
Spinal Cord Pdf Your spinal cord is a cylinder shaped tube of tissue that runs through the center of your spine, from your brainstem to your lower back. it’s made of nerves and cells that carry messages from your brain to the rest of your body. The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. the center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid.

Spinal Cord Overview Diagram Quizlet The spinal cord is an integral aspect of the central nervous system, which is cylindrical and elongated in structure. it is one of the most important contents of the vertebral canal. it presents as an extension of the lower part of the brain stem, i.e., the medulla oblongata. An essential feature of the central nervous system (cns), the spinal cord lies within the spinal column and extends from the brainstem to the lower back through the vertebral foramen of the vertebrae. in adults, the spinal cord terminates in the lumbar region at l1 l2, the conus medullaris. [1] . Spinal cord: a thick, whitish cord of nerve tissue which is a major part of the vertebrate central nervous system. it extends from the brain stem down through the spine, with nerves branching off to various parts of the body. Spinal cord – the longitudinal cord of nerve tissue enclosed in the spinal canal. it serves not only as a pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain, but also as a center for operating and coordinating reflex actions independent of the brain.
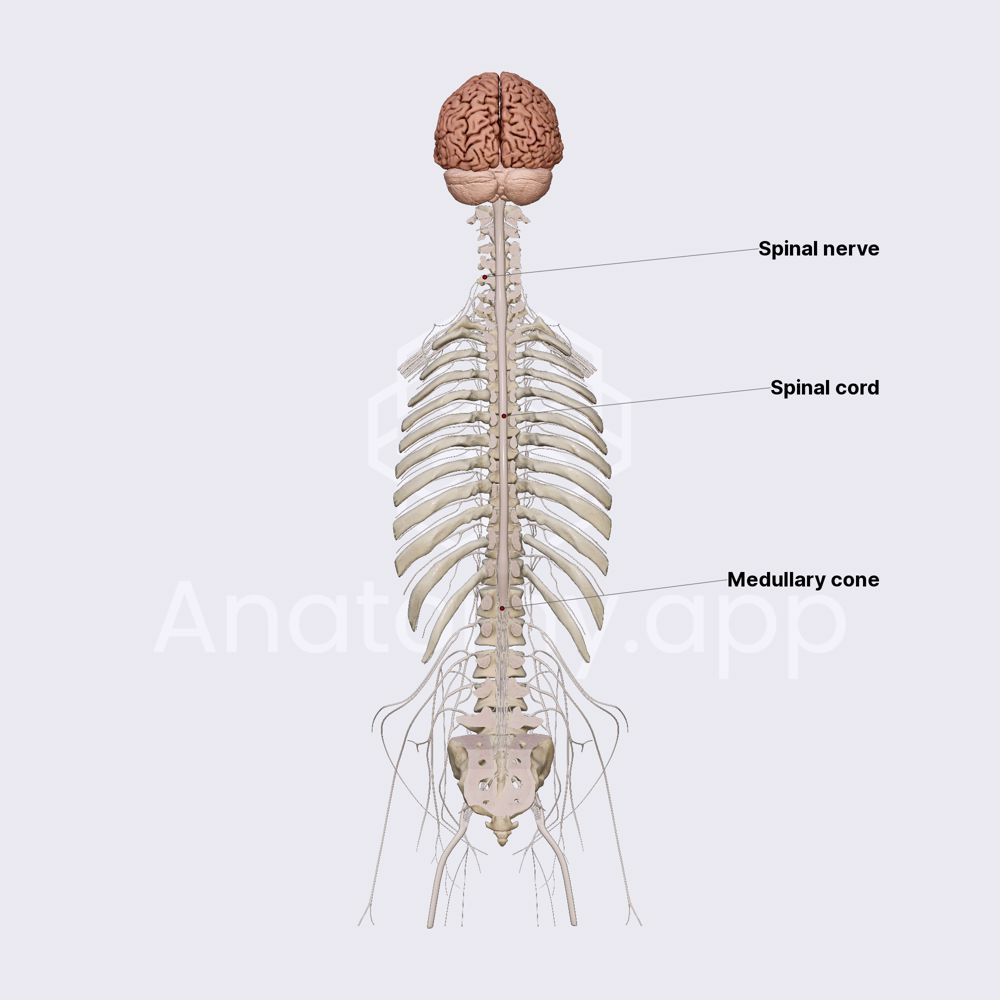
Spinal Cord Overview Anatomy App Spinal cord: a thick, whitish cord of nerve tissue which is a major part of the vertebrate central nervous system. it extends from the brain stem down through the spine, with nerves branching off to various parts of the body. Spinal cord – the longitudinal cord of nerve tissue enclosed in the spinal canal. it serves not only as a pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain, but also as a center for operating and coordinating reflex actions independent of the brain. Learn more about the spinal cord with our learning material. the spinal cord is made of gray and white matter just like other parts of the cns. it shows four surfaces: anterior, posterior, and two lateral. they feature fissures (anterior) and sulci (anterolateral, posterolateral, and posterior). The spinal cord is a tubular bundle of nervous tissue and supporting cells that extends from the brainstem to the lumbar vertebrae. together, the spinal cord and the brain form the central nervous system. in this article, we shall examine the macroscopic anatomy of the spinal cord – its structure, membranous coverings and blood supply. The spinal cord consists of bundles of nerve axons forming pathways that carry incoming and outgoing messages between the brain and the rest of the body. the spinal cord contains nerve cell circuits that control coordinated movements such as walking and swimming, as well as urinating. Causes of spinal cord disorders include injuries, infections, a blocked blood supply, and compression by a fractured bone or a tumor. typically, muscles are weak or paralyzed, sensation is abnormal or lost, and controlling bladder and bowel function may be difficult.
