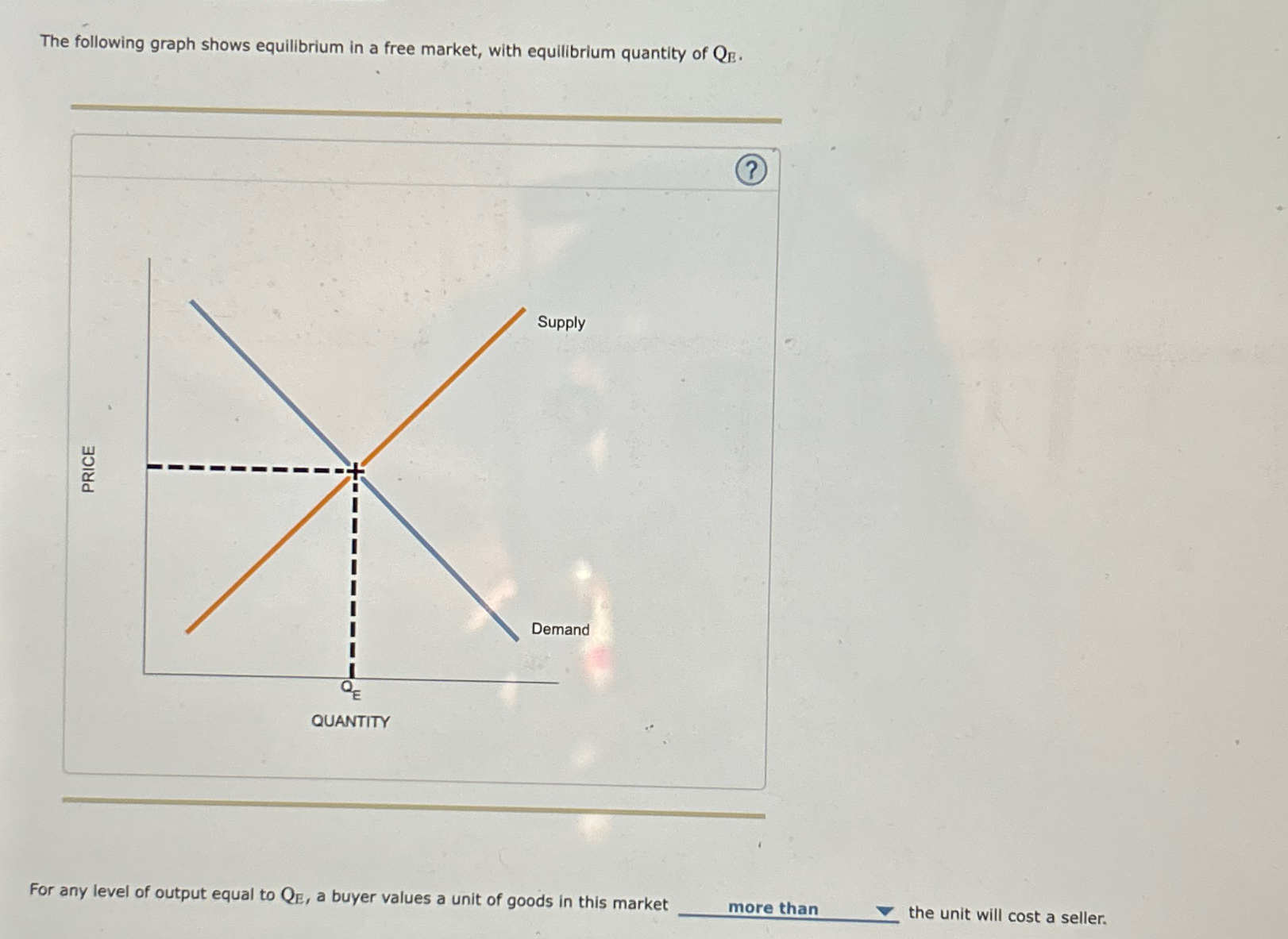
Solved The Following Graph Shows Equilibrium In A Free Market With The following graph shows equilibrium in a free market, with equilibrium quantity of qe for any level of output below qe, a buyer values a unit of goods in this market the unit will cost a seller. A graph plots equilibrium in a market, with price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis. an upward sloping straight line supply curve intersects a downward sloping straight line demand curve at equilibrium quantity of q sub e.
