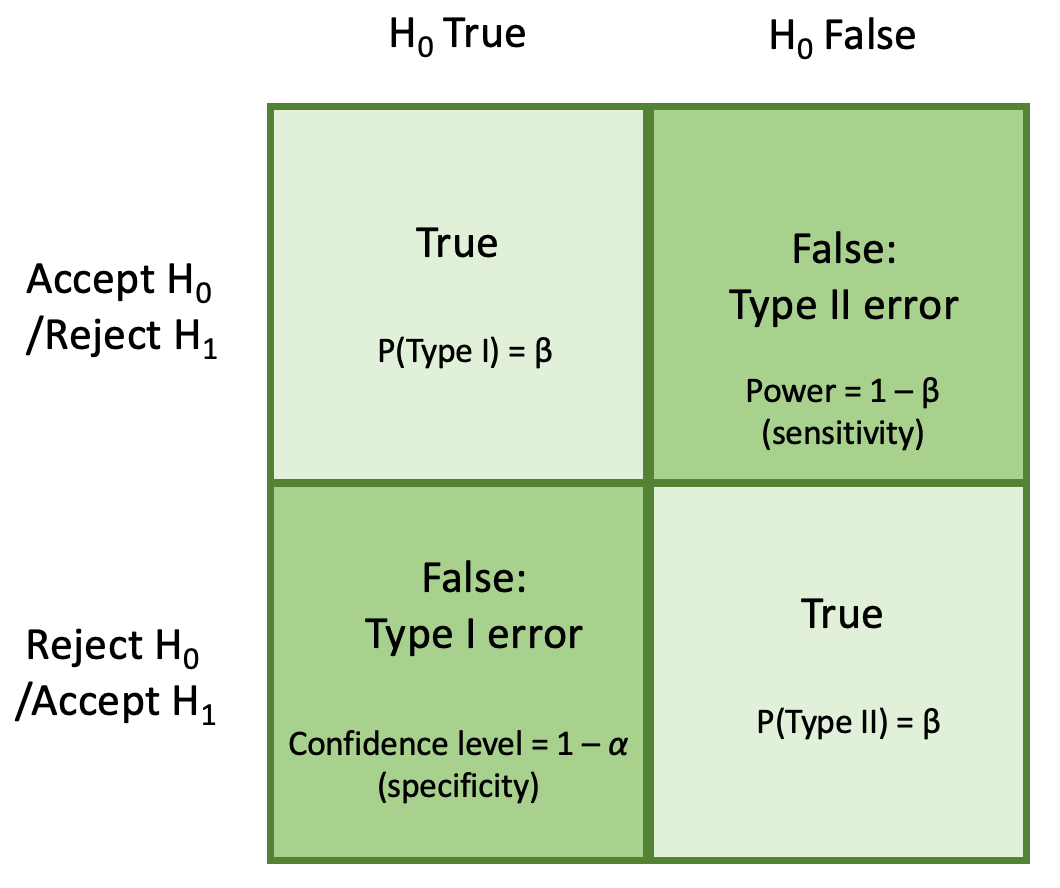
Type Ii Error Explained Plus Example Vs Type I Error True To Size A type i error occurs when a true null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected (false positive). a type ii error happens when a false null hypothesis isn't rejected (false negative). What is a type ii error? a type ii error is a statistical term used to describe the error that results when a null hypothesis that is actually false is not rejected by an investigator or.

Type I Type Ii Errors Explained Data Havilah Academy In simple words, type ii error means accepting the hypothesis when it should not have been accepted. the type ii error results in a false negative result. in other words, type ii is the error of failing to accept an alternative hypothesis when the researcher doesn’t have adequate power. A type i error is where we have a false positive conclusion, while a type ii error is when we have a false negative conclusion. type i error or false positive happens when you reject the null hypothesis while the null hypothesis is actually true. Type ii error: the researcher thinks the blood cultures do not contain traces of pathogen x x, when in fact, they do. suppose the null hypothesis, h0 h 0, is: the victim of an automobile accident is alive when he arrives at the emergency room of a hospital. Type i error, or a false positive, is the erroneous rejection of a true null hypothesis in statistical hypothesis testing. a type ii error, or a false negative, is the erroneous failure in bringing about appropriate rejection of a false null hypothesis. [1].

