Food Web Ecological Pyramid Food Chain Ecosystem Ecol Vrogue Co A food web is an intricate network of interrelated food chains in an ecosystem. it illustrates the various paths through which energy and nutrients move between organisms. Food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem.
Food Web Ecological Pyramid Food Chain Ecosystem Ecol Vrogue Co Food chains show the relationships between producers, consumers, and decomposers, showing who eats whom with arrows. the arrows show the movement of energy through the food chain. The difference between food chains and food webs? in summary, food chains are a single path showing how energy moves from organism to organism through an ecosystem, while a food web is a more complex network that maps the multiple feeding relationships of each organism in an ecosystem. Food chains show the transfer of energy that occurs when organisms feed. food web shows the complex feeding relationships within ecosystems. questions about interdependence in food webs are common, so be sure that you know how to follow chains of events through each food chain within a food web. A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that demonstrates the multiple feeding relationships in an ecosystem. food webs are more realistic representations of energy flow than linear food chains.
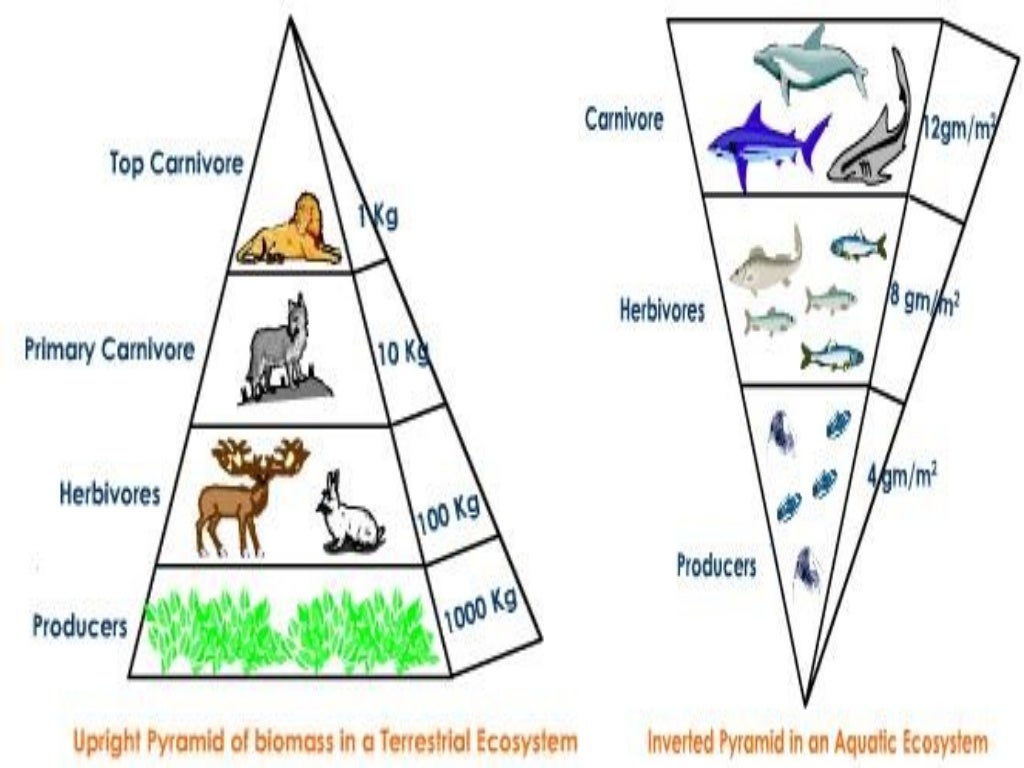
Food Web Ecological Pyramid Food Chain Ecosystem Ecology Png Food chains show the transfer of energy that occurs when organisms feed. food web shows the complex feeding relationships within ecosystems. questions about interdependence in food webs are common, so be sure that you know how to follow chains of events through each food chain within a food web. A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that demonstrates the multiple feeding relationships in an ecosystem. food webs are more realistic representations of energy flow than linear food chains. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. it from the basic input of the chain. relationships in ecosystems. energy transfer between trophic levels is inefficient (with a typical efficiency around 10\%10%10, percent). this. inefficiency limits the length of food chains. At the heart of every ecosystem lies a complex network of interrelated food chains known as a food web. a food web illustrates the intricate connections between various organisms within a community, showcasing the flow of energy and nutrients as they pass from one organism to another. Understanding the complexities of ecosystems requires a fundamental grasp of ecological concepts such as food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids. while they may initially appear distinct, these systems share profound similarities and are interlinked in the eternal dance of life. You can also refer to the diagrammatic representations of food chains, food webs and ecological pyramids. a food chain describes how energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem. at the basic level there are plants that produce the energy, then it moves up to higher level organisms like herbivores.
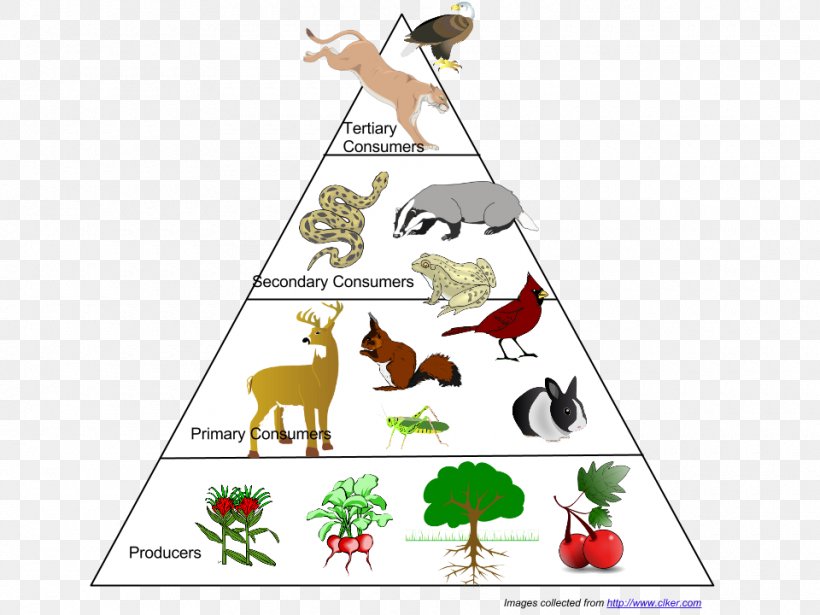
Food Chain Food Web And Energy Pyramid Match Up A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. it from the basic input of the chain. relationships in ecosystems. energy transfer between trophic levels is inefficient (with a typical efficiency around 10\%10%10, percent). this. inefficiency limits the length of food chains. At the heart of every ecosystem lies a complex network of interrelated food chains known as a food web. a food web illustrates the intricate connections between various organisms within a community, showcasing the flow of energy and nutrients as they pass from one organism to another. Understanding the complexities of ecosystems requires a fundamental grasp of ecological concepts such as food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids. while they may initially appear distinct, these systems share profound similarities and are interlinked in the eternal dance of life. You can also refer to the diagrammatic representations of food chains, food webs and ecological pyramids. a food chain describes how energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem. at the basic level there are plants that produce the energy, then it moves up to higher level organisms like herbivores.

Food Chain Food Web And Energy Pyramid Prairie Post Understanding the complexities of ecosystems requires a fundamental grasp of ecological concepts such as food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids. while they may initially appear distinct, these systems share profound similarities and are interlinked in the eternal dance of life. You can also refer to the diagrammatic representations of food chains, food webs and ecological pyramids. a food chain describes how energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem. at the basic level there are plants that produce the energy, then it moves up to higher level organisms like herbivores.