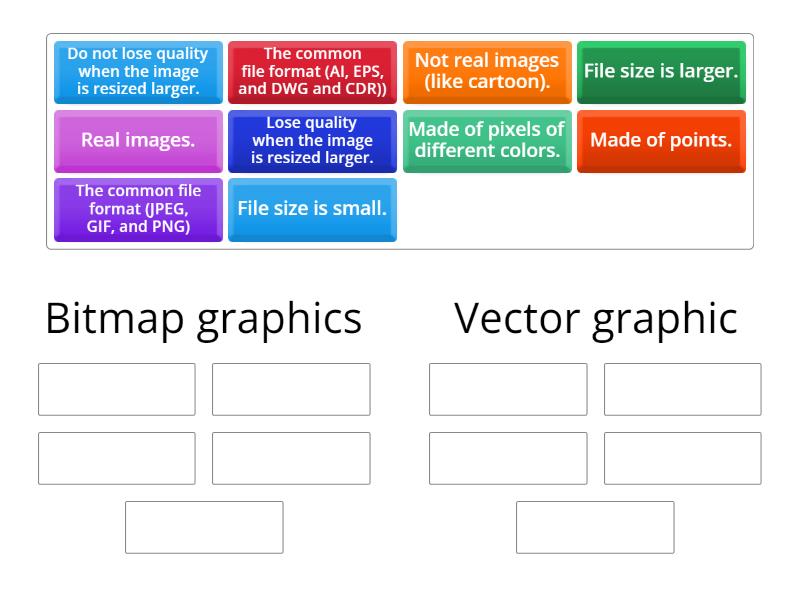
Diffrernce Between Bitmap And Vector Graphics Group Sort A continuous, insulating monolayer of cuboidal columnar epithelium which extends from the margins of the optic nerve head to the ora serrata where it is continuous with the pigment epithelium of the pars plana. Lynn s.a., ward g., keeling e., scott j.a., cree a.j., johnston d.a., page a., cuan urquizo e., bhaskar a., grossel m.c., et al. ex vivo models of the retinal pigment epithelium (rpe) in long term culture faithfully recapitulate key structural and physiological features of native rpe.
Diffrernce Between Bitmap And Vector Graphics Group Sort It is a hexagonally packed, tight junction, connected, single sheet of cells containing pigment granules (figures 1 and 2, pg) and organelles for digestion of photoreceptor outer segment membranes into phagosomes (figure 2, phagosomes, ph). Here we discuss the possibility of tweaking an ocular tissue, the retinal pigment epithelium (rpe), to produce photoreceptor cells in situ in the eye. unlike the neural retina, the rpe in adult mammals maintains cell proliferation capability. Structure of the retinal pigment epithelium 1. gross structure the rpe extends to the ora serrata where it is continuous with the ciliary pigment epithilium. it ends posteriorly at the border of the optic disc. 2. cellular organization [8, 9] the rpe contains approximately 3.5 million cells arranged in a regular hexagonal pattern. In this review, we aim to integrate these studies with an emphasis on appropriate models and techniques to investigate rpe cell biology and metabolism, and discuss how rpe cell biology informs our understanding of retinal disease.

Vector Vs Bitmap Graphics Difference Between Vector And Bitmap Structure of the retinal pigment epithelium 1. gross structure the rpe extends to the ora serrata where it is continuous with the ciliary pigment epithilium. it ends posteriorly at the border of the optic disc. 2. cellular organization [8, 9] the rpe contains approximately 3.5 million cells arranged in a regular hexagonal pattern. In this review, we aim to integrate these studies with an emphasis on appropriate models and techniques to investigate rpe cell biology and metabolism, and discuss how rpe cell biology informs our understanding of retinal disease. The fine structure of the retinal epithelium (rpe), choriocapillaris and bruch's membrane (complexus basalis) has been studied by electron microscopy in the red‐tailed hawk. The rpe is a monolayer of polygonal and pigmented cells strategically placed between the neuroretina and bruch membrane, adjacent to the fenestrated capillaries of the choriocapillaris. it shows strong apical (towards photoreceptors) to basal basolateral (towards bruch membrane) polarization. Changes in the retinal pigment epithelium (rpe) are a key clinical feature of amd 2. pigment epithelial detachment (ped) is commonly observed in patients with amd 3. Abstract: in this paper, we present the first numerical study on full metrics of wavelength dependent optical properties of melanosomes in retinal pigmented epithelial (rpe) cells.
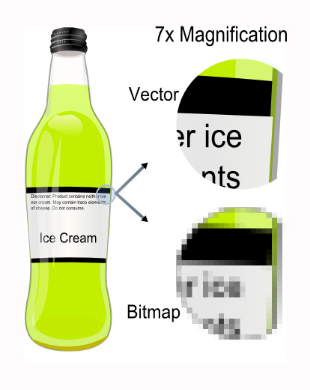
Difference Between Bitmap And Vector Graphics With Chart Viva The fine structure of the retinal epithelium (rpe), choriocapillaris and bruch's membrane (complexus basalis) has been studied by electron microscopy in the red‐tailed hawk. The rpe is a monolayer of polygonal and pigmented cells strategically placed between the neuroretina and bruch membrane, adjacent to the fenestrated capillaries of the choriocapillaris. it shows strong apical (towards photoreceptors) to basal basolateral (towards bruch membrane) polarization. Changes in the retinal pigment epithelium (rpe) are a key clinical feature of amd 2. pigment epithelial detachment (ped) is commonly observed in patients with amd 3. Abstract: in this paper, we present the first numerical study on full metrics of wavelength dependent optical properties of melanosomes in retinal pigmented epithelial (rpe) cells.