
Solved Solve For The Equilibrium Price And Quantity Show Chegg Solve for the equilibrium price and quantity for the following sets of demand and supply equations (2 points each): demand:𝑃=15−𝑄𝐷 supply: 𝑃 = 3 𝑄𝑆. In order to solve for the equilibrium price and quantity, we will set the two equations equal to each other. this works because we are trying to mathematically find the equilibrium point on the graph where price and quantity are equal (hence setting qs=qd).

Solved Solve For The Equilibrium Price And Equilibrium Chegg There are two settings where we derive equilibrium price and quantity. the first involves a price taking (i.e. perfectly competitive) industry, and the second involves a monopoly. let's consider each setting. a. finding equilibrium in a perfectly competitive industry: 1. set demand equal to marginal cost, and then solve for q*: 2. Solve for the equilibrium price 'p' and quantity (q: qd = qs): p* = $ 5 qd = qs = q* = 85 units given that qd = qs 90− p= 10 15p90− p= 10 15p collect like terms: 90− 10= 15p p 80= 16p divide by 16 to solve for p p = 8016= 5p = 8016= 5 substitute into either equation to solve for q: qd = 90− p*= 90− 5= 85. To find equilibrium, solve the supply and demand equations where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded. use graphs to check if calculated equilibrium price and quantity match the supply and demand curve intersection. Supply price = $ 6 q 100. demand price = $ 18 2 q 100. find the equilibrium price and quantity. solution 1. solution (a) we have started with an example that we can do by basic algebra without any technology. subtracting the two equations, we see that.
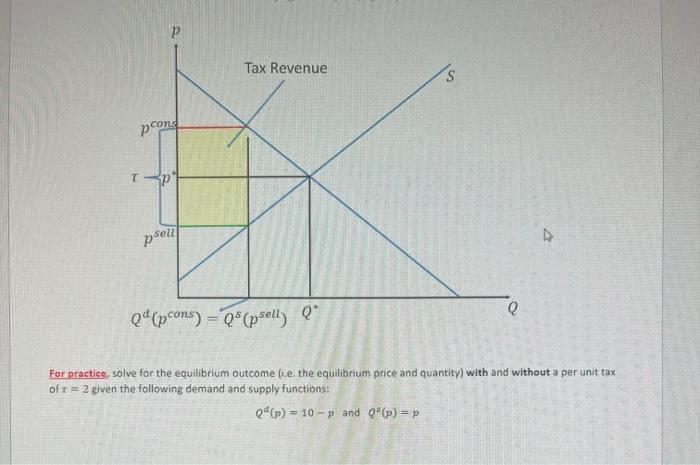
Solved For Practice Solve For The Equilibrium Outcome I E Chegg To find equilibrium, solve the supply and demand equations where quantity supplied equals quantity demanded. use graphs to check if calculated equilibrium price and quantity match the supply and demand curve intersection. Supply price = $ 6 q 100. demand price = $ 18 2 q 100. find the equilibrium price and quantity. solution 1. solution (a) we have started with an example that we can do by basic algebra without any technology. subtracting the two equations, we see that. Question: solving for the equilibrium price (p*) and equilibrium quantity (q*), we know that equilibrium price and quantity clear the market. at one certain price, there will be no surplus or shortage. supply and demand will be equal to each other. At the equilibrium values, calculate the cross price elasticity of demand for lychees with respect to the price of mangoes. what does the sign of this elasticity tell you about whether lychees and mangoes are substitutes or complements?. Learn about equilibrium price—or where the supply, demand and cost of a product is in balance—how to solve calculations for equilibrium price and see examples. (a) find the equilibrium quantity and price that is, the values of q and p where supply equals demand. (b) find the slope of this curve at (1, 1). the supply and demand functions (in namibian dollars) for crates of organic mangoes from zambia are given by: s (x) = x2 8x and d(x) = 1000−25x −x2 respectively where x is the number of crates.

Solved Equilibrium Quantity Equilibrium Price Chegg Question: solving for the equilibrium price (p*) and equilibrium quantity (q*), we know that equilibrium price and quantity clear the market. at one certain price, there will be no surplus or shortage. supply and demand will be equal to each other. At the equilibrium values, calculate the cross price elasticity of demand for lychees with respect to the price of mangoes. what does the sign of this elasticity tell you about whether lychees and mangoes are substitutes or complements?. Learn about equilibrium price—or where the supply, demand and cost of a product is in balance—how to solve calculations for equilibrium price and see examples. (a) find the equilibrium quantity and price that is, the values of q and p where supply equals demand. (b) find the slope of this curve at (1, 1). the supply and demand functions (in namibian dollars) for crates of organic mangoes from zambia are given by: s (x) = x2 8x and d(x) = 1000−25x −x2 respectively where x is the number of crates.