Type I Error Vs Type Ii Error Know The Difference Type ii error: the researcher thinks the blood cultures do not contain traces of pathogen x x, when in fact, they do. suppose the null hypothesis, h0 h 0, is: the victim of an automobile accident is alive when he arrives at the emergency room of a hospital. Type i error, or a false positive, is the erroneous rejection of a true null hypothesis in statistical hypothesis testing. a type ii error, or a false negative, is the erroneous failure in bringing about appropriate rejection of a false null hypothesis. [1]. Two fundamental types of errors, known as type i and type ii errors, are crucial to understand when interpreting statistical results and making decisions based on those results. Type i error occurs if they reject the null hypothesis and conclude that their new frying method is preferred when in reality is it not. this may occur if, by random sampling error, they happen to get a sample that prefers the new frying method more than the overall population does. Deciding whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis can lead to two types of errors. type 1 errors, also known as false positives, happen when we incorrectly reject a true null hypothesis. this means we conclude that a difference or relationship exists when it actually doesn't.
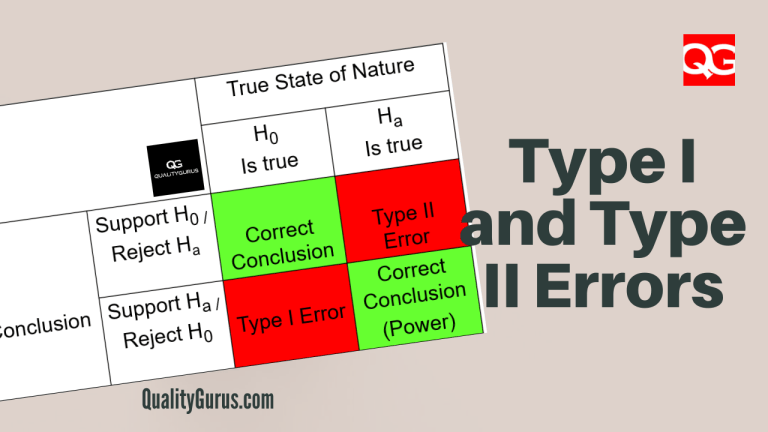
Type I And Type Ii Errors Explained Quality Gurus Two fundamental types of errors, known as type i and type ii errors, are crucial to understand when interpreting statistical results and making decisions based on those results. Type i error occurs if they reject the null hypothesis and conclude that their new frying method is preferred when in reality is it not. this may occur if, by random sampling error, they happen to get a sample that prefers the new frying method more than the overall population does. Deciding whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis can lead to two types of errors. type 1 errors, also known as false positives, happen when we incorrectly reject a true null hypothesis. this means we conclude that a difference or relationship exists when it actually doesn't.
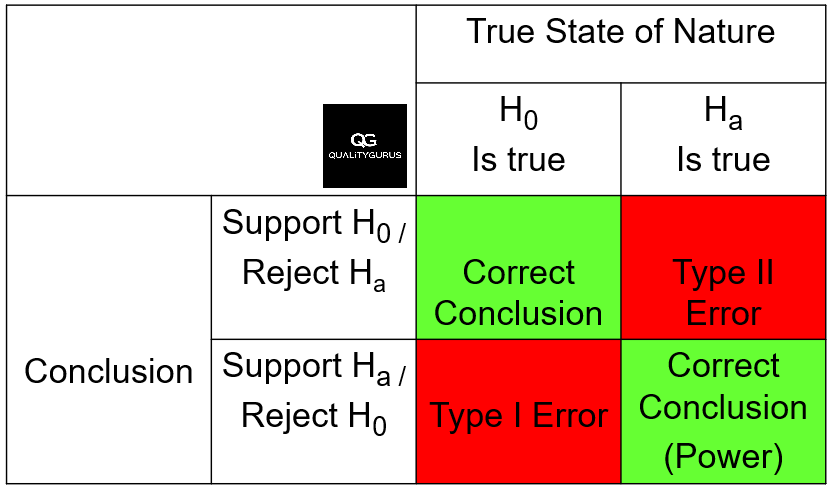
Type I And Type Ii Errors Explained Quality Gurus Deciding whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis can lead to two types of errors. type 1 errors, also known as false positives, happen when we incorrectly reject a true null hypothesis. this means we conclude that a difference or relationship exists when it actually doesn't.