Germ Layers Endoderm Mesoderm And Ectoderm A germ layer is any of three primary cell layers, formed in the earliest stages of embryonic development, consisting of the endoderm, the ectoderm, and the mesoderm. the germ layers form during the process of gastrulation and eventually give rise to certain tissue types in the body. Gastrulation is responsible for forming the 3 germ layers including the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. after the egg is fertilized by a sperm, the resulting zygote will eventually develop into.

Three Layers Of Embryo Ectoderm Mesoderm And Endoderm The process of gastrulation generates the three primary germ layers ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. gastrulation primes the system for organogenesis and is one of the most critical steps of development. Such movement of cells is called morphogenetic movements gastrulation results in the formation of three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. each germ layer gives rise to specific tissues, organs and organ systems. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation: the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. these three germ layers (of the embryo differentiate and further specialize to form the various organs of the body. Gastrulation – internalization of the prospective endoderm and non skeletogenic mesoderm – begins shortly thereafter with invagination and other cell rearrangements the vegetal pole, which contribute approximately 30% to the final archenteron length.
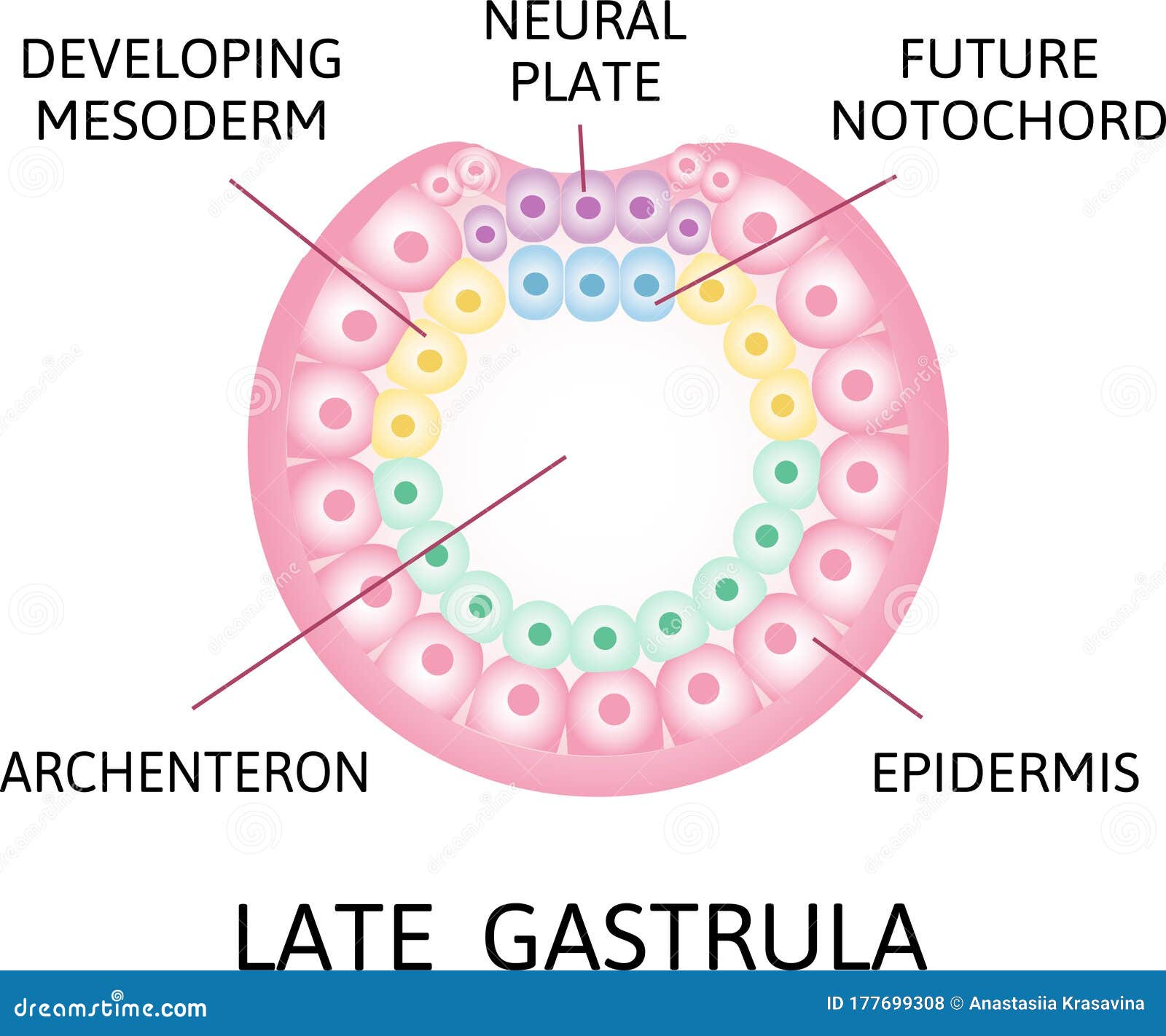
Endoderm Mesoderm And Ectoderm Vector Illustration Labeled Infographic During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation: the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. these three germ layers (of the embryo differentiate and further specialize to form the various organs of the body. Gastrulation – internalization of the prospective endoderm and non skeletogenic mesoderm – begins shortly thereafter with invagination and other cell rearrangements the vegetal pole, which contribute approximately 30% to the final archenteron length. Mesoderm – formed by epiblast cells that migrate through the primitive pit and lie between the epiblast layer and the newly created endoderm. ectoderm – formed by the epiblast cells that remain in position. these three cell layers are then responsible for forming the different tissues of the fetus. fig 2. The primary germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm) are formed and organized in their proper locations during gastrulation. endoderm, the most internal germ layer, forms the lining of the gut and other internal organs. Gastrulation is a crucial process in early embryonic development, involving the formation of three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. during gastrulation, the blastula reorganizes into a gastrula, setting the stage for subsequent tissue and organ formation. Gastrulation converts the spherical blastula into a more complex configuration of three germ layers. at the end of gastrulation, the ectoderm covers the embryo, and the mesoderm and endoderm have been brought inside.

