
Panic Attacks Causes Symptoms And Coping Strategies The New York Times It carries signals and sensory information from and to the brain, and regulates functions including heart rate, breathing rate and digestion. “ultimately, panic attacks are just fear of fear,” says clinical psychiatrist cindy aaronson phd. interestingly, your vagus nerve is a two way street. A panic attack can ensue if the brain does not react properly — a brain glitch of sorts. wellcome trust center for neuroimaging at university college london conducted tests by an mri in order to discern the part of the brain that is affected by stress and fear.

The Science Behind Panic Attacks What S Going On In Your Brain Recently researchers have identified certain regions of the brain that become hyperactive during a panic attack. these regions include the amygdala, which is the fear center of the brain, and. Explore the neurological processes behind panic attacks, including brain structures, neurotransmitters, and neuroplasticity. discover insights from neuroimaging studies. Far from being “all in your head,” panic attacks are grounded in a scientific process involving complex systems in your brain and body. by understanding the science behind them, you can demystify these experiences and take the first steps toward managing and overcoming them. Researchers have identified a novel brain pathway involved with panic like responses. neurons in the parabrachial nucleus influence the dorsal raphe nucleus, a key regulator of mood and stress .

The Science Behind Panic Attacks And What You Can Do To Manage Them Far from being “all in your head,” panic attacks are grounded in a scientific process involving complex systems in your brain and body. by understanding the science behind them, you can demystify these experiences and take the first steps toward managing and overcoming them. Researchers have identified a novel brain pathway involved with panic like responses. neurons in the parabrachial nucleus influence the dorsal raphe nucleus, a key regulator of mood and stress . Panic attacks begin with something that causes your heart to race — it could even be caused by something as innocuous as a jolt of caffeine. but once an attack is triggered, the cascade of physiological responses in the body is fairly universal. Learn why panic attacks happen, what role the amygdala plays, and discover practical coping strategies like breathing exercises, grounding techniques, and exposure therapy. At the center of panic attacks lies the amygdala, an almond shaped structure deep within the brain that serves as your personal security system. this region processes fear and other emotions, constantly scanning for potential threats in your environment. The current narrative review summarizes and examines several theories of panic disorder (pd) including biological theories, encompassing neurochemical factors, metabolic and genetic theories, respiratory and hyperventilation theories and cognitive.

Mapping The Brain Circuit Behind Panic Disorder Neuroscience News Panic attacks begin with something that causes your heart to race — it could even be caused by something as innocuous as a jolt of caffeine. but once an attack is triggered, the cascade of physiological responses in the body is fairly universal. Learn why panic attacks happen, what role the amygdala plays, and discover practical coping strategies like breathing exercises, grounding techniques, and exposure therapy. At the center of panic attacks lies the amygdala, an almond shaped structure deep within the brain that serves as your personal security system. this region processes fear and other emotions, constantly scanning for potential threats in your environment. The current narrative review summarizes and examines several theories of panic disorder (pd) including biological theories, encompassing neurochemical factors, metabolic and genetic theories, respiratory and hyperventilation theories and cognitive.
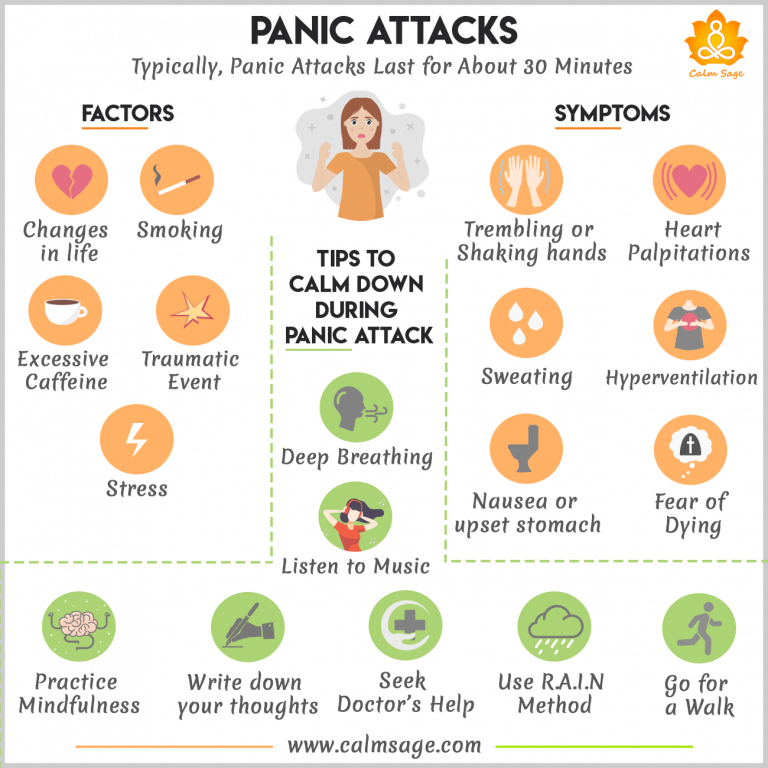
Panic Attacks Facts Natural Remedies All You Need To Know At the center of panic attacks lies the amygdala, an almond shaped structure deep within the brain that serves as your personal security system. this region processes fear and other emotions, constantly scanning for potential threats in your environment. The current narrative review summarizes and examines several theories of panic disorder (pd) including biological theories, encompassing neurochemical factors, metabolic and genetic theories, respiratory and hyperventilation theories and cognitive.