Genotype Vs Phenotype Definitions And Examples 45 Off In genetics, the genotype and phenotype are two ways of describing an organism’s traits. the genotype is the genetic code, while the phenotype is the physical expression of a trait. here is a closer look at what genotype and phenotype are, with examples. Genotype vs phenotype: what’s the difference? an individual’s genotype is the combination of alleles that they possess for a specific gene. an individual’s phenotype is the combination of their observable characteristics or traits. while an organism’s genotype is directly inherited from its parents, phenotype is merely influenced by.
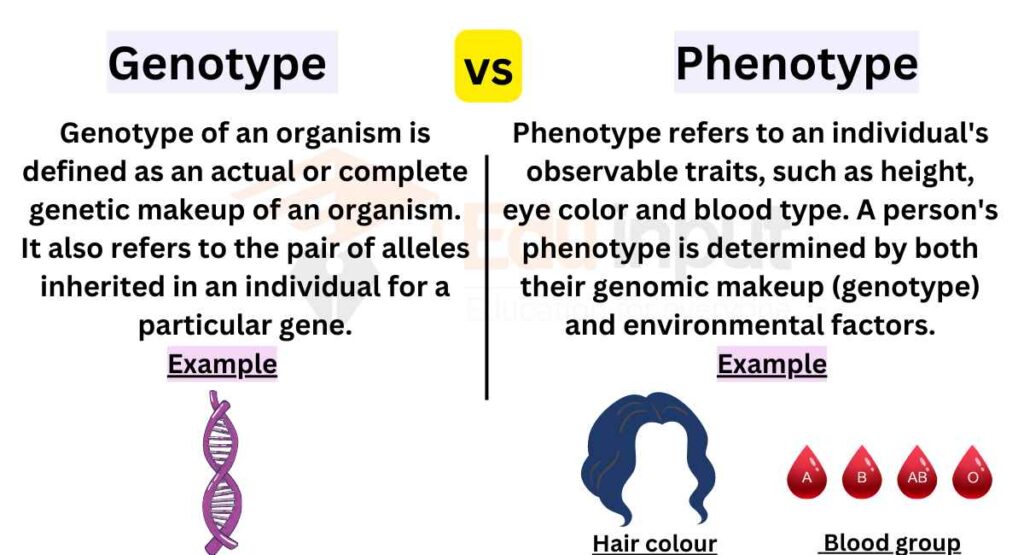
Genotype Vs Phenotype Definitions And Examples 45 Off Phenotype and genotype definition, examples. phenotype= melanin production, mendels’ peas. genotype= eye color, curly hair. 10 differences. Genotype refers to an individual’s unique dna sequence, specifically the variants inherited from each parent for a particular gene. in contrast, phenotype is the observable expression of the genotype, shaped by the interaction between genetic makeup and environmental factors. Genotype and phenotype are two fundamental terms in the science of genetics. the two terms are often used at the same time to describe the same organism, but there is a difference between genotype and phenotype: an organism’s genotype is the set of genes in its dna responsible for a particular trait. Uncover the difference between genotype and phenotype with clear explanations, practical examples, and ratio analyses. discover how genes and environment interact to shape traits.