Gastrulation And The 3 Germ Layers Ectoderm Endoderm Mesoderm Mesoderm – formed by epiblast cells that migrate through the primitive pit and lie between the epiblast layer and the newly created endoderm. ectoderm – formed by the epiblast cells that remain in position. these three cell layers are then responsible for forming the different tissues of the fetus. fig 2. The primary germ layers (endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm) are formed and organized in their proper locations during gastrulation. endoderm, the most internal germ layer, forms the lining of the gut and other internal organs. Gastrulation is a crucial process in early embryonic development, involving the formation of three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. during gastrulation, the blastula reorganizes into a gastrula, setting the stage for subsequent tissue and organ formation. Gastrulation converts the spherical blastula into a more complex configuration of three germ layers. at the end of gastrulation, the ectoderm covers the embryo, and the mesoderm and endoderm have been brought inside.

Gastrulation Gastrula Tri Layer Stage Of Embryonic Development Gastrulation is a crucial process in early embryonic development, involving the formation of three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. during gastrulation, the blastula reorganizes into a gastrula, setting the stage for subsequent tissue and organ formation. Gastrulation converts the spherical blastula into a more complex configuration of three germ layers. at the end of gastrulation, the ectoderm covers the embryo, and the mesoderm and endoderm have been brought inside.
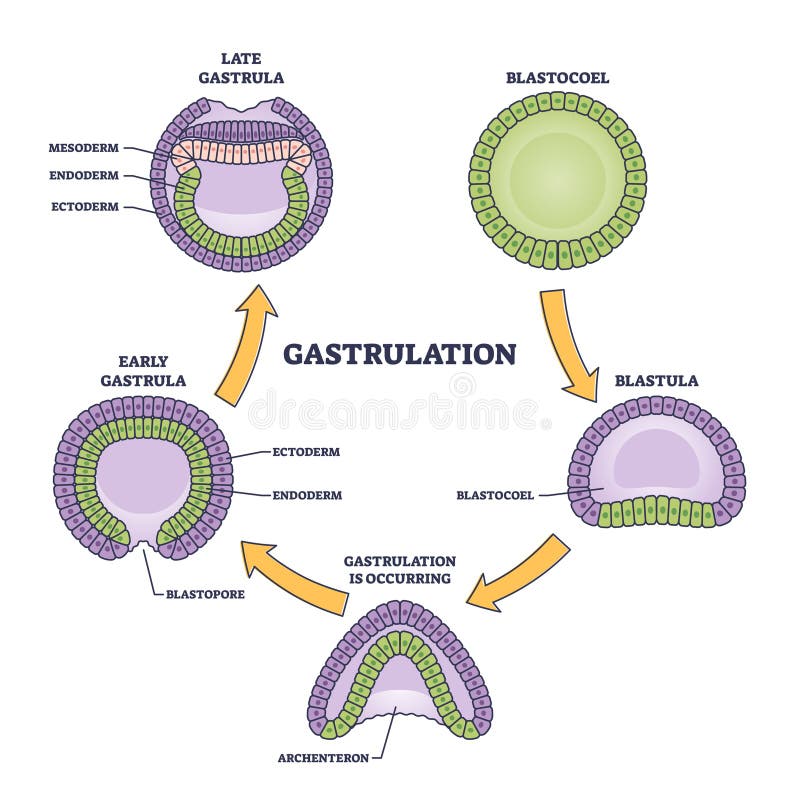
Ectoderm Endoderm Stock Illustrations 46 Ectoderm Endoderm Stock