaries or hot spots, then rises toward the surface.
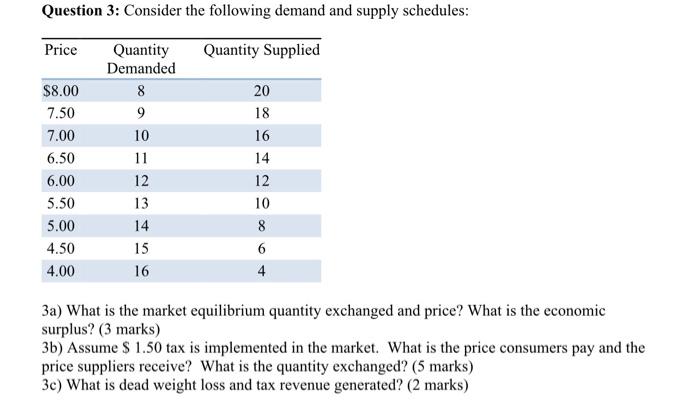
Solved Question 3 Consider The Following Demand And Supply Chegg Intrusive igneous rocks crystallize below earth's surface, and the slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. examples of intrusive igneous rocks are: diabase, diorite, gabbro, granite, pegmatite, and peridotite. Igneous rocks (from the latin word for fire) form when hot, molten rock crystallizes and solidifies. the melt originates deep within the earth near active plate boundaries or hot spots, then rises toward the surface. Igneous rocks are one of the three main types of rocks found on earth, the other two being sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. these rocks form from the solidification and cooling of molten material, known as magma, which originates deep within the earth's crust and occasionally even in the mantle. Igneous rocks are rocks that formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. magma is molten rock that is below the surface of the earth, and lava is molten rock that has reached the surface. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of molten rock, either magma beneath the surface or lava at the surface. they are one of the three main rock types, alongside sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the earth or while the melted rock is still inside the crust. all magma develops underground, in the lower crust or upper mantle, because of the intense heat there.

Solved 3 Question 3 Consider The Following Supply And Chegg Igneous rocks are one of the three main types of rocks found on earth, the other two being sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. these rocks form from the solidification and cooling of molten material, known as magma, which originates deep within the earth's crust and occasionally even in the mantle. Igneous rocks are rocks that formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. magma is molten rock that is below the surface of the earth, and lava is molten rock that has reached the surface. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of molten rock, either magma beneath the surface or lava at the surface. they are one of the three main rock types, alongside sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks form when magma (molten rock) cools and crystallizes, either at volcanoes on the surface of the earth or while the melted rock is still inside the crust. all magma develops underground, in the lower crust or upper mantle, because of the intense heat there.