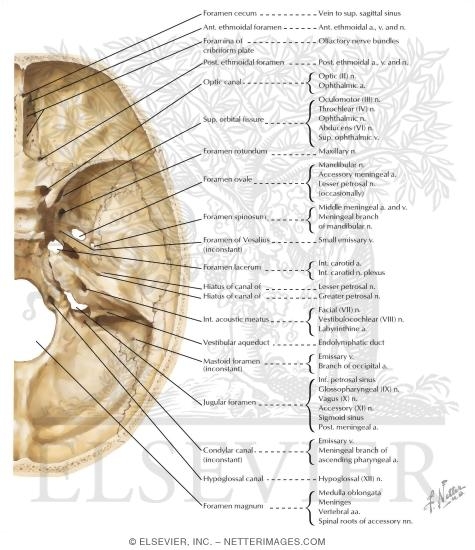
Foramina In The Base Of The Adult Skull Internal Aspect Of Base Of Foramina in the base of the adult skull internal aspect of base of sku… please describe! how you will use this image and then you will be able to add this image to your shopping basket. just copy the linking code into your your web page or blog and customize as you see fit. In this article we will be focusing on the foramina and fissures located on the inside and floor, or base, of the skull. in a nutshell, a foramen means a hole that can allow various structures to pass through them, ranging from nerves all the way to vessels.
Foramina In The Base Of The Adult Skull Internal Aspect Of Base Of The foramina in the base of the skull allow major nerves and blood vessels to course through the skull. pressure, traction, and masses can damage structures traversing these small spaces that snugly confine the structures. Associated structures nestled at the base of the skull, the foramen magnum is surrounded by several crucial structures that contribute to its general function and significance in the human body. this large opening, situated in the occipital bone, serves as the critical passageway for the medulla oblongata, linking the brainstem to the spinal cord. Most cranial foramina are at the base of skull: supraorbital foramen. optic canal. additional cranial foramina include congenital calvarial defects, such as parietal foramen. other foramina in the skull are not strictly related to the cranium (bones surrounding the intracranial cavity) but rather to the bones of the face and jaw:. The internal carotid artery enters the skull by passing through the carotid canal and through the upper part of the foramen lacerum. inferiorly, the foramen lacerum is closed by a plate of cartilage.
Foramina In The Base Of The Adult Skull Internal Aspect Of Base Of Most cranial foramina are at the base of skull: supraorbital foramen. optic canal. additional cranial foramina include congenital calvarial defects, such as parietal foramen. other foramina in the skull are not strictly related to the cranium (bones surrounding the intracranial cavity) but rather to the bones of the face and jaw:. The internal carotid artery enters the skull by passing through the carotid canal and through the upper part of the foramen lacerum. inferiorly, the foramen lacerum is closed by a plate of cartilage. Base of the skull, internal aspect showing the anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossa (divided by red doted line). in the anterior cranial fossa, identify the cribriform plate of the ethmoid. A foramen (pl. foramina) is an opening that allows the passage of structures from one region to another. in the skull base, there are numerous foramina that transmit cranial nerves, blood vessels and other structures – these are collectively referred to as the cranial foramina. The internal surface of the neurocranium base has 3 depressions which create the bowl shape of the cranial cavity that accommodate the brain. figure 1 displays the 3 depressions fossae. Co draw a oval line that passes through the medial ends of the lesser wings of the sphenoid (a), the petrous temporal bones (b) and the centre of the foramen magnum (c). all but three of the important internal skull foramina lie on this line. foramina 1 optic canal 2 superior orbital fissure .
Foramina In The Base Of The Adult Skull Internal Aspect Of Base Of Base of the skull, internal aspect showing the anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossa (divided by red doted line). in the anterior cranial fossa, identify the cribriform plate of the ethmoid. A foramen (pl. foramina) is an opening that allows the passage of structures from one region to another. in the skull base, there are numerous foramina that transmit cranial nerves, blood vessels and other structures – these are collectively referred to as the cranial foramina. The internal surface of the neurocranium base has 3 depressions which create the bowl shape of the cranial cavity that accommodate the brain. figure 1 displays the 3 depressions fossae. Co draw a oval line that passes through the medial ends of the lesser wings of the sphenoid (a), the petrous temporal bones (b) and the centre of the foramen magnum (c). all but three of the important internal skull foramina lie on this line. foramina 1 optic canal 2 superior orbital fissure .