
Genotype To Phenotype Introduction To Biology Lecture Slides Docsity These are the lecture slides of introduction to biology. key important points are: genotype to phenotype, dna to protein, gene one polypeptide, rna processing, comparing rna to dna, uracil replaces thymine, genetic code, nucleotide bases, rna polymerase, terminator sequence. Genotype refers to the alleles in an individual's dna, while phenotype describes physical traits. the different genotypes are defined as homozygous recessive, heterozygous, and homozygous dominant. sample questions are provided to illustrate how genotypes determine phenotypes for traits like eye color. download as a pdf or view online for free.

Genotype And Phenotype Genetics Biology Lecture Slides Docsity Phenotype any observable trait or characteristic of an organism when the committee is deciding on what the animal will look like (phenotype), the genes split up into little sub committees for. From dna to protein: genotype to phenotype. biochemical biosynthesis pathways lead to understanding of gene enzyme relationship. biosynthesis of arginine. ornithine transcarbamylase. argininosuccinate lyase. argininosuccinate synthetase. acetylornithinase. n acetylornithine. ornithine . These are the lecture slides of biology. key important points are: genotype and phenotype, genetics, dominant trait, recessive trait, emotional qualities of organism, category of trait, genes code for specific trait, types of genotype, outward appearance. Phenotypes of offspring. on board!.

Genotype And Phenotype 2nd Lecture Pdf These are the lecture slides of biology. key important points are: genotype and phenotype, genetics, dominant trait, recessive trait, emotional qualities of organism, category of trait, genes code for specific trait, types of genotype, outward appearance. Phenotypes of offspring. on board!. The document outlines the principles of genetics, covering key concepts such as heredity, genotype, phenotype, and mendelian inheritance laws. it details gregor mendel's experiments with pea plants, which led to the formulation of the laws of segregation and independent assortment, explaining how traits are inherited across generations. Genotype • gene: a specific region of a chromosome which is capable of determining the development of a specific trait; composed of dna • allele: a pair of genes located at the same place on a homologous chromosome. The document is from the website easybiologyclass and provides an introduction to genetics concepts. it explains monohybrid and dihybrid crosses through examples and steps. Key important points are: genotype to phenotype, genetic code, watson and crick, chromosome theory of inheritance, patterns of inheritance, hereditary factors, metabolic pathways, biochemical basis of genetic diseases.

Genotype And Phenotype Continued Lecture Slides Anth 102 Docsity The document outlines the principles of genetics, covering key concepts such as heredity, genotype, phenotype, and mendelian inheritance laws. it details gregor mendel's experiments with pea plants, which led to the formulation of the laws of segregation and independent assortment, explaining how traits are inherited across generations. Genotype • gene: a specific region of a chromosome which is capable of determining the development of a specific trait; composed of dna • allele: a pair of genes located at the same place on a homologous chromosome. The document is from the website easybiologyclass and provides an introduction to genetics concepts. it explains monohybrid and dihybrid crosses through examples and steps. Key important points are: genotype to phenotype, genetic code, watson and crick, chromosome theory of inheritance, patterns of inheritance, hereditary factors, metabolic pathways, biochemical basis of genetic diseases.
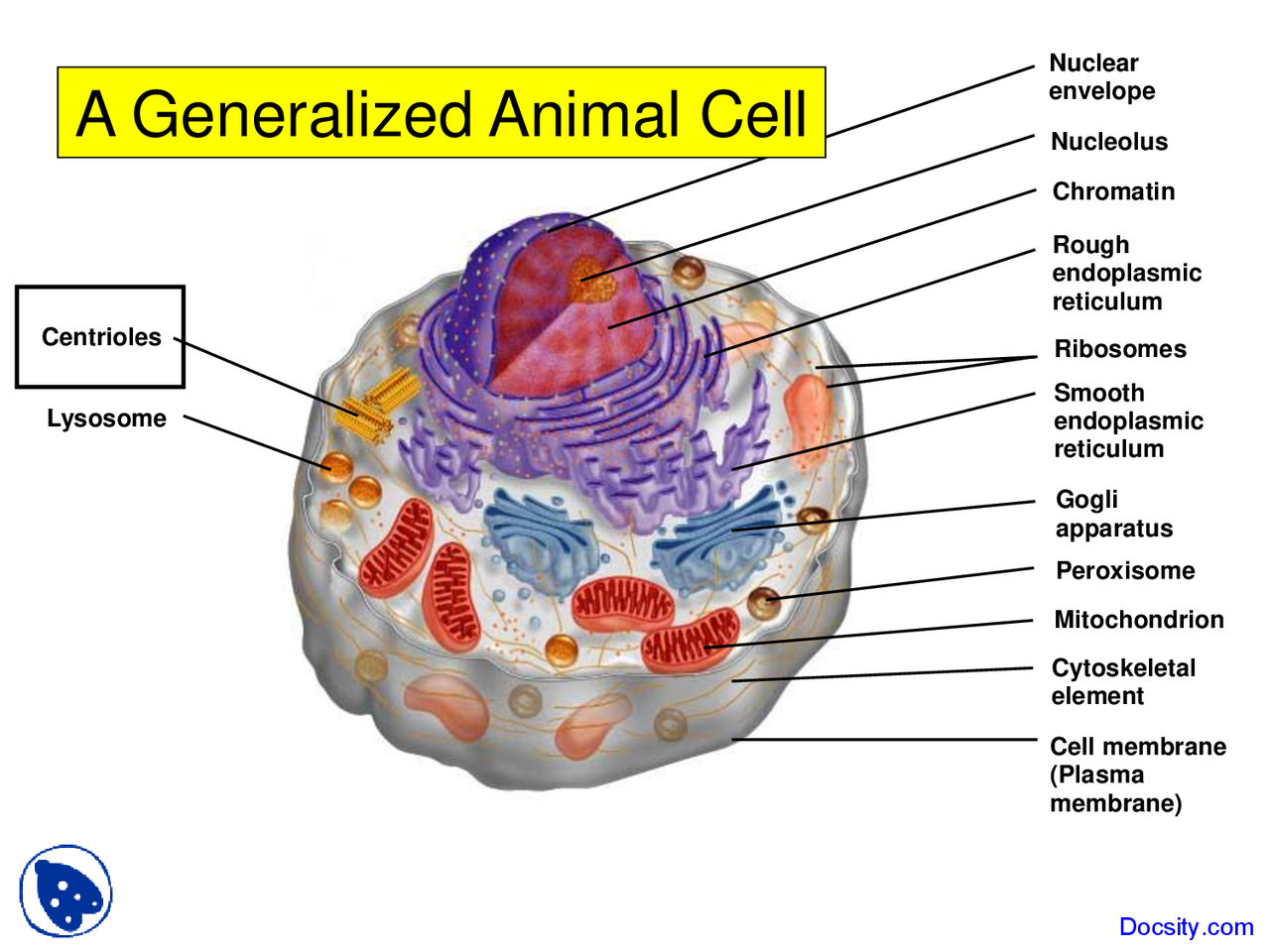
Generalized Animal Cell Introduction To Biology Lecture Slides The document is from the website easybiologyclass and provides an introduction to genetics concepts. it explains monohybrid and dihybrid crosses through examples and steps. Key important points are: genotype to phenotype, genetic code, watson and crick, chromosome theory of inheritance, patterns of inheritance, hereditary factors, metabolic pathways, biochemical basis of genetic diseases.

Genotype To Phenotype Fundametnals Of Biology Lecture Notes Docsity