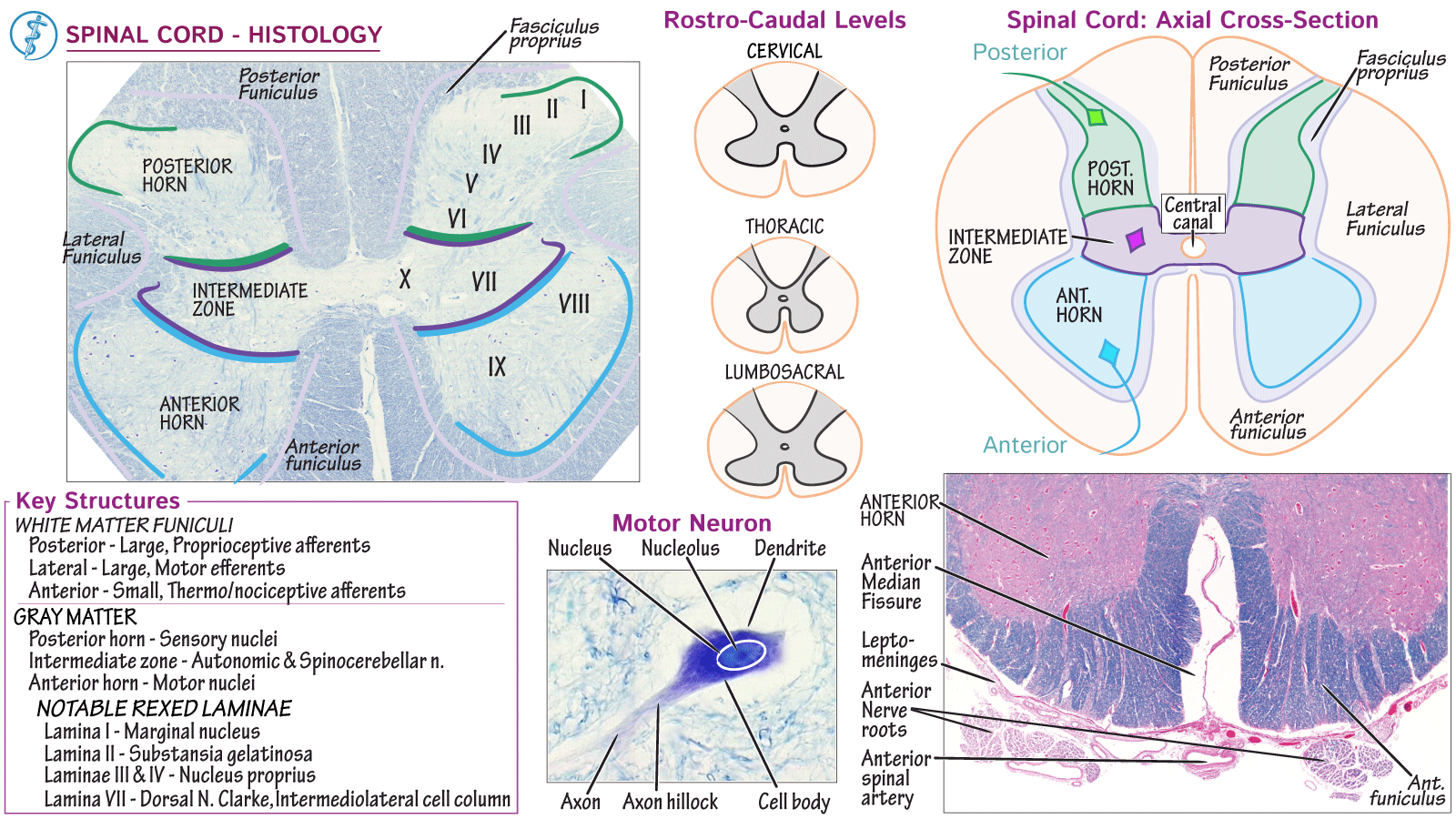
Neuroanatomy Spinal Cord Overview Anatomy Histology Ditki Medical Learn more about the spinal cord with our learning material. the spinal cord is made of gray and white matter just like other parts of the cns. it shows four surfaces: anterior, posterior, and two lateral. they feature fissures (anterior) and sulci (anterolateral, posterolateral, and posterior). The spinal cord is a tubular bundle of nervous tissue and supporting cells that extends from the brainstem to the lumbar vertebrae. together, the spinal cord and the brain form the central nervous system. in this article, we shall examine the macroscopic anatomy of the spinal cord – its structure, membranous coverings and blood supply. The spinal cord consists of bundles of nerve axons forming pathways that carry incoming and outgoing messages between the brain and the rest of the body. the spinal cord contains nerve cell circuits that control coordinated movements such as walking and swimming, as well as urinating. Causes of spinal cord disorders include injuries, infections, a blocked blood supply, and compression by a fractured bone or a tumor. typically, muscles are weak or paralyzed, sensation is abnormal or lost, and controlling bladder and bowel function may be difficult.