
Type I Type Ii Errors With Examples Pdf Type I And Type Ii Errors In statistics, a type i error is a false positive conclusion, while a type ii error is a false negative conclusion. making a statistical decision always involves uncertainties, so the risks of making these errors are unavoidable in hypothesis testing. Type i error, or a false positive, is the erroneous rejection of a true null hypothesis in statistical hypothesis testing. a type ii error, or a false negative, is the erroneous failure in bringing about appropriate rejection of a false null hypothesis. [1].
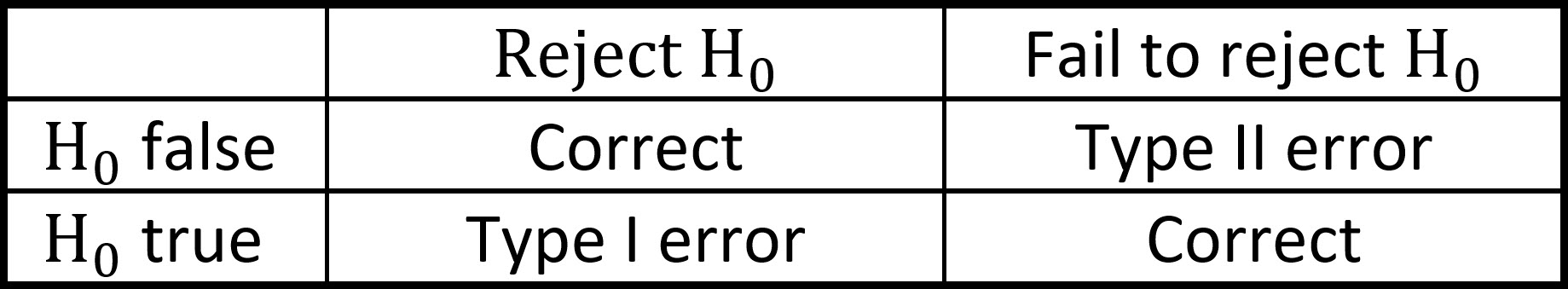
Type I And Type Ii Errors A type i error occurs when a true null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected (false positive). a type ii error happens when a false null hypothesis isn't rejected (false negative). In statistics, type i and type ii errors represent two kinds of errors that can occur when making a decision about a hypothesis based on sample data. understanding these errors is crucial for interpreting the results of hypothesis tests. Type ii error, also known as a "false negative": the error of not rejecting a null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is the true state of nature. in other words, this is the error of failing to accept an alternative hypothesis when you don't have adequate power. Type i and type ii errors can lead to confusion as providers assess medical literature. a vignette that illustrates the errors is the boy who cried wolf. first, the citizens commit a type i error by believing there is a wolf when there is not. second, the citizens commit a type ii error by believing there is no wolf when there is one.
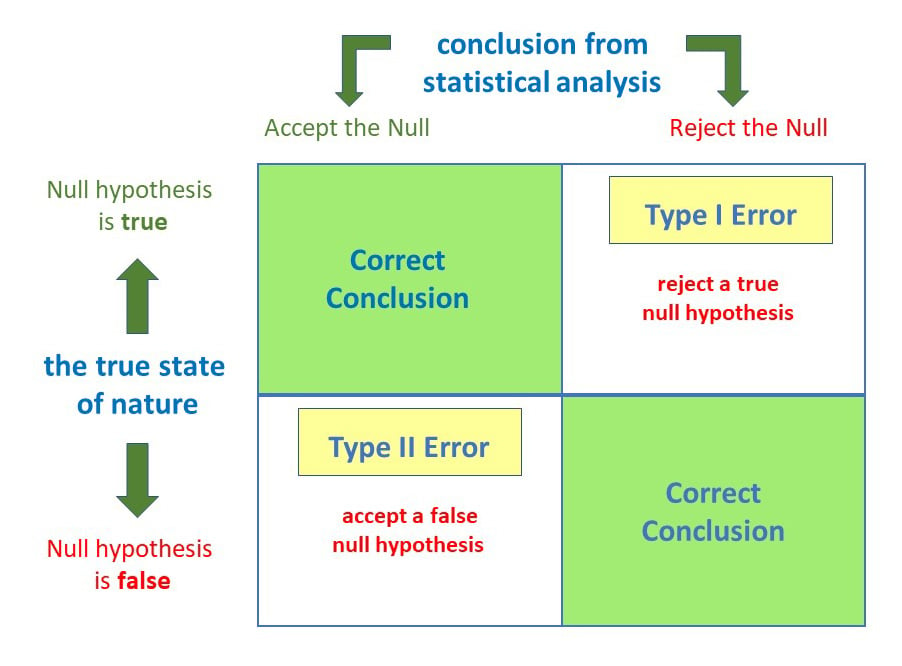
What Are Type 1 And Type 2 Errors In Statistics Type ii error, also known as a "false negative": the error of not rejecting a null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is the true state of nature. in other words, this is the error of failing to accept an alternative hypothesis when you don't have adequate power. Type i and type ii errors can lead to confusion as providers assess medical literature. a vignette that illustrates the errors is the boy who cried wolf. first, the citizens commit a type i error by believing there is a wolf when there is not. second, the citizens commit a type ii error by believing there is no wolf when there is one. In simple words, type ii error means accepting the hypothesis when it should not have been accepted. the type ii error results in a false negative result. in other words, type ii is the error of failing to accept an alternative hypothesis when the researcher doesn’t have adequate power. What is a type ii error? (false negative) a type ii error happens when we fail to reject a false hypothesis. this means we miss something that’s actually there. example: a test fails to detect a disease when the person actually has it. a security scanner at the airport misses a hidden weapon. Type i error occurs if they reject the null hypothesis and conclude that their new frying method is preferred when in reality is it not. this may occur if, by random sampling error, they happen to get a sample that prefers the new frying method more than the overall population does. A type i error occurs when we reject a null hypothesis that is actually true, while a type ii error happens when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis. get the full details here.