
Solved Solve The Following Equilibrium Equations 1 If You Chegg Solve the following equilibrium equations: 1. if you are given the following equations: 2 f1−f2 3 f3=5 f1 4 f2−2 f3=13 f1 f2 5 f3=2 determine f1, f2, and f3 your solution’s ready to go! our expert help has broken down your problem into an easy to learn solution you can count on. Sometimes the mathematical expression used in solving an equilibrium problem can be solved by taking the square root of both sides of the equation. this can be done when the variables in the numerator and in the denominator of the equilibrium expression are multiplied by themselves (squared).

Solved Solve The Following Problem 1 By Applying The Chegg In addition to equilibrium constant expressions, two other equations are important to this systematic approach to solving an equilibrium problem. the first of these equations is a mass balance equation, which simply is a statement that matter is conserved during a chemical reaction. Sum f x = 0, sum f y = 0 and sum m = 0. begin with the sum of the forces equations. the simplest way to solve these force systems would be to break the diagonal forces into their component pars. from observation, each diagonal is the "5" side of a 3 4 5 triangle. An “equilibrium problem” in general chemistry typically involves one to solve for the equilibrium concentrations of the reaction given some starting information. this section introduces a variety of equilibrium type problems, each one illustrating the method in solving for the equilibrium concentrations. We'll learn how to calculate equilibrium concentrations or the equilibrium constant (k) itself using stoichiometry and algebra; specifically, we'll practice how to set up an ice (initial,.

Solved You Do Not Need To Solve For The New Equilibrium Chegg An “equilibrium problem” in general chemistry typically involves one to solve for the equilibrium concentrations of the reaction given some starting information. this section introduces a variety of equilibrium type problems, each one illustrating the method in solving for the equilibrium concentrations. We'll learn how to calculate equilibrium concentrations or the equilibrium constant (k) itself using stoichiometry and algebra; specifically, we'll practice how to set up an ice (initial,. For the first type of equilibrium problem, we can to solve for k by directly substituting given equilibrium quantities into the reaction quotient: for example, let’s use the following reaction: n2(g) 3h2(g) 2nh3(g). In this study guide we will solve problems either to calculate the equilibrium constant or to determine the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and products once the system is at equilibrium. Solve the following equilibrium equations for the forces f o a, f a c and f a b in n (si units). that means, determine the values of f o a, f a c and f a b. Step 1. write all pertinent reactions step 2. write the charge balance equation step 3. write the mass balance equation step 4. write the equilibrium constant for each chemical reaction (should use activities but we will ignore them) step 5. count the equations and unknowns (# equations = # unknowns) step 6. solve the unknowns 3.
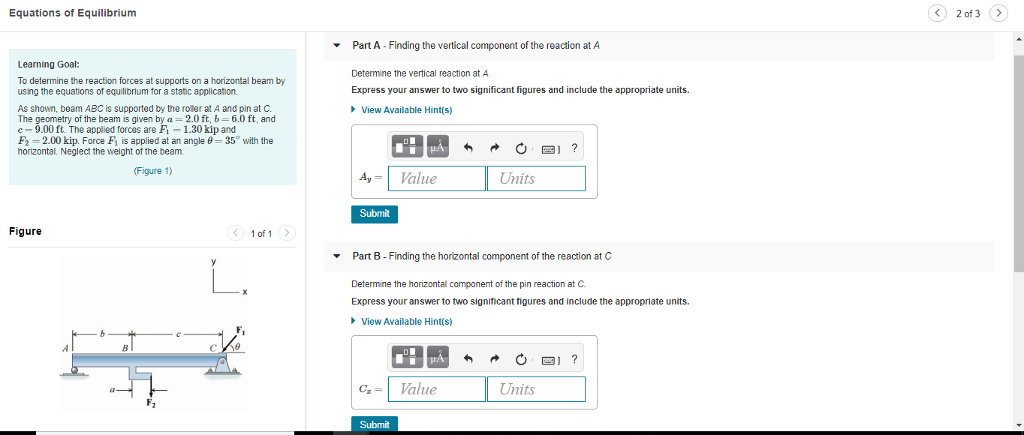
Solved Equations Of Equilibrium For the first type of equilibrium problem, we can to solve for k by directly substituting given equilibrium quantities into the reaction quotient: for example, let’s use the following reaction: n2(g) 3h2(g) 2nh3(g). In this study guide we will solve problems either to calculate the equilibrium constant or to determine the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and products once the system is at equilibrium. Solve the following equilibrium equations for the forces f o a, f a c and f a b in n (si units). that means, determine the values of f o a, f a c and f a b. Step 1. write all pertinent reactions step 2. write the charge balance equation step 3. write the mass balance equation step 4. write the equilibrium constant for each chemical reaction (should use activities but we will ignore them) step 5. count the equations and unknowns (# equations = # unknowns) step 6. solve the unknowns 3.

Solved Using Equilibrium Equations Show Chegg Solve the following equilibrium equations for the forces f o a, f a c and f a b in n (si units). that means, determine the values of f o a, f a c and f a b. Step 1. write all pertinent reactions step 2. write the charge balance equation step 3. write the mass balance equation step 4. write the equilibrium constant for each chemical reaction (should use activities but we will ignore them) step 5. count the equations and unknowns (# equations = # unknowns) step 6. solve the unknowns 3.