
Probability Density Functions Pdf Random Variable Probability We describe the probabilities of a real valued scalar variable x with a probability density function (pdf), written p(x). any real valued function p(x) that satisfies: is a valid pdf. i will use the convention of upper case p for discrete probabilities, and lower case. p for pdfs. this can be visualized by plotting the curve p(x). Probability density functions p.d.f. calculations continuous random variable x with probability density function f ( x ) given by.
4 1 Probability Density Functions Pdfs And Cumulative Distribution We describe the probabilities of a real valued scalar variable x with a probability density function (pdf), written p (x). any real valued function p (x) that satisfies: z ∞ p (x) ≥ 0 for all x p (x)dx = 1 (1) (2) −∞ is a valid pdf. i will use the convention of upper case p for discrete probabilities, and lower case p for pdfs. Probability density functions • probability density function – in simple terms, a probability density function (pdf) drawing a smooth curve fit through the vertically normalized histogram as sketched. you can think of a pdf as the smooth limit of a vertically normalized histogram if there were millions of measurements and a huge number of bins. In this chapter we will formalize this procedure, identifying exactly when we can scale a given measure to reproduce the expectation values of a target probability distribution and how we can use scalings to specify new probability distributions in the context of a given measure. Mathematical expectation definition: if u (x) is a function of the random variable x and f (x) is a probability density function of x, then: −∞ ∫ ∞ ( ) ( ).

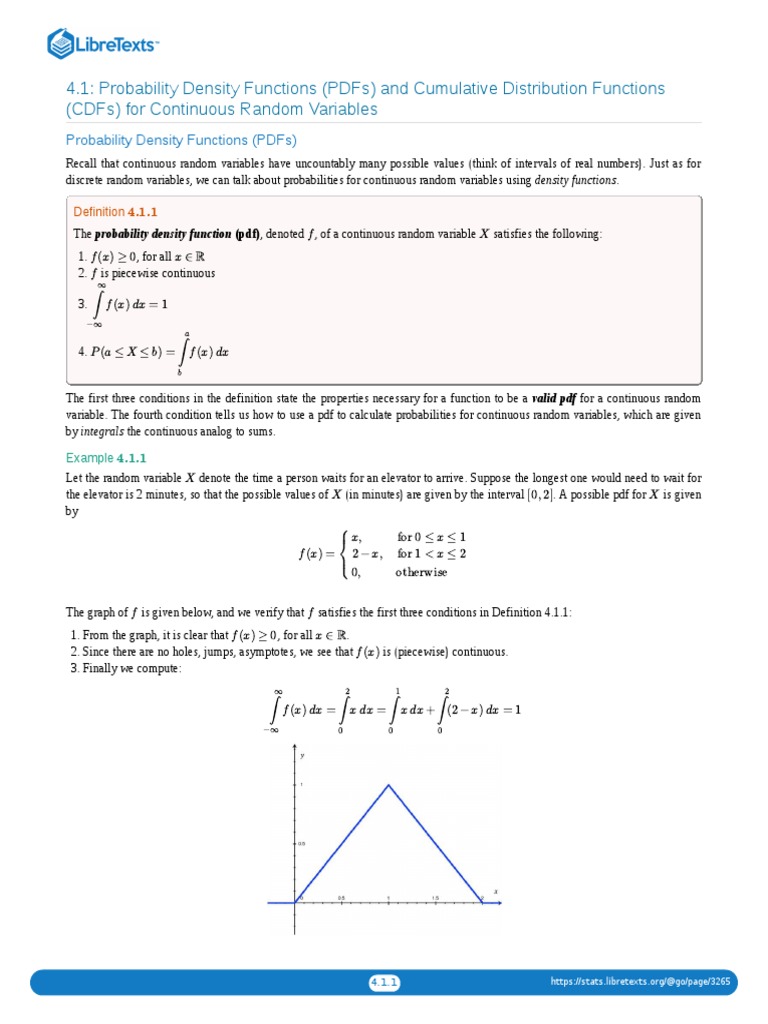
Chapter6 Probability Pdf Probability Distribution Probability In this chapter we will formalize this procedure, identifying exactly when we can scale a given measure to reproduce the expectation values of a target probability distribution and how we can use scalings to specify new probability distributions in the context of a given measure. Mathematical expectation definition: if u (x) is a function of the random variable x and f (x) is a probability density function of x, then: −∞ ∫ ∞ ( ) ( ). Just as for discrete random variables, we can talk about probabilities for continuous random variables using density functions. the probability density function (pdf), denoted f f, of a continuous random variable x x satisfies the following:. Probability density functions of various statistical distributions (continuous and discrete). the probability density function returns the probability that the variate has the value x. in statistics the pdf is also called the frequency function. Probability density function figure: [left] a probability mass function (pmf) tells us the relative frequency of a state when computing the probability. in this example, the \size" of a is px(x2) px(x3). [right] a probability density function (pdf) is the in nitesimal version of the pmf. thus, the \size" of a is the integration over the pdf. Probability density functions a probability density function (pdf) f(x) describes the probability of an outcome x:.