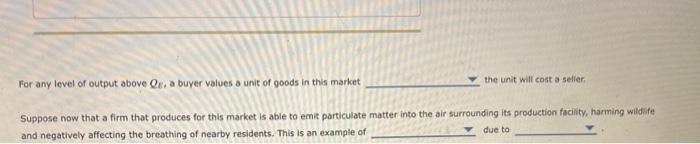
Solved The Following Graph Shows Equilibrium In A Free M In a free market, the equilibrium is determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves. the equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, and the equilibrium quantity is the quantity of goods or services that will be exchanged at that price. In a free market, the equilibrium price and quantity are determined where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. for any output level below , the price buyers are willing to pay (as indicated by the demand curve) is more than the price sellers are willing to accept (as indicated by the supply curve). 1 recognize that at the equilibrium quantity q {e} qe, the market is in equilibrium, meaning the value to buyers is equal to the cost to sellers. 2 understand that for any level of output below q {e} qe, a buyer values a unit of goods more than the unit will cost a seller. Suppose now that an individual firm that produces goods in this market has the power to influence market price, leading to an outcome different from the free market equilibrium illustrated in the previous graph.
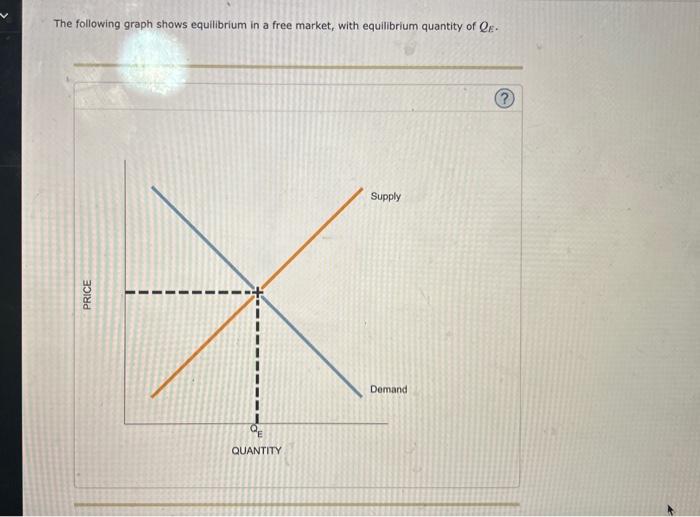
Solved The Following Graph Shows Equilibrium In A Free M 1 recognize that at the equilibrium quantity q {e} qe, the market is in equilibrium, meaning the value to buyers is equal to the cost to sellers. 2 understand that for any level of output below q {e} qe, a buyer values a unit of goods more than the unit will cost a seller. Suppose now that an individual firm that produces goods in this market has the power to influence market price, leading to an outcome different from the free market equilibrium illustrated in the previous graph. The graph you've described illustrates the basic principle of market equilibrium in a free market, where the supply and demand curves intersect. at the equilibrium quantity, denoted as ( q e ), the amount of goods that sellers are willing to supply at a certain price is exactly equal to the amount of goods that buyers are willing to purchase at. Suppose now that an individual firm that produces goods in this market has the power to influence market price, leading to an outcome different from the free market equilibrium illustrated in the previous graph. In a free market, equilibrium is the point where the supply curve intersects the demand curve. at this point, the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, which is the equilibrium quantity, qe. A graph plots equilibrium in a market, with price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis. an upward sloping straight line supply curve intersects a downward sloping straight line demand curve at equilibrium quantity of q sub e.
