Types Of Neurons Structure Sensory Motor Neuron Vecto Vrogue Co Neuron publishes outstanding research spanning all neuroscience sub disciplines from molecular, to systems level, including cognitive and theoretical domains. the editorial team also commissions reviews and commentaries to highlight themes, synthesize insights and promote discussions at the interface of science and society. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain.
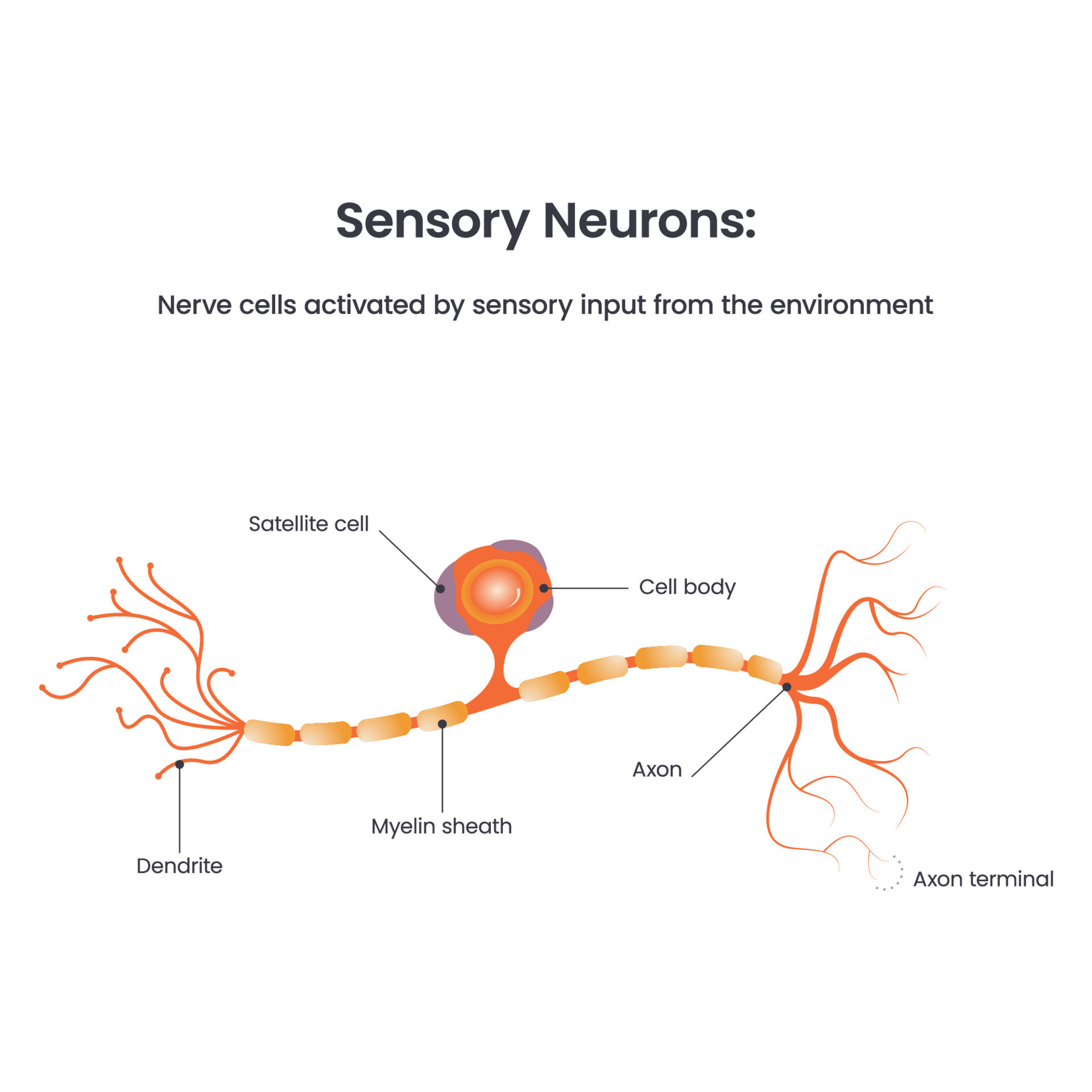
Types Of Neurons Structure Sensory Motor Neuron Vecto Vrogue Co A neuron is a nerve cell that processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system. neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites (which receive signals), and an axon (which sends signals). Neurons, also known as nerve cells, send and receive signals from your brain. while neurons have a lot in common with other types of cells, they’re structurally and functionally unique . Neurons are the primary cells responsible for receiving and sending signals throughout the brain and nervous system. like a person in a crowded room, each neuron can interact with others nearby, letting it direct and modify signals locally. local signals can get passed on within groups of cells, permitting a signal to travel longer distances. Neuron, basic cell of the nervous system in vertebrates and most invertebrates from the level of the cnidarians (e.g., corals, jellyfish) upward. a typical neuron has a cell body containing a nucleus and two or more long fibres.

Structure Of Neuron Or Nerve Cell Artofit Neurons are the primary cells responsible for receiving and sending signals throughout the brain and nervous system. like a person in a crowded room, each neuron can interact with others nearby, letting it direct and modify signals locally. local signals can get passed on within groups of cells, permitting a signal to travel longer distances. Neuron, basic cell of the nervous system in vertebrates and most invertebrates from the level of the cnidarians (e.g., corals, jellyfish) upward. a typical neuron has a cell body containing a nucleus and two or more long fibres. What is a neuron? neurons are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. all neurons have three different parts – dendrites, cell body and axon. the neuron structure is specially adapted to carry messages over large distances in the body quickly in the form of electrical signals. A neuron is not just a cell; it is the unit of communication within the nervous system, responsible for carrying electrical impulses throughout the body. it’s these impulses that allow us to sense the world, react to stimuli, learn new information, and remember the past. A neuron is a nerve cell that is the basic building block of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. neurons are similar to other cells in the human body in a number of ways, but there is one key difference between neurons and other cells. Neurons are the architects of communication within the nervous system, orchestrating signaling pathways that underpin physiological processes. each neuron generates and propagates electrical impulses, known as action potentials, which are the primary currency of neural communication.

