
Solved Solve For The Equilibrium Price And Equilibrium Chegg Question: solving for the equilibrium price (p*) and equilibrium quantity (q*), we know that equilibrium price and quantity clear the market. at one certain price, there will be no surplus or shortage. supply and demand will be equal to each other. There are two settings where we derive equilibrium price and quantity. the first involves a price taking (i.e. perfectly competitive) industry, and the second involves a monopoly. let's consider each setting. a. finding equilibrium in a perfectly competitive industry: 1. set demand equal to marginal cost, and then solve for q*: 2.

Solved Solve For The Equilibrium Price And Quantity Show Chegg Supply price = $ 6 q 100. demand price = $ 18 2 q 100. find the equilibrium price and quantity. solution 1. solution (a) we have started with an example that we can do by basic algebra without any technology. subtracting the two equations, we see that. Learn about equilibrium price—or where the supply, demand and cost of a product is in balance—how to solve calculations for equilibrium price and see examples. This intersection of the supply and the demand functions is called the point of market equilibrium, or equilibrium point. the price at this point is referred to as the equilibrium price. the standard economic theory says that a free and open market will naturally settle on the equilibrium price. Show all necessary steps to solve for p. do a quality check and put your answer back into the supply and demand equations to see that it is correct. we need to make the quantity supplied equal to.
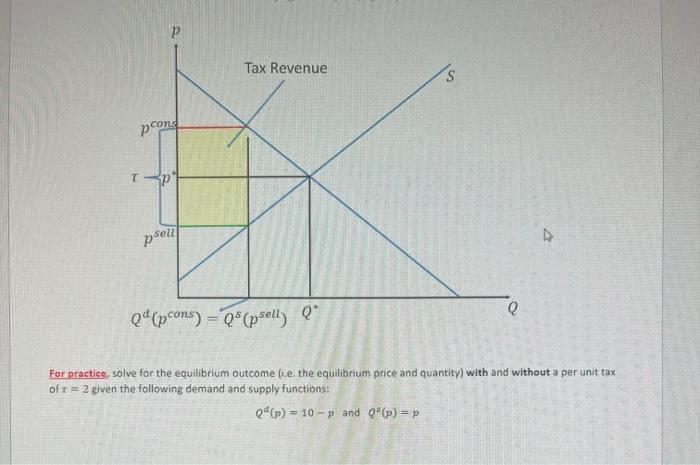
Solved For Practice Solve For The Equilibrium Outcome I E Chegg This intersection of the supply and the demand functions is called the point of market equilibrium, or equilibrium point. the price at this point is referred to as the equilibrium price. the standard economic theory says that a free and open market will naturally settle on the equilibrium price. Show all necessary steps to solve for p. do a quality check and put your answer back into the supply and demand equations to see that it is correct. we need to make the quantity supplied equal to. Here’s the best way to solve it. question 4: sunglass market this one is slightly different, but we know we are looking for the equilibrium quantity (q) where q, is equal to q . since these two must represent the same number, we can call them both q. Fullscreen figure 1 equilibrium in the market for bread. to find the equilibrium price and quantity, we need to solve a pair of simultaneous equations—the demand curve and the supply curve—for 𝑃 p and 𝑄 q. The purpose of this lab is to cement your understanding of those concepts by asking you to do three things: (1) set up and solve a simple equilibrium problem, (2) explore the equilibration process under different assumptions about the nature of the feedback mechanism, and (3) generate some simple comparative statics results. 【solved】 500 thousand cell phones explanation 1. calculate quantity demanded at below equilibrium price quantity demanded is 2 times the equilibrium quantity .