
80 Of All Premature Births Are Due To Preterm Labor Timely Approximately 10 percent of babies in the united states are born preterm; 80 percent of these are due to preterm labor that begins on its own or after preterm prelabor rupture of the fetal membranes (or "broken bag of waters"). these are called spontaneous preterm labor. Preterm birth is when a baby is born too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy have been completed. in 2022, preterm birth affected about 1 of every 10 infants born in the united states. the preterm birth rate declined 1% from 2021 to 2022, to 10.4%, following an increase of 4% from 2020 to 2021.
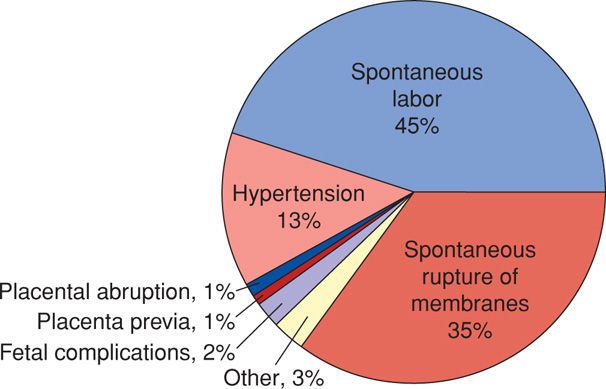
Preterm Labor Obgyn Key Unplanned preterm births have several reasons, including the black race, periodontal disease, low mother body mass index (bmi), and previous preterm births. a short cervical length and a high cervical vaginal fetal fibronectin concentration are the two best signs of premature birth. Preterm birth is the leading cause of child deaths, accounting for more than 1 in 5 of all deaths of children occurring before their 5th birthday [3]. from 2010 to 2020, an estimated 152 million babies were born preterm. yet, rates of preterm birth have remained stagnant, with some regions even witnessing an increase. Major geographic and racial disparities in preterm birth rates continue to exist, and these variations offer potential opportunities to better understand the population based risk factors for preterm birth and the impacts of preterm birth prevention programs and policies. Educating pregnant women about early recognition of preterm labor warning signs and symptoms allows for timely diagnosis, interventions, and treatment. informed and collaborative nursing practice improves quality of clinical care based on individualized interactions.
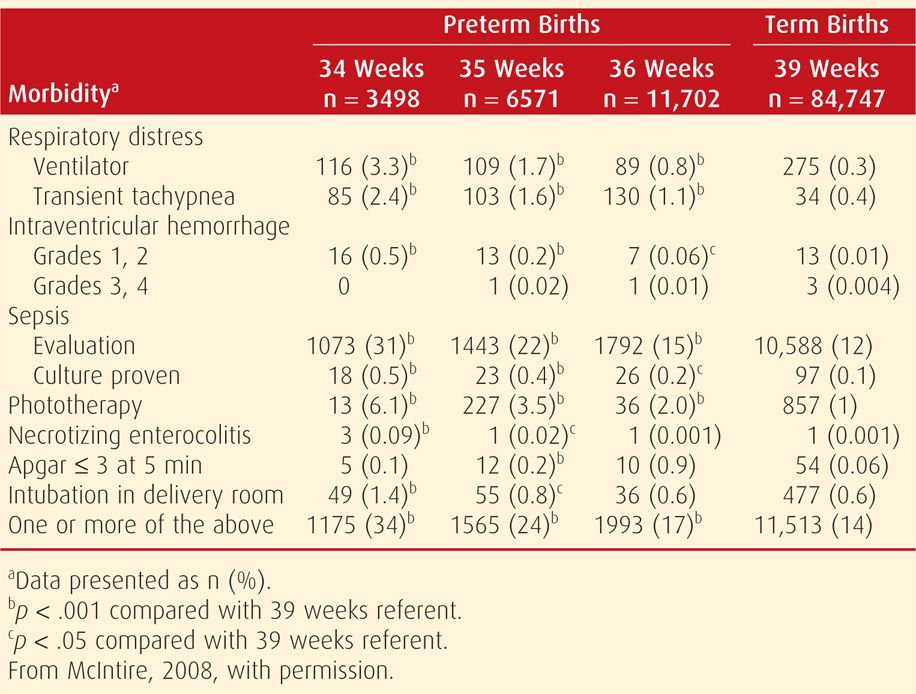
Preterm Labor Obgyn Key Major geographic and racial disparities in preterm birth rates continue to exist, and these variations offer potential opportunities to better understand the population based risk factors for preterm birth and the impacts of preterm birth prevention programs and policies. Educating pregnant women about early recognition of preterm labor warning signs and symptoms allows for timely diagnosis, interventions, and treatment. informed and collaborative nursing practice improves quality of clinical care based on individualized interactions. Preterm birth is a leading cause of perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide. this guideline covers the care of women with signs symptoms of preterm birth aiming to give recommendations to reduce both the risk of unnecessary treatment as well as the consequences of prematurity. The rate of preterm birth has risen from 10.6 for every 100 live births in 1990 to 12.7 per 100 live births in 2005 (the most recent year for which final data is available), with the increase primarily attributed to infants born at 34 to 36 weeks' gestation. 1 preterm birth is a strong predictor of infant mortality and morbidity, and is shown. Preterm birth (delivery before 37 weeks and 0 7 days of gestation) is a leading cause of infant morbidity and mortality in the united states. in 2013, 11.4% of the nearly 4 million u.s. live births were preterm; however, 36% of the 8,470 infant deaths were attributed to preterm birth (1). Importance: preterm labor (ptl) is one of the most common and serious pregnancy complications associated with significant perinatal morbidity and mortality, as well as long term neurologic impairment in the offspring.

Premature Birth Preterm Birth Faqs Pretrm Preterm birth is a leading cause of perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide. this guideline covers the care of women with signs symptoms of preterm birth aiming to give recommendations to reduce both the risk of unnecessary treatment as well as the consequences of prematurity. The rate of preterm birth has risen from 10.6 for every 100 live births in 1990 to 12.7 per 100 live births in 2005 (the most recent year for which final data is available), with the increase primarily attributed to infants born at 34 to 36 weeks' gestation. 1 preterm birth is a strong predictor of infant mortality and morbidity, and is shown. Preterm birth (delivery before 37 weeks and 0 7 days of gestation) is a leading cause of infant morbidity and mortality in the united states. in 2013, 11.4% of the nearly 4 million u.s. live births were preterm; however, 36% of the 8,470 infant deaths were attributed to preterm birth (1). Importance: preterm labor (ptl) is one of the most common and serious pregnancy complications associated with significant perinatal morbidity and mortality, as well as long term neurologic impairment in the offspring.