
4 Types Of Data With Nominal Ordinal Discrete And Continuous Data Nominal data is used to label variables without any order or quantitative value. the color of hair can be considered nominal data, as one color can’t be compared with another color. the name “nominal” comes from the latin name “nomen,” which means “name.”. In statistics, there are four main types of data: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. these types of data are used to describe the nature of the data being collected or analyzed, and they help determine the appropriate statistical tests to use.
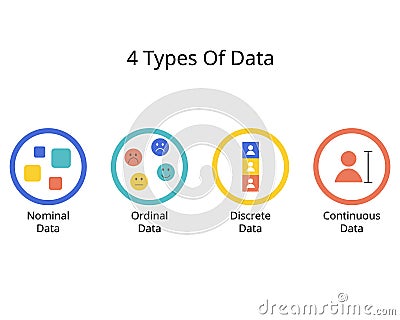
4 Types Of Data With Nominal Ordinal Discrete And Continuous Data There are actually four different data measurement scales that are used to categorize different types of data: 1. nominal. 2. ordinal. 3. interval. 4. ratio. in this post, we define each measurement scale and provide examples of variables that can be used with each scale. Nominal, ordinal, discrete and continuous data are the main data types used in statistics. here's what to know about categorical, numerical and more of the data types seen in the field. Ordinal and nominal data both fall under the category of qualitative (or categorical) data. discrete and continuous data fall under the category of quantitative (or numerical) data. Nominal data are used to label variables without any quantitative value. common examples include male female (albeit somewhat outdated), hair color, nationalities, names of people, and so on. in plain english: basically, they're labels (and nominal comes from "name" to help you remember). you have brown hair (or brown eyes). you are american.
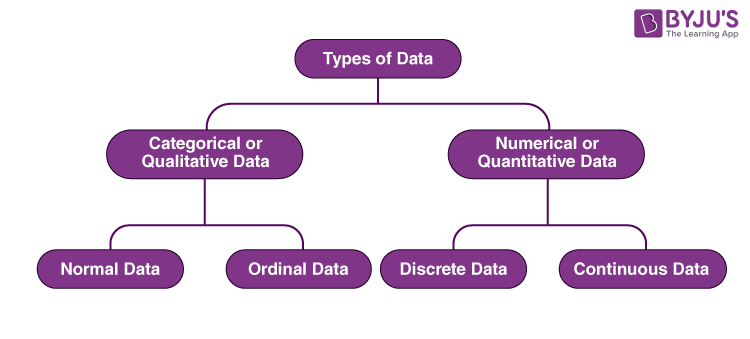
Types Of Data In Statistics 4 Types Nominal Ordinal Discrete Ordinal and nominal data both fall under the category of qualitative (or categorical) data. discrete and continuous data fall under the category of quantitative (or numerical) data. Nominal data are used to label variables without any quantitative value. common examples include male female (albeit somewhat outdated), hair color, nationalities, names of people, and so on. in plain english: basically, they're labels (and nominal comes from "name" to help you remember). you have brown hair (or brown eyes). you are american. Ordinal data is the second level of measurement. it builds on nominal data by introducing an order to the categories. ordinal data maintains distinct categories like nominal data, but it also adds the important dimension of relative position or preference. these are the key characteristics of ordinal data:. There are broadly four main types of data: nominal data, which involves labels or categories; ordinal data, which shows order without precise differences; discrete data, which includes countable values; and continuous data, which represents measurable quantities that can take any value within a range. Discrete data is information that can only take certain values and can't be made more precise. this might only be whole numbers, like the numbers on a die (any number from 1 to 6) or could be other types of fixed number scheme, such as shoe sizes (2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, etc.). Nominal data, which cannot be sorted in order, and ordinal data, which has a specific order, are subtypes of qualitative data. on the other hand, quantitative data, which includes numerical values, is suitable for statistical data analysis and can be represented using various graphs.

4 Types Data Nominal Ordinal Discrete Stock Vector Royalty Free Ordinal data is the second level of measurement. it builds on nominal data by introducing an order to the categories. ordinal data maintains distinct categories like nominal data, but it also adds the important dimension of relative position or preference. these are the key characteristics of ordinal data:. There are broadly four main types of data: nominal data, which involves labels or categories; ordinal data, which shows order without precise differences; discrete data, which includes countable values; and continuous data, which represents measurable quantities that can take any value within a range. Discrete data is information that can only take certain values and can't be made more precise. this might only be whole numbers, like the numbers on a die (any number from 1 to 6) or could be other types of fixed number scheme, such as shoe sizes (2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, etc.). Nominal data, which cannot be sorted in order, and ordinal data, which has a specific order, are subtypes of qualitative data. on the other hand, quantitative data, which includes numerical values, is suitable for statistical data analysis and can be represented using various graphs.

4 Types Of Data Nominal Ordinal Discrete Continuous Discrete data is information that can only take certain values and can't be made more precise. this might only be whole numbers, like the numbers on a die (any number from 1 to 6) or could be other types of fixed number scheme, such as shoe sizes (2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, etc.). Nominal data, which cannot be sorted in order, and ordinal data, which has a specific order, are subtypes of qualitative data. on the other hand, quantitative data, which includes numerical values, is suitable for statistical data analysis and can be represented using various graphs.

4 Types Of Data Nominal Ordinal Discrete Continuous