
Type 1 Vs Type 2 Errors Pdf In statistics, a type i error is a false positive conclusion, while a type ii error is a false negative conclusion. making a statistical decision always involves uncertainties, so the risks of making these errors are unavoidable in hypothesis testing. Type i error, or a false positive, is the erroneous rejection of a true null hypothesis in statistical hypothesis testing. a type ii error, or a false negative, is the erroneous failure in bringing about appropriate rejection of a false null hypothesis. [1].

Type 1 Error Vs Type 2 Error Medicosplexus Which type of error is more risky between type i and type ii errors? traditionally, committing type i error has been considered more risky, and thus more strict control of type i error has been performed in statistical inference. Type 1 error, in statistical hypothesis testing, is the error caused by rejecting a null hypothesis when it is true. type 1 error is caused when the hypothesis that should have been accepted is rejected. By utilizing adequately designed studies, balancing the likelihood of type i and type ii errors, and understanding power, providers, and researchers can determine which studies are clinically significant and should be implemented into practice. In hypothesis testing, two types of errors can occur: type i and type ii. these errors refer to the incorrect rejection or acceptance of the null hypothesis respectively. a type i error occurs when the null hypothesis is true but is rejected in favour of the alternative hypothesis.
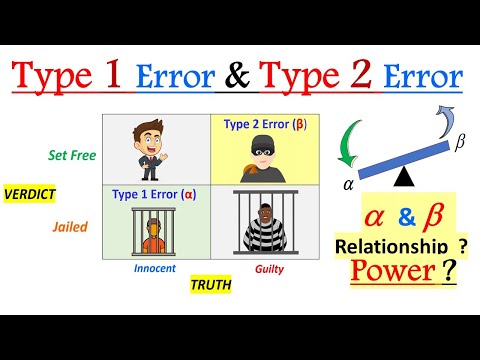
Type 1 Error Vs Type 2 Error Statistics Type 1 Error And Type 2 Error By utilizing adequately designed studies, balancing the likelihood of type i and type ii errors, and understanding power, providers, and researchers can determine which studies are clinically significant and should be implemented into practice. In hypothesis testing, two types of errors can occur: type i and type ii. these errors refer to the incorrect rejection or acceptance of the null hypothesis respectively. a type i error occurs when the null hypothesis is true but is rejected in favour of the alternative hypothesis. Type i error is an error that takes place when the outcome is a rejection of null hypothesis which is, in fact, true. type ii error occurs when the sample results in the acceptance of null hypothesis, which is actually false. The difference between type 1 and type 2 errors is that type 1 mistake happens when a researcher rejects the null hypothesis when it is true actuality. in contrast to that, type 2 error occurs when a researcher takes the wrong decision of accepting a null hypothesis because it is wrong in reality. We commit a type 1 error if we reject the null hypothesis when it is true. this is a false positive, like a fire alarm that rings when there's no fire. a type 2 error happens if we fail to reject the null when it is not true. this is a false negative—like an alarm that fails to sound when there is a fire.

Type 1 Error Vs Type 2 Error Aprogrammerlife Type i error is an error that takes place when the outcome is a rejection of null hypothesis which is, in fact, true. type ii error occurs when the sample results in the acceptance of null hypothesis, which is actually false. The difference between type 1 and type 2 errors is that type 1 mistake happens when a researcher rejects the null hypothesis when it is true actuality. in contrast to that, type 2 error occurs when a researcher takes the wrong decision of accepting a null hypothesis because it is wrong in reality. We commit a type 1 error if we reject the null hypothesis when it is true. this is a false positive, like a fire alarm that rings when there's no fire. a type 2 error happens if we fail to reject the null when it is not true. this is a false negative—like an alarm that fails to sound when there is a fire.

Type 1 Vs Type 2 Error We commit a type 1 error if we reject the null hypothesis when it is true. this is a false positive, like a fire alarm that rings when there's no fire. a type 2 error happens if we fail to reject the null when it is not true. this is a false negative—like an alarm that fails to sound when there is a fire.