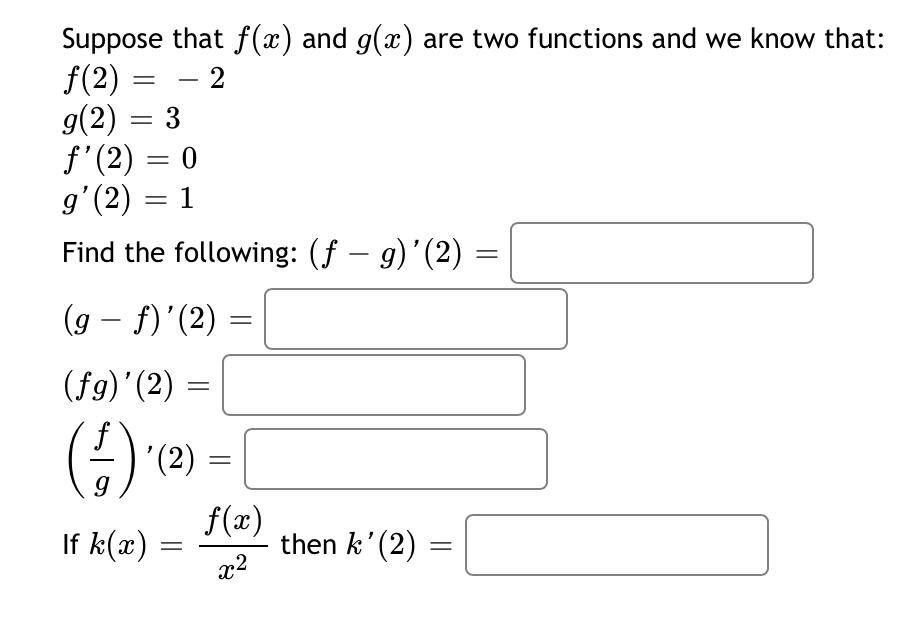
Solved Suppose That F X And G 2 Are Two Functions And We Chegg This video explains how to determine the difference of two quadratic functions. then a function value is determined using two methods. mathispower4u more. Get the sum, product, quotient and difference of functions steps by step. save to notebook!.

Answered 2 2 Algebra Of Functions Algebra Of Functions Sums Algebra Generally, an arithmetic combination of two functions f and g at any x that is in the domain of both f and g, with one exception. the quotient f g is not defined at values of x where g is equal to 0. for example, if f (x) = 2x 1 and g (x) = x 3, then the doamins of f g, f g, and f*g are all real numbers. This video explains how to determine the difference of two quadratic functions. then a function value is determined using two methods . Compute the difference quotient of a quadratic and linear function. the domain and range of the functions within a composition. 1. given tables. 2. use the graphs to evaluate the expressions below. 3. given formulas. The domains of the sum, difference, product, and quotient functions consist of the x values that are in the domains of both f and g. additionally, the domain of the quotient does not include x values for which g(x) 0.
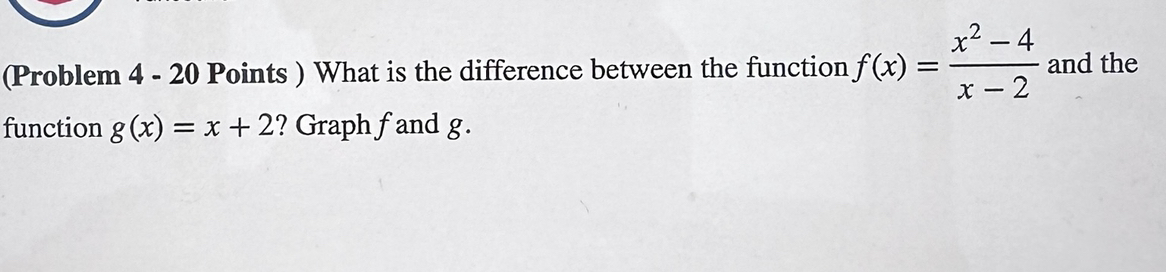
Solved Problem 4 20 Points What Is The Difference Between The Compute the difference quotient of a quadratic and linear function. the domain and range of the functions within a composition. 1. given tables. 2. use the graphs to evaluate the expressions below. 3. given formulas. The domains of the sum, difference, product, and quotient functions consist of the x values that are in the domains of both f and g. additionally, the domain of the quotient does not include x values for which g(x) 0. Let f and g be two n ary quadratic forms. we say that f and g are equivalent, written. f = g, if there exists an invertible matrix c 2 gln(f ) such that f(x) = g(cx). this is the same as saying that there is an invertible homogeneous linear substitution of the variables x1; : : : ; xn which takes the form g to the form f. since. Consider the function: f (x) = 48 x 2 x 2. notice that the equation has two terms: the first term: 48 x. the second term: 2 x 2. therefore we can think of the function f (x) as the sum of two other functions: the reciprocal function g (x) = 48 x. the quadratic function b (x) = 2 x 2. In the following examples, let f (x) = 5x 2 and g (x) = x 2 1. we will then evaluate each combination at the point x=4. f (4)=5 (4) 2=22 and g (4)=4 2 1=15. as you can see from the examples, it doesn't matter if you combine and then evaluate or if you evaluate and then combine. Free online difference quotient calculator calculate the difference quotient of functions step by step.
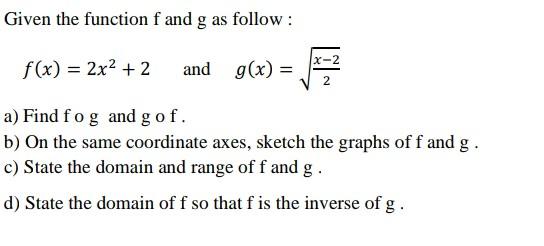
Solved Given The Function F And G As Follow F X 2x2 2 And Chegg Let f and g be two n ary quadratic forms. we say that f and g are equivalent, written. f = g, if there exists an invertible matrix c 2 gln(f ) such that f(x) = g(cx). this is the same as saying that there is an invertible homogeneous linear substitution of the variables x1; : : : ; xn which takes the form g to the form f. since. Consider the function: f (x) = 48 x 2 x 2. notice that the equation has two terms: the first term: 48 x. the second term: 2 x 2. therefore we can think of the function f (x) as the sum of two other functions: the reciprocal function g (x) = 48 x. the quadratic function b (x) = 2 x 2. In the following examples, let f (x) = 5x 2 and g (x) = x 2 1. we will then evaluate each combination at the point x=4. f (4)=5 (4) 2=22 and g (4)=4 2 1=15. as you can see from the examples, it doesn't matter if you combine and then evaluate or if you evaluate and then combine. Free online difference quotient calculator calculate the difference quotient of functions step by step.