
Ecology Ii Part B Ecological Interactions Food Chains Food Webs Food chains are more flexible for analytical modeling, are easier to follow, and are easier to experiment with, whereas food web models more accurately represent ecosystem structure and dynamics, and data can be directly used as input for simulation modeling. The web like structure if formed with the interlinked food chain and such matrix that is interconnected is known as a food web. food webs are an inseparable part of an ecosystem; these food webs permit an organism to obtain food from more than one type of organism of the lower trophic level.

Ecology Iii Ecological Interactions Food Chains Food Webs Sh2021 The distinction between a food chain and a food web is that a food chain describes a linear relationship among trophic levels whereas a food web describes the interconnected relationships among trophic structures in nature. Food webs: a complex network of interconnected food chains of different tropic levels in a biotic community is termed as a food web. the complexity of any food web depends upon the diversity of organisms in that ecosystem. Food chains show the relationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers, showing who eats whom with arrows. the arrows show the movement of energy through the food chain. Functional webs (or interaction food webs): these food webs represent the importance of each species in maintaining the integrity of a community and reflect influence on the growth rate of other species populations.
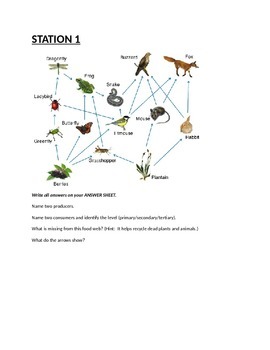
Ecosystem Interactions Food Chains Food Webs By Meep For Science Food chains show the relationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers, showing who eats whom with arrows. the arrows show the movement of energy through the food chain. Functional webs (or interaction food webs): these food webs represent the importance of each species in maintaining the integrity of a community and reflect influence on the growth rate of other species populations. A food chain is a model that identifies the feeding relationships and the flow of energy in an ecosystem. select a producer and a consumer from your piles, then fill in the blanks below and select which model (a or b) correctly shows the flow of energy. Maybe you’ve studied a little ecology and come across the terms “food chain” and “food web.” both help ecologists explain the ways that energy from food travels through an ecosystem. in this post, we will dive into the differences between food chains and food webs, and look at some examples of both!. Food chains are more flexible for analytical modeling, are easier to follow, and are easier to experiment with, whereas food web models more accurately represent ecosystem structure and dynamics, and data can be directly used as input for simulation modeling. Trophic interactions in a community can be represented by diagrams called food chains and food webs. before discussing these representations in detail, we must first review the basics of energy.

Ecology Food Chains Webs A food chain is a model that identifies the feeding relationships and the flow of energy in an ecosystem. select a producer and a consumer from your piles, then fill in the blanks below and select which model (a or b) correctly shows the flow of energy. Maybe you’ve studied a little ecology and come across the terms “food chain” and “food web.” both help ecologists explain the ways that energy from food travels through an ecosystem. in this post, we will dive into the differences between food chains and food webs, and look at some examples of both!. Food chains are more flexible for analytical modeling, are easier to follow, and are easier to experiment with, whereas food web models more accurately represent ecosystem structure and dynamics, and data can be directly used as input for simulation modeling. Trophic interactions in a community can be represented by diagrams called food chains and food webs. before discussing these representations in detail, we must first review the basics of energy.

Natural Science Grade 8 Term 1 Topic 2 Part 2 Interactions And Food chains are more flexible for analytical modeling, are easier to follow, and are easier to experiment with, whereas food web models more accurately represent ecosystem structure and dynamics, and data can be directly used as input for simulation modeling. Trophic interactions in a community can be represented by diagrams called food chains and food webs. before discussing these representations in detail, we must first review the basics of energy.