Timeвђ Temperatureвђ Transformation Ttt Diagram For Pd 40 Cu 30 Ni 10 P 20

Time Temperature Transformation Ttt Diagram Mechanicstips Download scientific diagram | time–temperature–transformation ttt diagram for pd 40 cu 30 ni 10 p 20 pcnp. the solid line describes the fit using the inverse function of t(t), given in eq. 3. Isothermal crystallization studies were performed on the bulk glass forming alloy pd 40 cu 30 ni 10 p 20 in the undercooled liquid region between the glass transition and liquidus temperature, resulting in a complete time–temperature–transformation (ttt) diagram for crystallization. the ttt diagram shows a typical “c” shape with the.
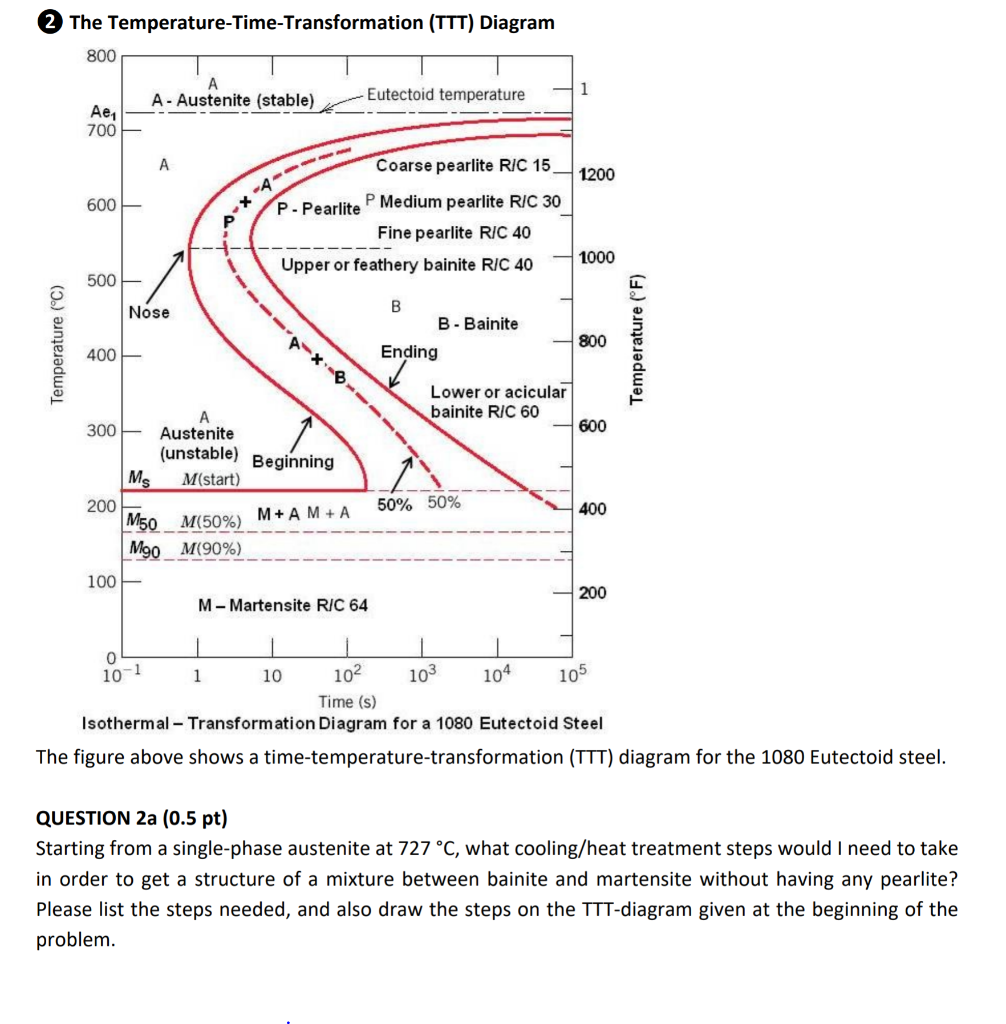
Time Transformation Temperature Diagram Time–temperature–transformation ttt diagram for pd 40 cu 30 ni 10 p 20 pcnp. the solid line describes the fit using the inverse function of t(t), given in eq. 3. Fig. 1. time–temperature–transformation ~ttt! diagram for pd40cu30ni10p20 ~pcnp!. the solid line describes the fit using the inverse function of t(t), given in eq. ~3!. fig. 2. cooling diagram for pcnp. no recalescence is detected at cooling rates larger than 0.33 k s. for lower rates, the onset of recalescence is. Time temperature transformation (ttt ) diagram. t (time) t (temperature) t (transformation) diagram is a plot of temperature versus the logarithm of time for a steel alloy of definite composition. it is used to determine when transformations begin and end for an isothermal (constant temperature) heat treatment of a previously austenitized alloy. Isothermal crystallization studies were performed on the bulk glass forming alloy pd40cu30ni10p20 in the undercooled liquid region between the glass transition and liquidus temperature, resulting in a complete time–temperature–transformation (ttt) diagram for crystallization. the ttt diagram shows a typical "c" shape with the nose at 50 s and 680 k. assuming steady state nucleation and a.

Comments are closed.