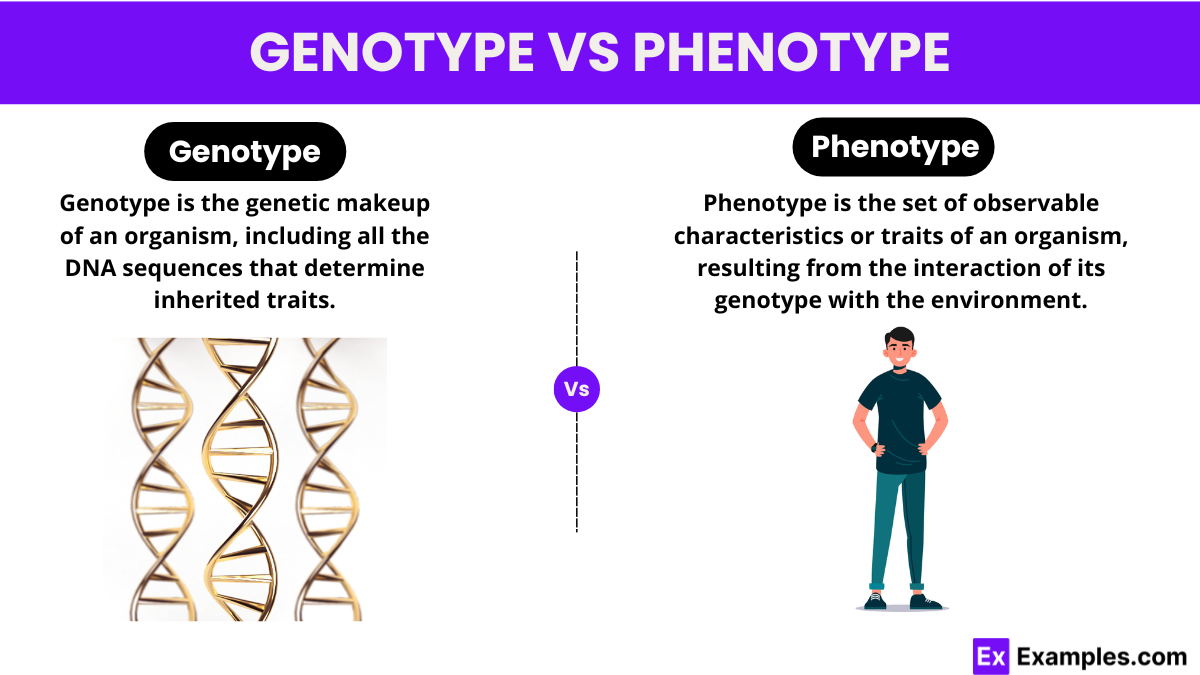
Genotype Vs Phenotype Understanding Genetic And Observable Genotype and phenotype are two fundamental terms in the science of genetics. the two terms are often used at the same time to describe the same organism, but there is a difference between genotype and phenotype: an organism’s genotype is the set of genes in its dna responsible for a particular trait. Uncover the difference between genotype and phenotype with clear explanations, practical examples, and ratio analyses. discover how genes and environment interact to shape traits. In the realm of biology, the terms "genotype" and "phenotype" are fundamental, often intertwined concepts, yet they each carry distinct meanings and significance. let's delve deeper into the intricacies of genotype and phenotype. what does genotype mean? at its core, the genotype represents the genetic blueprint of an organism. Learn more about genotype and phenotype in context: the genes that lie beneath: the work of leslea hlusko, a research profile. coping with climate change, a news brief with discussion questions. A great example that explains this concept is gregor mendel’s experiments with true breeding yellow and green pea plants (p 1). the phenotype of the plants is their color, yellow and green. when mendel crossed these two plants, all the offspring (f 1) were yellow. but the green color was not lost as it showed up again in the next generation (f 2). Genotype and phenotype are two fundamental terms in the science of genetics used to explicate the appearance, function and behavior of an organism. the two terms are often used at the same time to describe the same organism but there is a big difference between.

Differences Between Genotype And Phenotype Summary And 48 Off In the realm of biology, the terms "genotype" and "phenotype" are fundamental, often intertwined concepts, yet they each carry distinct meanings and significance. let's delve deeper into the intricacies of genotype and phenotype. what does genotype mean? at its core, the genotype represents the genetic blueprint of an organism. Learn more about genotype and phenotype in context: the genes that lie beneath: the work of leslea hlusko, a research profile. coping with climate change, a news brief with discussion questions. A great example that explains this concept is gregor mendel’s experiments with true breeding yellow and green pea plants (p 1). the phenotype of the plants is their color, yellow and green. when mendel crossed these two plants, all the offspring (f 1) were yellow. but the green color was not lost as it showed up again in the next generation (f 2). Genotype and phenotype are two fundamental terms in the science of genetics used to explicate the appearance, function and behavior of an organism. the two terms are often used at the same time to describe the same organism but there is a big difference between.

Genotype Vs Phenotype An Introduction And A Great Memorization Trick A great example that explains this concept is gregor mendel’s experiments with true breeding yellow and green pea plants (p 1). the phenotype of the plants is their color, yellow and green. when mendel crossed these two plants, all the offspring (f 1) were yellow. but the green color was not lost as it showed up again in the next generation (f 2). Genotype and phenotype are two fundamental terms in the science of genetics used to explicate the appearance, function and behavior of an organism. the two terms are often used at the same time to describe the same organism but there is a big difference between.
Phenotype Vs Genotype 10 Differences Examples