Solved Suppose That The Following Graph Shows A Free Market Chegg The graph you've described illustrates the basic principle of market equilibrium in a free market, where the supply and demand curves intersect. at the equilibrium quantity, denoted as ( q e ), the amount of goods that sellers are willing to supply at a certain price is exactly equal to the amount of goods that buyers are willing to purchase at. Suppose now that an individual firm that produces goods in this market has the power to influence market price, leading to an outcome different from the free market equilibrium illustrated in the previous graph. In a free market, equilibrium is the point where the supply curve intersects the demand curve. at this point, the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, which is the equilibrium quantity, qe. A graph plots equilibrium in a market, with price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis. an upward sloping straight line supply curve intersects a downward sloping straight line demand curve at equilibrium quantity of q sub e.
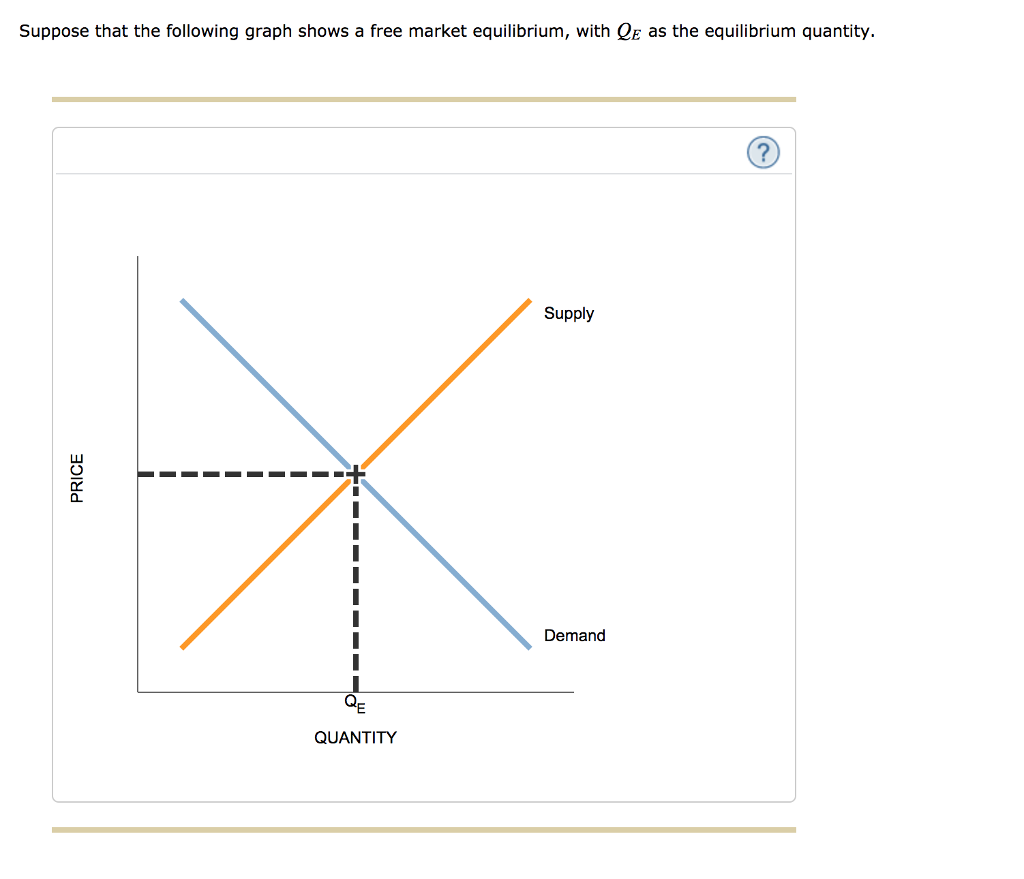
Solved Suppose That The Following Graph Shows A Free Market Chegg In a free market, equilibrium is the point where the supply curve intersects the demand curve. at this point, the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, which is the equilibrium quantity, qe. A graph plots equilibrium in a market, with price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis. an upward sloping straight line supply curve intersects a downward sloping straight line demand curve at equilibrium quantity of q sub e.
Solved The Following Graph Shows Equilibrium In A Free Chegg