
U1 Exploring One Variable Data Pdf Quartile Statistics Quantitative variables: these variables take on numerical values for a. 1. frequency tables give the number of cases falling into each category, aka a. a. frequency = counts. 2. relative frequency table: gives the proportion of cases falling into each. a. proportion: part divided by whole. same as decimal form of a percentage. b. In this unit, students will define and represent categorical and quantitative variables, describe and compare distributions of one variable data, and interpret statistical calculations to assess claims about individual data points or samples.

Week1 Statistics Pdf Probability Distribution Random Variable Unit 1: exploring one variable data introduction: statistics and statistical methods let us collect, describe, analyze, and draw conclusions about data. understanding variability is a key to understanding data. imagine if a population of students who all had exactly the same height and weight. this population would have no variability. Explain the meaning of single variable data. for the data set described by the box plot below, state. the median. the greatest value. the lowest value. the range. the value of the first quartile. the value of the third quartile. the interquartile range. create a box plot for each of the following data sets. 4 4 6 7 7 9 11 12. 1c: students will be able to represent, describe, and compare quantitative data using histograms, stem and leaf graphs, dotplots, ogives, and box and whisker plots. 1d: students will be able to calculate measures of center (mean, median, mode), variability (standard deviation, iqr, range), and position (percentiles and z scores) in a distribution. The spread of distribution. the 0th percentile is the minimum, the 25th percentile is quartile 1, the 50th percentile is the median, the 75th percentile is quartile 3, and the 100.

One Variable Data Ap Statistics Unit 1 Slides And Guided Notes Tpt 1c: students will be able to represent, describe, and compare quantitative data using histograms, stem and leaf graphs, dotplots, ogives, and box and whisker plots. 1d: students will be able to calculate measures of center (mean, median, mode), variability (standard deviation, iqr, range), and position (percentiles and z scores) in a distribution. The spread of distribution. the 0th percentile is the minimum, the 25th percentile is quartile 1, the 50th percentile is the median, the 75th percentile is quartile 3, and the 100. 15 – 23% exam weight *note: schedule is subject to change, please check moodle for most updated information. Quartiles uses three points to divide a data set into four groups, each with an equal number of values. these points are the rst quartile ( q 1), the second quartile ( q 2) and the third quartile ( q 3). Unit 1: one variable data ap statistics course review study guide statistics facts: descriptive statistics describing distributions: socs = shape, outliers unusual, center, spread (use comparison language if comparing). Interquartile range (iqr) formula: iqr = q3 q1 resistant to outliers. standard deviation (s or σ) measures how far data points deviate from the mean. larger s = more spread out. empirical rule (for normal distributions): 68% within 1 standard deviation. 95% within 2 standard deviations. 99.7% within 3 standard deviations.
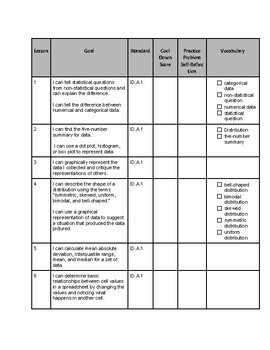
One Variable Statistics Illustrative Mathematics Algebra 1 Unit Overview 15 – 23% exam weight *note: schedule is subject to change, please check moodle for most updated information. Quartiles uses three points to divide a data set into four groups, each with an equal number of values. these points are the rst quartile ( q 1), the second quartile ( q 2) and the third quartile ( q 3). Unit 1: one variable data ap statistics course review study guide statistics facts: descriptive statistics describing distributions: socs = shape, outliers unusual, center, spread (use comparison language if comparing). Interquartile range (iqr) formula: iqr = q3 q1 resistant to outliers. standard deviation (s or σ) measures how far data points deviate from the mean. larger s = more spread out. empirical rule (for normal distributions): 68% within 1 standard deviation. 95% within 2 standard deviations. 99.7% within 3 standard deviations.