
Solved Solve For The Equilibrium Price And Quantity Show Chegg Question: solving for the equilibrium price (p*) and equilibrium quantity (q*), we know that equilibrium price and quantity clear the market. at one certain price, there will be no surplus or shortage. supply and demand will be equal to each other. There are two settings where we derive equilibrium price and quantity. the first involves a price taking (i.e. perfectly competitive) industry, and the second involves a monopoly. let's consider each setting. a. finding equilibrium in a perfectly competitive industry: 1. set demand equal to marginal cost, and then solve for q*: 2.

Solved Solve For The Equilibrium Price And Equilibrium Chegg Practice problem solutions for quiz 1 use a supply and demand diagram to analyze each of the following scenarios. explain briefly. be sure to show how both the equilibrium price and quantity change in each case. In order to solve for the equilibrium price and quantity, we will set the two equations equal to each other. this works because we are trying to mathematically find the equilibrium point on the graph where price and quantity are equal (hence setting qs=qd). In this article, we’ll walk you through the simple linear equations you need to know in order to find equilibrium price and quantity in just a few minutes. use qd = qs to find the equilibrium price. plug the price, or p, into either the supply equation or the demand equation to solve for equilibrium quantity. Solve for the equilibrium price and quantity for the following sets of demand and supply equations (2 points each): demand:𝑃=15−𝑄𝐷 supply: 𝑃 = 3 𝑄𝑆.
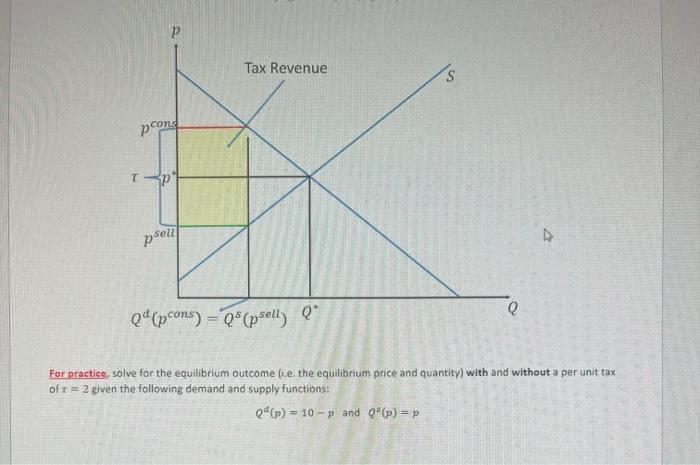
Solved For Practice Solve For The Equilibrium Outcome I E Chegg In this article, we’ll walk you through the simple linear equations you need to know in order to find equilibrium price and quantity in just a few minutes. use qd = qs to find the equilibrium price. plug the price, or p, into either the supply equation or the demand equation to solve for equilibrium quantity. Solve for the equilibrium price and quantity for the following sets of demand and supply equations (2 points each): demand:𝑃=15−𝑄𝐷 supply: 𝑃 = 3 𝑄𝑆. This equilibrium price and quantity calculator can help you calculate both the equilibrium price & quantity in case you have a demand and a supply function both dependants on price. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like equilibrium point, equilibrium price, excess demand and more. Ideas for solving the problem equilibrium point: the equilibrium point is where the supply and demand functions intersect, meaning s (x) = d(x). quadratic formula: the quadratic formula is used to solve equations of the form ax2 bx c = 0, given by x = 2a−b± b2−4ac . derivative for slope: the derivative of a function at a point gives the slope of the tangent line to the curve at that. Summary: to solve for equilibrium price and quantity you should perform the following steps: 1) solve for the demand function and the supply function in terms of q (quantity). 2) set qs (quantity supplied) equal to qd (quantity demanded). the equations will be in terms of price (p).

Solved Equilibrium Quantity Equilibrium Price Chegg This equilibrium price and quantity calculator can help you calculate both the equilibrium price & quantity in case you have a demand and a supply function both dependants on price. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like equilibrium point, equilibrium price, excess demand and more. Ideas for solving the problem equilibrium point: the equilibrium point is where the supply and demand functions intersect, meaning s (x) = d(x). quadratic formula: the quadratic formula is used to solve equations of the form ax2 bx c = 0, given by x = 2a−b± b2−4ac . derivative for slope: the derivative of a function at a point gives the slope of the tangent line to the curve at that. Summary: to solve for equilibrium price and quantity you should perform the following steps: 1) solve for the demand function and the supply function in terms of q (quantity). 2) set qs (quantity supplied) equal to qd (quantity demanded). the equations will be in terms of price (p).
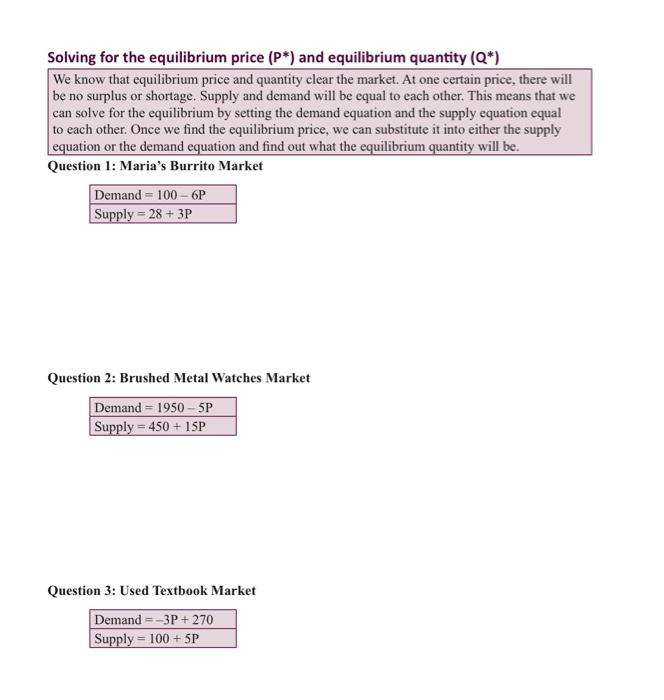
Solved Solving For The Equilibrium Price P And Chegg Ideas for solving the problem equilibrium point: the equilibrium point is where the supply and demand functions intersect, meaning s (x) = d(x). quadratic formula: the quadratic formula is used to solve equations of the form ax2 bx c = 0, given by x = 2a−b± b2−4ac . derivative for slope: the derivative of a function at a point gives the slope of the tangent line to the curve at that. Summary: to solve for equilibrium price and quantity you should perform the following steps: 1) solve for the demand function and the supply function in terms of q (quantity). 2) set qs (quantity supplied) equal to qd (quantity demanded). the equations will be in terms of price (p).