Solution Neuron Types And Structure And Function Studypool What is a neuron? neurons are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. all neurons have three different parts – dendrites, cell body and axon. the neuron structure is specially adapted to carry messages over large distances in the body quickly in the form of electrical signals. A neuron is not just a cell; it is the unit of communication within the nervous system, responsible for carrying electrical impulses throughout the body. it’s these impulses that allow us to sense the world, react to stimuli, learn new information, and remember the past. A neuron is a nerve cell that is the basic building block of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. neurons are similar to other cells in the human body in a number of ways, but there is one key difference between neurons and other cells. Neurons are the architects of communication within the nervous system, orchestrating signaling pathways that underpin physiological processes. each neuron generates and propagates electrical impulses, known as action potentials, which are the primary currency of neural communication.

5 Ways To Make Structure And Function Of Neurons Interesting For Students A neuron is a nerve cell that is the basic building block of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. neurons are similar to other cells in the human body in a number of ways, but there is one key difference between neurons and other cells. Neurons are the architects of communication within the nervous system, orchestrating signaling pathways that underpin physiological processes. each neuron generates and propagates electrical impulses, known as action potentials, which are the primary currency of neural communication.
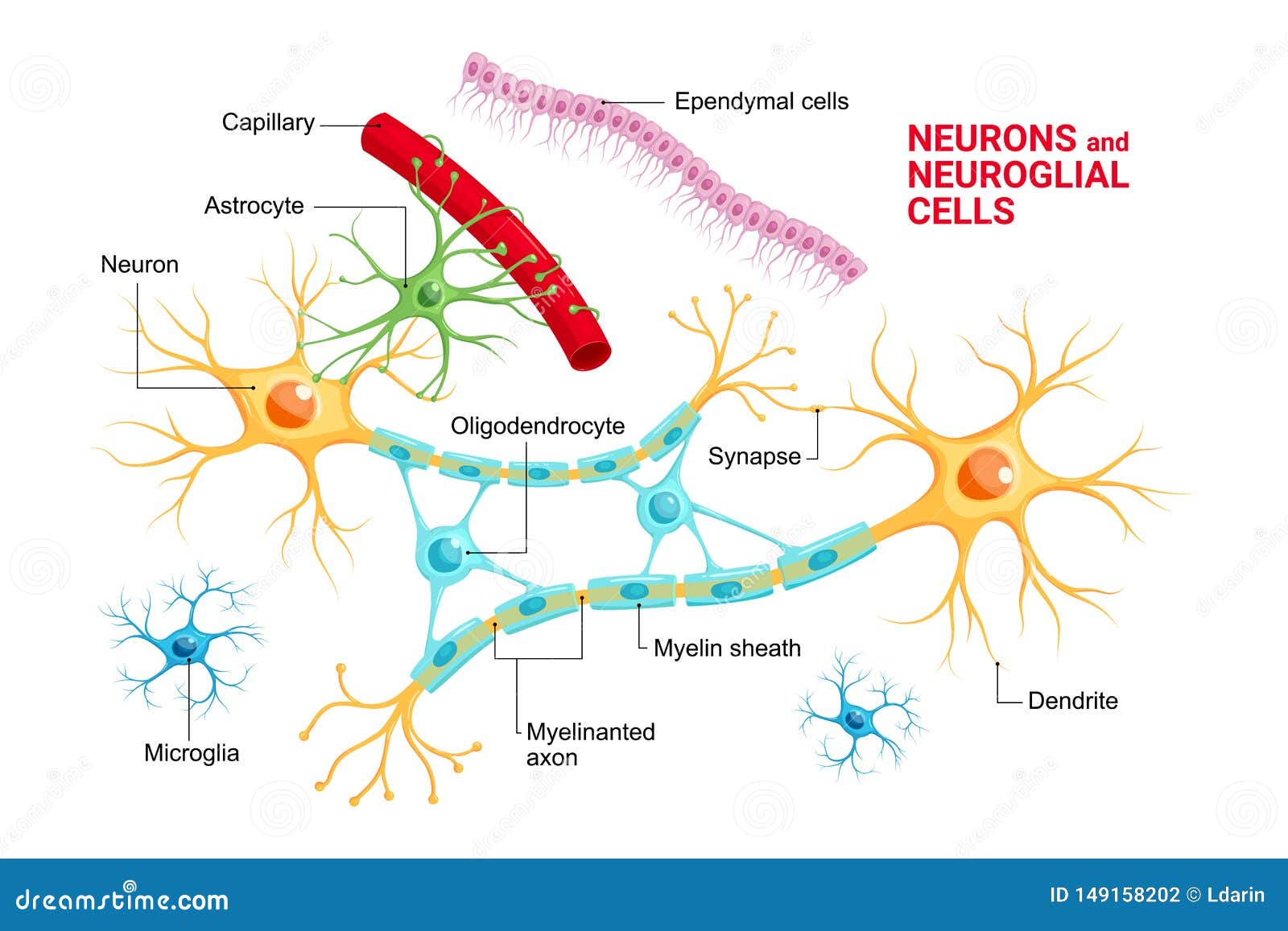
Structure Of Nerve Cell